JEE Main Previous Year Question of Math with Solutions are available at eSaral. Practicing JEE Main Previous Year Papers Questions of mathematics will help the JEE aspirants in realizing the question pattern as well as help in analyzing weak & strong areas.
eSaral helps the students in clearing and understanding each topic in a better way. eSaral is providing complete chapter-wise notes of Class 11th and 12th both for all subjects.
Besides this, eSaral also offers NCERT Solutions, Previous year questions for JEE Main and Advance, Practice questions, Test Series for JEE Main, JEE Advanced and NEET, Important questions of Physics, Chemistry, Math, and Biology and many more.
Download eSaral app for free study material and video tutorials.
Q. The values of p and q for which the function f(x) =$\left\{\begin{aligned} \frac{\sin (\mathrm{p}+1) \mathrm{x}+\sin \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}} &, \quad \mathrm{x}<0 \\ \mathrm{q} &, \quad \mathrm{x}=0 \\ \frac{\sqrt{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{x}^{2}}-\sqrt{\mathrm{x}}}{\mathrm{x}^{\frac{3}{2}}} &, \quad \mathrm{x}>0 \end{aligned}\right.$ is continuous for all x in R, are :-
(1) $\mathrm{p}=-\frac{3}{2}, \mathrm{q}=\frac{1}{2}$
(2) $\mathrm{p}=\frac{1}{2}, \mathrm{q}=\frac{3}{2}$
(3) $\mathrm{p}=\frac{1}{2}, \mathrm{q}=-\frac{3}{2}$
(4) $\mathrm{p}=\frac{5}{2}, \mathrm{q}=\frac{1}{2}$
[AIEEE 2011]
Ans. (1)
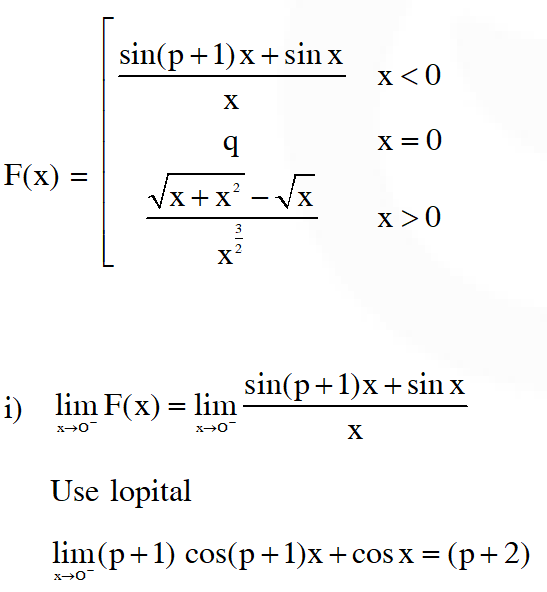
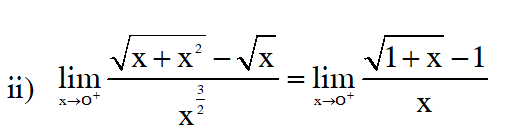
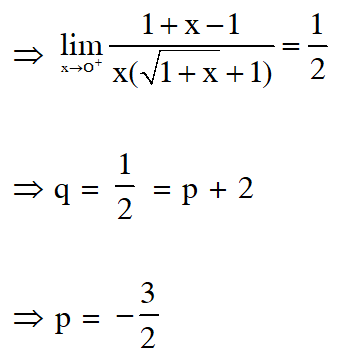
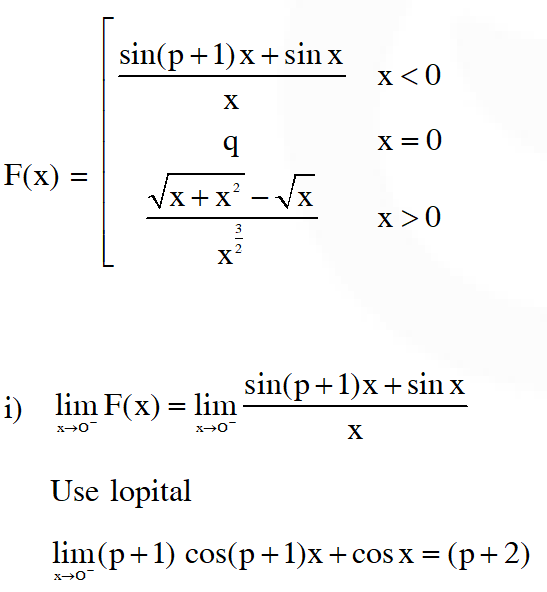
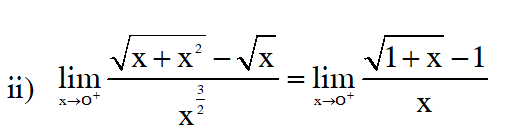
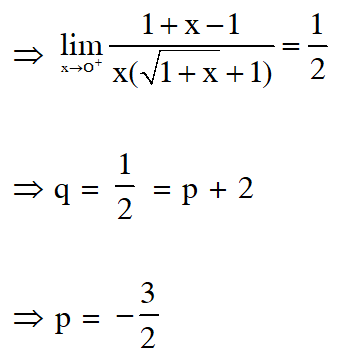
Q. Define $F(x)$ as the product of two real functions $f_{1}(x)=x, x \in \mathbb{R},$ and $f_{2}(x) $=\left\{\begin{array}{ccc}{\sin \frac{1}{x},} & {\text { if }} & {x \neq 0} \\ {0,} & {\text { if }} & {x=0}\end{array}\right.$ as follows : $\mathrm{F}(\mathrm{x})=\left\{\begin{array}{cc}{\mathrm{f}_{1}(\mathrm{x}) \cdot \mathrm{f}_{2}(\mathrm{x})} & {\text { if } \quad \mathrm{x} \neq 0} \\ {0,} & {\text { if } \quad \mathrm{x}=0}\end{array}\right.$
