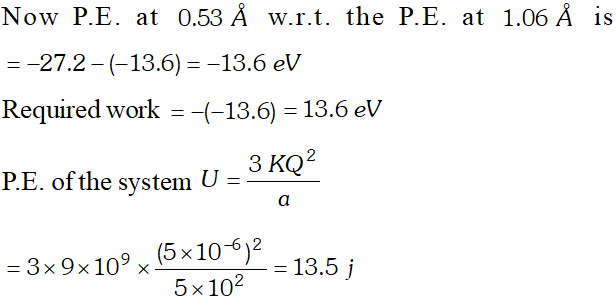Find some very important Electrostatics questions and answers for Class 12 board exams. These are developed by the experienced and expert faculties to help the students in their preparation. Not only Electrostatics topic,you can get almost all the topics from class 11 and 12 board physics with important questions and answers. These are designed keeping NCERT in the mind. All the best and prepare well for the exams. Download our app and Subscribe to our youtube channel. So learn Electrostatics using these questions and answers for Class 12 board and JEE exams.
Q. Why can we ignore quantisation of electric charge when dealing with macroscopic charges. [NCERT]
Ans. For macroscopic charges, e is very small, and n in very large. As q = ne, it behaves as if it were continuous.
Q. Consider three charged bodies P, Q and R. If P and Q repel each other and P attracts R, what will be the nature of force between Q and R.
Ans. Q will attract R.
Q. Consider the situation shown in the figure. What are the signs of Q1 and Q2?
Ans. is negative and is positive.
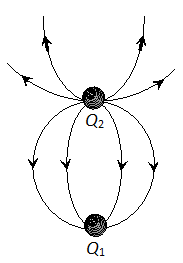
Q. The weight of a positively-charged particle is balanced by producing electric field between two parallel plates. State the direction of the electric field.
Ans. The electric field is vertically upward.
\
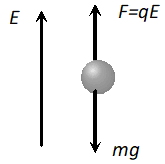
Q. Sketch the electric lines of force for two positive charge $Q_{1}$ and $Q_{2}\left(Q_{1}>Q_{2}\right)$ separated by a distance $d$.
Ans. Lines of force around $Q_{1}$ and $Q_{2}\left(Q_{1}>Q_{2}\right)$ shown in figure
Q. You are given electric lines of forces as shown :
At what point (A, B or C) is electric field minimum. 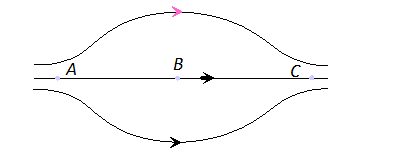
Ans. At B, electric field will be minimum, as the field lines are far apart.
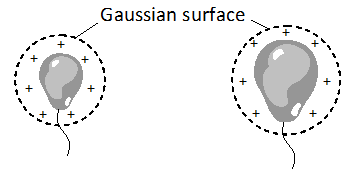
Q. What is the use of Gaussian surface ?
Ans. It is used to easily compute the electric field intensities due to certain charge systems or charged bodies, where use of coulomb’s law is quite difficult.
Q. An electric dipole of moment p is aligned parallel to a uniform electric field E. How much work will be done by an external field in rotating the dipole through (i) 90o (ii) 180o (end for end) (iii) 360o from the direction of field.
Ans. As, $W=p E\left(\cos \theta_{1}-\cos \theta_{2}\right)$ (i) ${{\theta }_{1}}={{0}^{{}^\circ }}\text{ }\!\!\And\!\!\text{ }{{\theta }_{2}}={{90}^{{}^\circ }},\quad W=pE$ (ii) ${{\theta }_{1}}={{0}^{{}^\circ }}\text{ }\!\!\And\!\!\text{ }{{\theta }_{2}}={{180}^{{}^\circ }},\quad W=2pE$ (iii) ${{\theta }_{1}}={{0}^{{}^\circ }}\text{ }\!\!\And\!\!\text{ }{{\theta }_{2}}={{360}^{{}^\circ }},\quad W=0$
Q. How much work is required in turning an electric dipole of dipole moment $\vec{P}$ from its position of stable equilibrium to its position of unstable equilibrium in a uniform electrostatic field $\vec{E}$ .
Ans. In stable equilibrium angle between $\vec{p}$ and $\vec{E}$ is $0^{\circ}$ and in unstable equilibrium this angle becomes $180^{\circ} .$ Work done $=p E\left(\cos \theta_{1}-\cos \theta_{2}\right)$ Hence, $\theta_{1}=0^{\circ}, \theta_{2}=180^{\circ}=p E(1+1)=2 p E$
Q. What will be the equipotential surfaces corresponding to (i) A constant electric field in the z-direction. (ii) A field that uniformly increase in magnitude but its direction remains unchanged along the z-axis.
