Find the foot of perpendicular from the point $(2,3,-8)$ to the line $\frac{4-x}{2}=\frac{y}{6}=\frac{1-z}{3}$.
Also, find the perpendicular distance from the given point to the line.
Given,
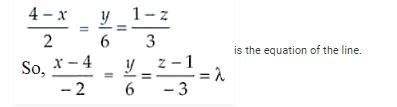
Now, the coordinates of any point Q on the line are
x = -2λ + 4, y = 6λ and z = -3λ + 1 and the given point is P(2, 3, -8)
The direction ratios of PQ are -2λ + 4 – 2, 6λ – 3, -3λ + 1 + 8 i.e. -2λ + 2, 6λ – 3, -3λ + 9
And the direction ratios of the given line are -2, 6, -3.
If PQ ⊥ line, then
-2(-2λ + 2) + 6(6λ – 3) – 3(-3λ + 9) = 0
4λ – 4 + 36λ – 18 + 9λ – 27 = 0
49λ – 49 = 0
λ = 1
Now, the foot of the perpendicular is -2(1) + 4, 6(1), -3(1) + 1 i.e. 2, 6, -2
Hence, the distance PQ is
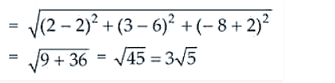
Thus, the required coordinates of the foot of perpendicular are 2, 6, -2 and the required distance is 3√5 units.
