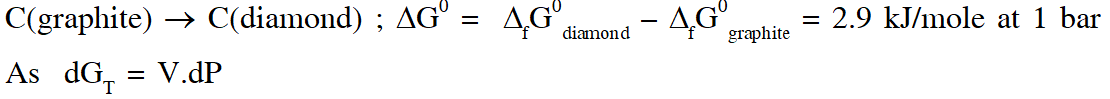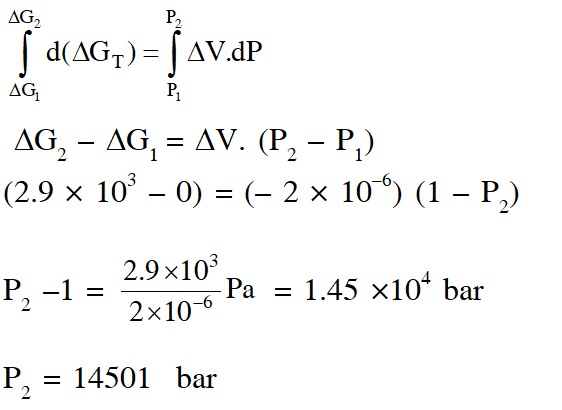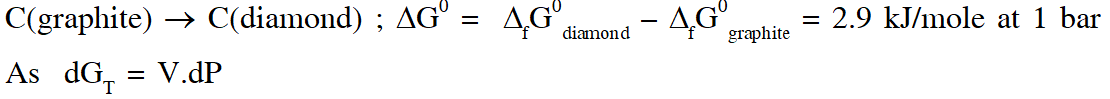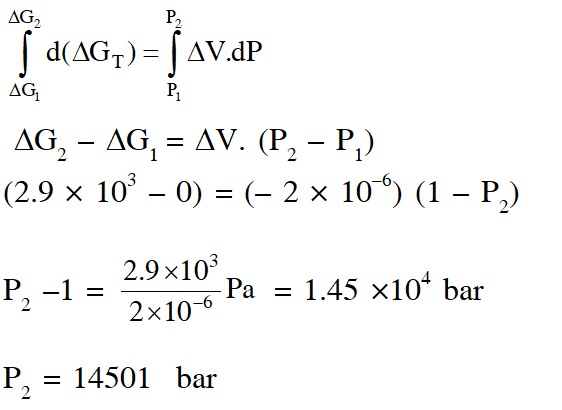JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions of Chemistry with Solutions are available at eSaral. Practicing JEE Advanced Previous Year Papers Questions of Chemistry will help the JEE aspirants in realizing the question pattern as well as help in analyzing weak & strong areas.
Simulator
Previous Years JEE Advance Questions
Paragraph 1 (2 TO 3)
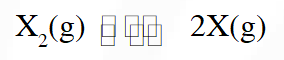
Thermal decomposition of gaseous $\mathrm{X}_{2}$ to gaseous X at 298 K takes place according to the following equation :
 The standard reaction Gibbs energy,
The standard reaction Gibbs energy, 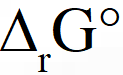 , of this reaction is positive. At the start of the
reaction, there is one mole of X2 and no X. As the reaction proceeds, the number of moles of
X formed is given
, of this reaction is positive. At the start of the
reaction, there is one mole of X2 and no X. As the reaction proceeds, the number of moles of
X formed is given 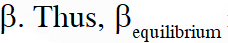 is the number of moles of X formed at equilibrium. The
reaction is carried out at a constant total pressure of 2
bar. Consider the gases to behave ideally.
(Given $\left.: \mathrm{R}=0.083 \mathrm{L} \text { bar } \mathrm{K}^{-1} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}\right)$
is the number of moles of X formed at equilibrium. The
reaction is carried out at a constant total pressure of 2
bar. Consider the gases to behave ideally.