Ans. (i) Equidistant planes parallel to the
x – y plane,
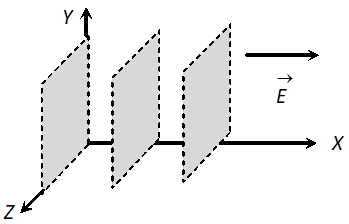
(ii) Again the equipotential surface are planes parallel to the
x – y plane but they become closer together as the field increases,
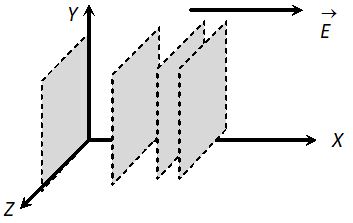
(iii) Concentric spheres with centre at the origin.
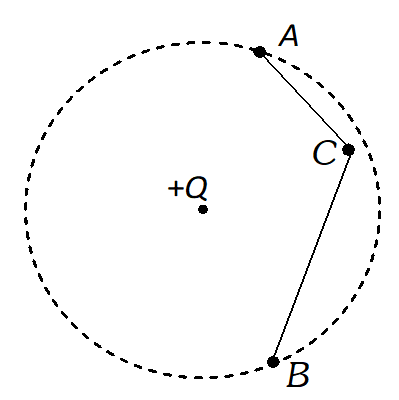
Q. If a point charge +Q, is taken first from A to C and then form C to B of a circle drawn with another point-charge +Q as centre, then along which path more work will be done?
Ans. As explained points
A and
B are at same potential. It follows that $V_{C}-V_{A}=V_{C}-V_{B}$ Hence, work done in taking a point charge from
A to
C or from
C to
B will be the same.
 Short Answer (2 Marks)
Short Answer (2 Marks) Q. An electric dipole with dipole moment $4 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{C}^{m}$ is aligned at $30^{\circ}$ with direction of uniform electric field of magnitude $5 \times 10^{4} N C^{-1}$ . Calculate the magnitude of the torque acting on the dipole. [NCERT]
Ans. Given $P=4 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{cm}, \theta=30^{\circ}, E=5 \times 10^{4} \mathrm{NC}^{-1}$ $\tau=P E \sin \theta=4 \times 10^{-9} \times 5 \times 10^{4} \times \sin 30^{\circ}$ $=4 \times 5 \times 10^{-5} \times \frac{1}{2}=10^{-4} \mathrm{Nm}$
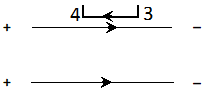
Q. A uniform electric field E exists between two charged plates. What will be the work done in moving a charge Q along a closed rectangular path?
Ans. Suppose the breadth of rectangular path is
d. The force on the charge
Q is
QE. The work in taking charge from $1 \rightarrow 2$ is $Q E \times d$ and that from $3 \rightarrow 4$ will be $-Q E \times d$ No work will be done in taking the charge from $2 \rightarrow 3$ and $4 \rightarrow 1$ because along these paths the direction of the force acting on the charge is perpendicular to the displacement. Hence net work done along the rectangular path will be zero.
Q. Derive an expression for the potential at a point along the axial line of a short electric dipole.
Ans. Let us consider an electric dipole
AB and a point
P on its axial line at a distance
r from its centre where we have to find electric potential
, Potential at $P$ due to charge at $A, V_{P A}=-\frac{k Q}{r+a}$
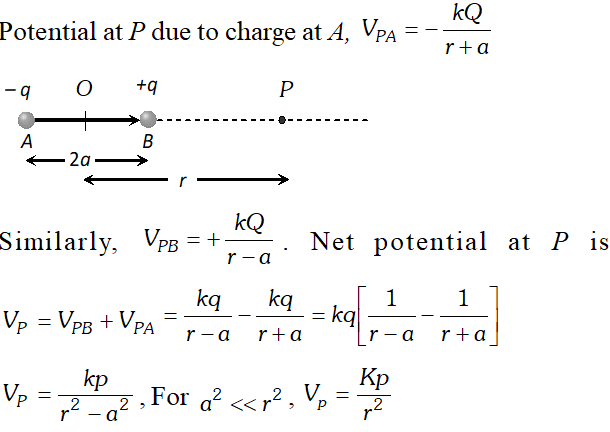
Q. An electric dipole is situated in a uniform electric field such that its moment is aligned in the direction of the field . Is the equilibrium of the dipole stable or unstable ? If and are in opposite directions, then ?
