What is meant by the term bond order? Calculate the bond order of: $\mathrm{N}_{2}, \mathrm{O}_{2}, \mathrm{O}_{2}^{+}$and $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$.
Bond order is defined as one half of the difference between the number of electrons present in the bonding and anti-bonding orbitals of a molecule.
If Na is equal to the number of electrons in an anti-bonding orbital, then Nb is equal to the number of electrons in a bonding orbital.
Bond order $=\frac{1}{2}\left(N_{\mathrm{b}}-N_{\mathrm{a}}\right)$
If Nb > Na, then the molecule is said be stable. However, if Nb ≤ Na, then the molecule is considered to be unstable.
Bond order of N2 can be calculated from its electronic configuration as:
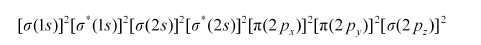
Number of bonding electrons, Nb = 10
Number of anti-bonding electrons, Na = 4
Bond order of nitrogen molecule $=\frac{1}{2}(10-4)$
= 3
There are 16 electrons in a dioxygen molecule, 8 from each oxygen atom. The electronic configuration of oxygen molecule can be written as:
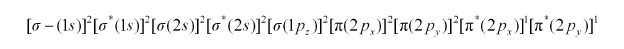
Since the 1s orbital of each oxygen atom is not involved in boding, the number of bonding electrons = 8 = Nb and the number of anti-bonding electrons = 4 = Na.
Bond order $=\frac{1}{2}\left(N_{b}-N_{a}\right)$
$=\frac{1}{2}(8-4)$
= 2
Hence, the bond order of oxygen molecule is 2.
Similarly, the electronic configuration of $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{+}$can be written as:
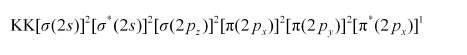
Nb = 8
Na = 3
Bond order of $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{+}=\frac{1}{2}(8-3)$
= 2.5
Thus, the bond order of $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{+}$is $2.5$.
The electronic configuration of $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$ion will be:
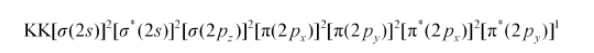
Bond order of $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}=\frac{1}{2}(8-5)$
= 1.5
Thus, the bond order of $\mathrm{O}_{2}^{-}$ion is $1.5$.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