(Given $\left.: \mathrm{R}=0.083 \mathrm{L} \text { bar } \mathrm{K}^{-1} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}\right)$
Q. The thermal dissociation equilibrium of $\mathrm{CaCO}_{3}(\mathrm{s})$ is studied under different conditions.
$\mathrm{CaCO}_{3}(\mathrm{s}) \square \mathrm{CaO}(\mathrm{s})+\mathrm{CO}_{2}(\mathrm{g})$
For this equilibrium, the correct statement(s) is(are)
(A) $\Delta \mathrm{H}$ is dependent on $\mathrm{T}$
(B) $\mathrm{K}$ is independent of the initial amount of $\mathrm{CaCO}_{3}$
(C) $\mathrm{K}$ is dependent on the pressure of $\mathrm{CO}_{2}$ at a given $\mathrm{T}$
(D) $\Delta \mathrm{H}$ is independent of the catalyst, if any
[JEE 2013]
Ans. (A,B,D)
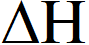 s independent of catalyst but dependent on temperature
s independent of catalyst but dependent on temperature
Q. The equilibrium constant KP for this reaction at 298 K, in terms of 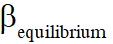 , is
, is
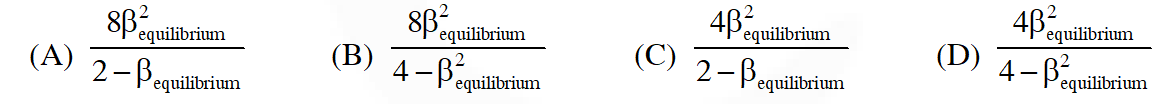 [JEE - Adv. 2016]
[JEE - Adv. 2016]
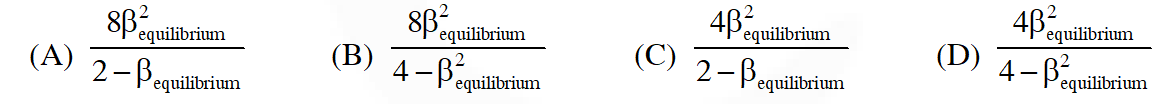 [JEE - Adv. 2016]
[JEE - Adv. 2016]
Ans. (B)
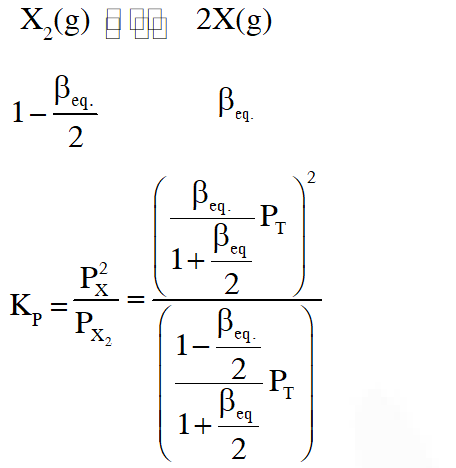
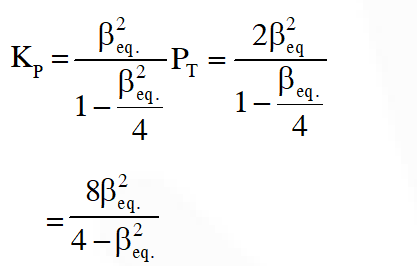
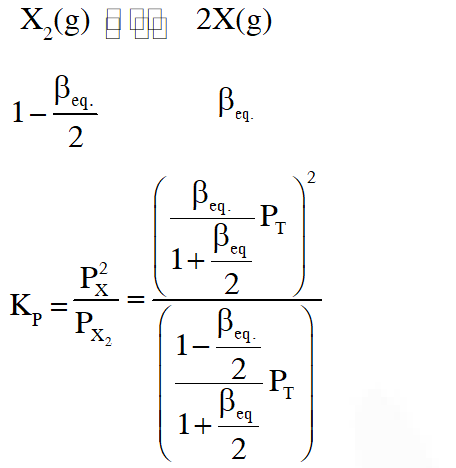
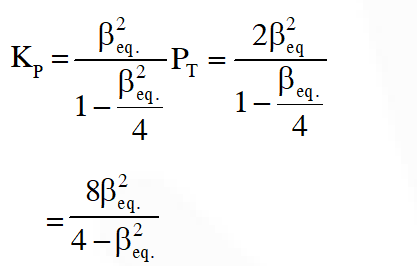
Q. The INCORRECT statement among the following , for this reaction, is
(A) Decrease in the total pressure will result in formation of more moles of gaseous X
(B) At the start of the reaction, dissociation of gaseous $\mathrm{X}_{2}$ takes place spontaneously
(C) $\beta_{\text {equilibrium }}=0.7$
(D) $\mathrm{K}_{\mathrm{C}}<1$
[JEE - Adv. 2016]
Ans. (C)