Ans. When the dipole moment is in the direction of the electric field the dipole is in ‘stable’ equilibrium because as soon as it is displaced through an angle, say a torque acts upon it bringing it back along the field. When and are in opposite directions the torque on the dipole is zero and the dipole is again in equilibrium. But, now the equilibrium is ‘unstable’ because any displacement from this position gives rise to a torque which sets the dipole in the direction of the field.
Q. What does the negative sign in the expression for potential energy $(U=-p E \cos \theta)$ signify $?$
Ans. While deriving the expression for potential energy, the potential energy of the dipole is taken as zero, when it is oriented perpendicular to the direction of the electric field. In any other orientation between $\theta=0^{\circ}$ to $\theta=90^{\circ}$ the potential energy of the dipole is less than zero and hence the negative sign.
Q. An electric dipole is placed in uniform external field field : (i) Show that the torque on the dipole moment of the dipole (ii) Show that no translatory force act on it. OR Derive an expression for the maximum torque acting on an electric dipole, when held in a uniform electric field. [NCERT]
Ans. Suppose an electric dipole $A B$ of dipole moment $\vec{p}$ is kept in uniform electric field $E$ by making angle $\theta$ with the direction of field
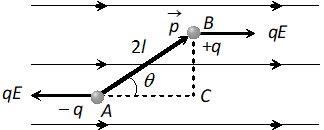
Force on charge $+q$ at $B$ is $F=q E,$ along the direction of $\vec{E}$ force on charge $-q$ at $A$ is also in opposite direction of . Since, these two forces are parallel and equal and also acting at different points so they will form a couple which rotates the dipole in clockwise direction. Draw a line , perpendicular distance between the forces = $A C=A B \sin \theta=2 l \sin \theta$ As torque $\tau=$ force $\times$ perpendicular distance between forces $\Rightarrow \tau=(q E) \times 2 l \sin \theta \Rightarrow \tau=(q \times 2 l) E \sin \theta=p E \sin \theta$ In vector form $\vec{\tau}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}$ (ii) Since two equal and opposite forces are acting on dipole so net force on it is zero
i.e. it will not execute translatory motion.
Q. An electric dipole is held at an angle $\theta$ in a uniform external electric field $\vec{E}$. Will there be any (i) net translatory force, (ii) torque acting on it ? Explain what happens to the dipole on being released.
Ans. The electric field exerts a force QE on charge +Q and a force – QE on charge – Q of the dipole. Hence there is no net translatory force, but a torque $p E \sin \theta$ acts on the dipole which aligns the dipole parallel to the field when the dipole is released.
Q. A spherical surface surrounds a point charge. Describe what happens to the total flux through the surface if : (a) the charge is tripled (b) the volume of the sphere is doubled (c) the surface is changed to a cube and (d) the charge is moved to some other location inside the surface.
Ans. (a) If the charge is tripled, the flux through the surface is also tripled, because the net flux is proportional to the charge inside the surface. (b) The flux remains constant when the volume changes. Because the surface surrounds the same amount of charge, regardless of its volume. (c) The total flux does not change when the shape of the closed surface changes. (d) The total flux through the closed surface remains unchanged when the charge inside the surface is moved to another location inside the surface.
Q. A spherical rubber balloon carries a charge that is uniformly distributed over its surface. As the balloon is blown it’s surface. As the balloon is blown up and increases in size, how does the total electric flux coming out of the surface change? Give reason.
Ans. The flux coming out of the surface doesn’t change because the flux through the Gaussian surface changes only when enclosed charge changes.
Q. A long charged cylinder of linear charged density is surrounded by a hollow co-axial conducting cylinder. What is the electric field in the space between the two cylinders. [NCERT]
Ans. Suppose we have to find electric field at a distance
r from the axis. Imagine a Gaussian surface (cylindrical) of radius ‘
r’ and length
L, in between the cylinders. Charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface is $=\lambda L$ At each point electric field vector and area vector are in the same direction. Thus,
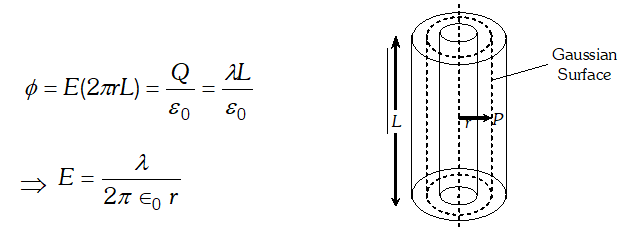
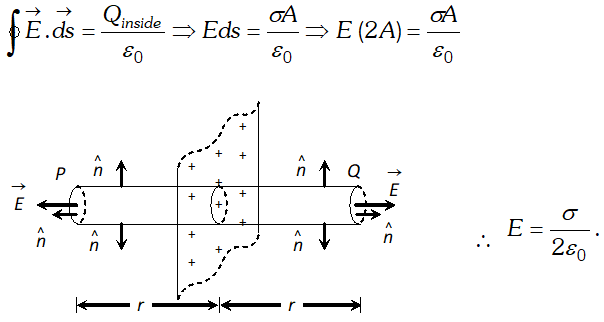
Q. Using Gauss’s theorem, derive an expression for electric field intensity at a point near a thin infinite plane sheet of electric charge.