Statement-1 : F(x) is continuous on IR.
Statement-2 : f1(x) and f2(x) are continuous on IR.
(1) Statemen-1 is false, statement-2 is true.
(2) Statemen-1 is true,statement-2 is true;Statement-2 is correct explanation for
statement1.
(3) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is true, statement-2 is not a correct explanation for statement1
(4) Statement-1 is true, statement-2 is false
[AIEEE 2011]
Ans. (4)
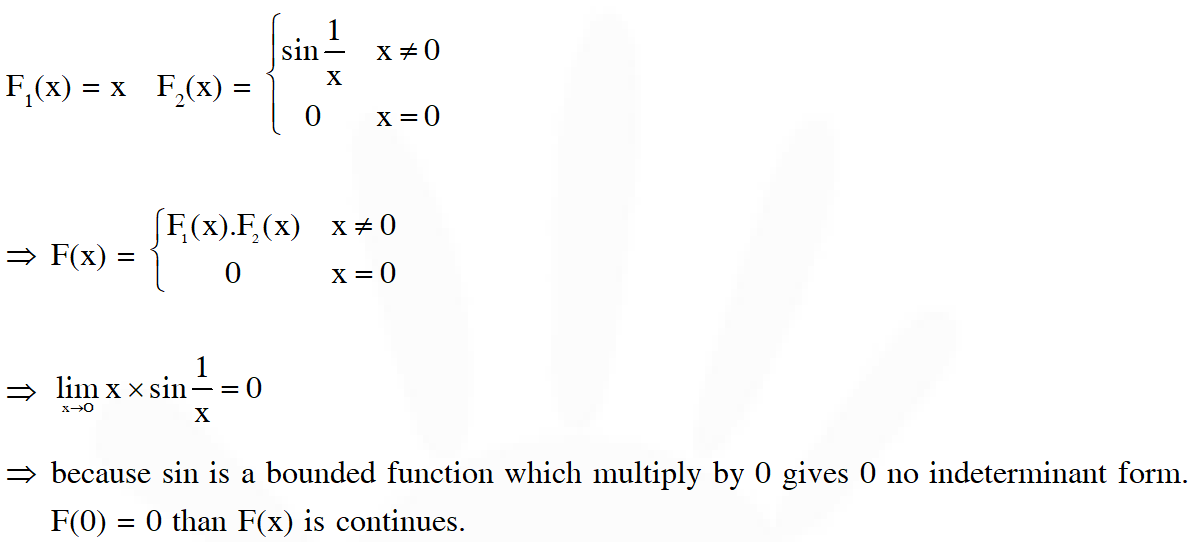
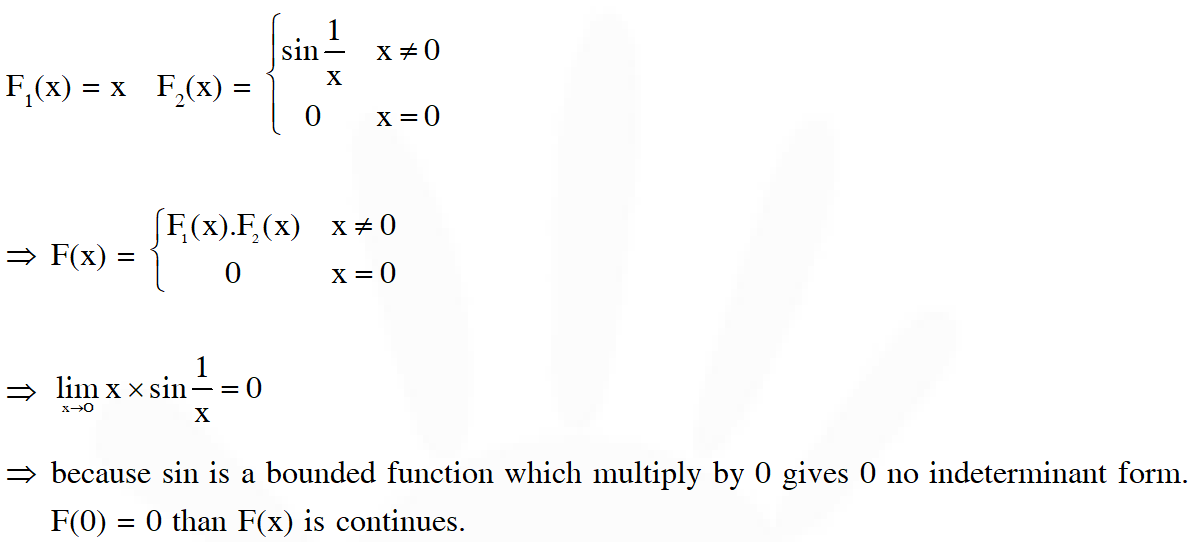
Q. If $\mathrm{f}(\mathrm{x})$ is continuous and $\mathrm{f}(9 / 2)=2 / 9,$ then $\lim _{\mathrm{x} \rightarrow 0} \mathrm{f}\left(\frac{1-\cos 3 \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}^{2}}\right)$ is equal to:
(1) 9/2 (2) 0 (3) 2/9 (4) 8/9
[JEE Mains Offline-2014]
Ans. (3)
$\mathrm{F}\left(\frac{9}{2}\right)=\frac{2}{9} \quad \lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \mathrm{F}\left[\frac{1-\cos 3 \mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{x}^{2}}\right]$
F(x) is continues and well defined than we can take limit inside.