(A) On decreasing $\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{T}}\left[\mathrm{Q}=\frac{\mathrm{n}_{x} \mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{T}}}{\mathrm{n}_{\mathrm{x}_{2}} \mathrm{n}_{\mathrm{T}}}\right]$ Q will be less than Kp reaction will move in forward direction
(B) At the start of the reaction $\Delta \mathrm{G}=\Delta \mathrm{G}^{0}+\mathrm{RT} \ln \mathrm{Q}$
$\mathrm{t}=0, \mathrm{Q}=0 \Rightarrow \Delta_{\mathrm{rxn}} \mathrm{G}=-\mathrm{ve} \quad$ (spontaneous)
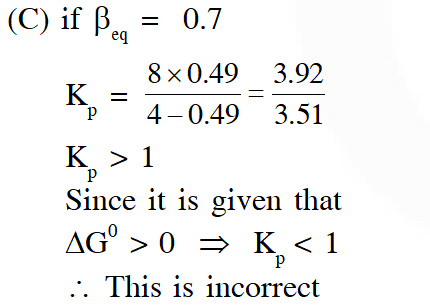
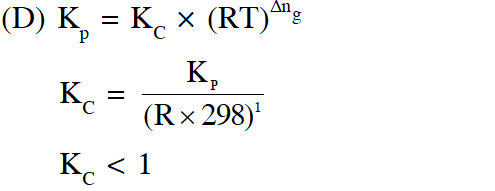
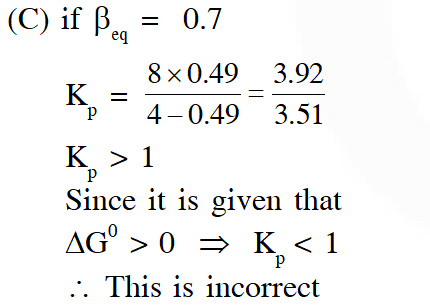
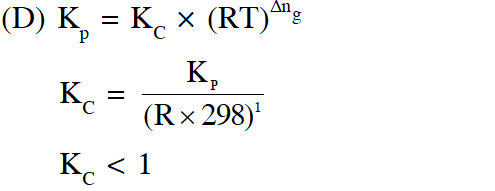
Q. The standard state Gibbs free energies of formation of C(graphite) and C(diamond) at T = 298 K are
$\Delta_{f} \mathrm{G}^{\circ}[\mathrm{C}(\text { graphite })]=0 \mathrm{kJ} \operatorname{mol}^{-1} \Delta_{f} \mathrm{G}^{\circ}[\mathrm{C}(\text { diamond })]=2.9 \mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}$
The standard state means that the pressure should be 1 bar , and substance should be pure at a given temperature. The conversion of graphite [C(graphite)] to diamond [C(diamond)] reduces its volume by $2 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{m}^{3} \mathrm{mol}^{-1}$. If C(graphite) is converted to C(diamond) isothermally at T = 298 K, the pressure at which C(graphite) is in equilibrium with C(diamond), is
[Useful information : $\left.1 \mathrm{J}=1 \mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^{2} \mathrm{s}^{-2} ; 1 \mathrm{Pa}=1 \mathrm{kg} \mathrm{m}^{-1} \mathrm{s}^{-2} ; 1 \text { bar }=10^{5} \mathrm{Pa}\right]$
(A) 14501 bar (B) 29001 bar (C) 58001 bar (D) 1405 bar
[JEE - Adv. 2017]
Ans. (A)