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{F}\left[\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{1-\cos 3 x}{x^{2}}\right]$ use lopital
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{F}\left[\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{+3 \sin 3 \mathrm{x}}{2 \mathrm{x}}\right]=\operatorname{again}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{F}\left[\lim _{x \rightarrow 0} \frac{+9 \cos 3 x}{2}\right]=\mathrm{F}\left[\frac{9}{2}\right]=\frac{2}{9}$
Q. If the function $f(x)=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}{\frac{\sqrt{2+\cos x}-1}{(\pi-x)^{2}},} & {x \neq \pi} \\ {k} & {, x=\pi}\end{array}\right.$ is continuous at $x=\pi,$ then $k$ equals:-
(1) $\frac{1}{4}$
( 2)$\frac{1}{2}$
(3) 2
(4) 0
[JEE Mains Offline-2014]
Ans. (1)
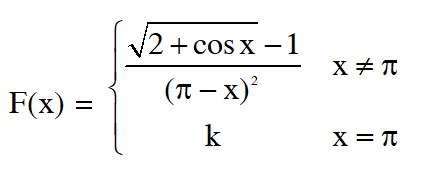
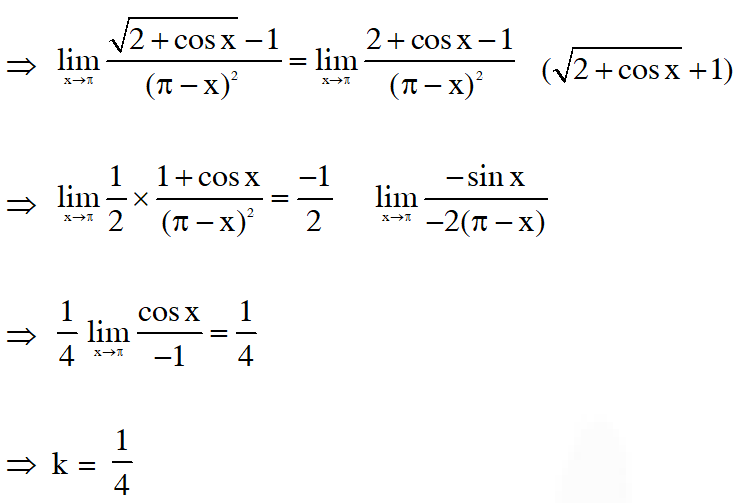
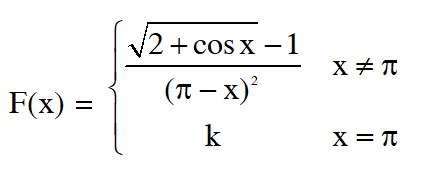
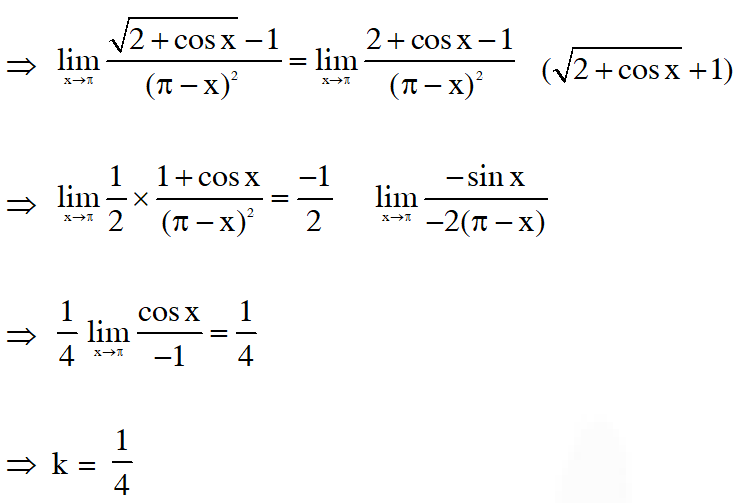
Q. If the function $f$ defined as $f(x)=\frac{1}{x}-\frac{k-1}{e^{2 x}-1}, x \neq 0,$ is continuous at $x=0,$ then the ordered pair $(k, f(0))$ is equal to :
( 1)$\left(\frac{1}{3}, 2\right)$
(2) (3, 2)
(3) (2, 1)
(4) (3, 1)
[JEE Mains-2018]
Ans. (4)
Q. Let $\mathrm{f}(\mathrm{x})=\left\{\begin{array}{ll}{(\mathrm{x}-1)^{\frac{1}{2-\mathrm{x}}},} & {\mathrm{x}>1, \mathrm{x} \neq 2} \\ {\mathrm{k}} & {, \mathrm{x}=2}\end{array}\right.$
The value of k for which f is continuous at x = 2 is :
(1) $\mathrm{e}^{-1}$
(2) e
(3) $\mathrm{e}^{-2}$
(4) 1
[JEE Mains-2018]
Ans. (1)