Ans. Field due to an infinite plane sheet of charge : Consider an infinite plane sheet of charge having surface charge density $\sigma$ Let
P be a point at a distance
r from it where the field strength is to be determined using Gauss’ theorem. Let us consider a Gaussian surface in the form of a cylinder of length 2
r and area of cross-section
A arranged such that its lateral surface is parallel to the field lines and its ends are normal to the field lines as shown. For this reason. $\int E \cdot \overrightarrow{d s}$will be zero for the lateral surface and it will be simply
Eds for the end faces of the cylinder. Moreover, the charge enclosed by the Gaussian surface will be $\sigma A$.So according to Gauss’ theorem
Q. Vehicles carrying inflammable material usually have metallic chains touching the ground during motion. Why?
Ans. When a vehicle moves, its body gets charged on account of friction due to air. The tyres also accumulate the charge on account of friction between the tyres and the road. The metallic ropes from the vehicle touching the ground enable the accumulated charges to flow to earth. This would otherwise be hazardous to the inflammable materials.
Q. Ordinary rubber is an insulator. But the special rubber tyres of air crafts are made slightly conducting. Why is this necessary ? [NCERT]
Ans. The special rubber tyres of air crafts are made slightly conducting so that electricity generated on account of friction between the tyres and the runway goes to earth.
Q. Four point charges [NCERT] $q_{A}=2 \mu C, q_{B}=-5 \mu C, q_{C}=2 \mu C,$ and $q_{D}=-5 \mu C$ are located at the corners of a square ABCD of side 10cm. What is the force on a charge of placed at the centre of the square.
Ans. Given $q_{A}=2 \mu C, q_{B}=5 \mu C, q_{C}=2 \mu C, q_{D}=-5 \mu C$ Distance of all the charges from the centre is same Charge at opposite corners are making pairs by producing electric field at the centre equal in magnitude and opposite in direction. So, net electric field at the centre,
i.e., force on a charge of $1 \mu C$ will be zero.
Q. A polythene piece rubbed with wool is found to have a negative charge of $3 \times 10^{-7} C$ (i) Estimate the number of electrons transferred (from which to which ?) (ii) It there a transfer of mass from wool to polythene? [NCERT]
Ans. 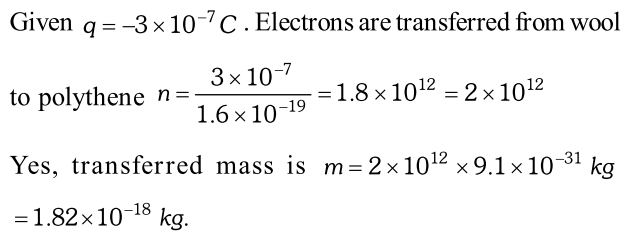
Q. There point charges of $+2 \mu C,-3 \mu C$ and $-3 \mu C$ are kept
at the vertices, $A, B$ and $C$ respectively of an equilateral triangle of side $20 c m$ as shown in the figure. What should be the sign and magnitude of the charge to be placed at the mid-point (M) of side BC so that the charge at A remains in equilibrium ? 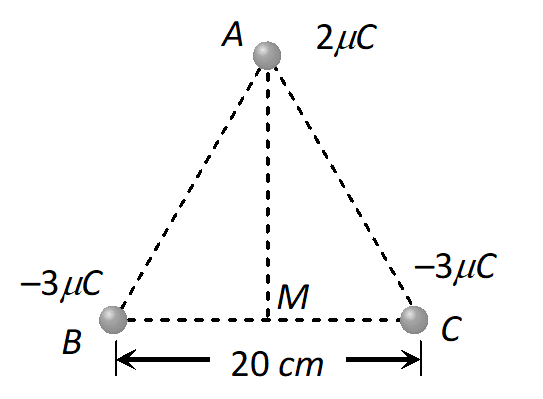
Ans. Force exerted on $+2 \mu C$ charge by charge at $A$
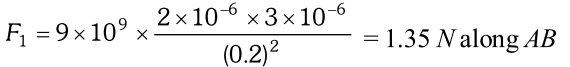
Force exerted on charge by charge at $C$$=1.35 \mathrm{N}$ along $\mathrm{A} C$ The resultant force of $\mathrm{F}_{1}$ and $\mathrm{F}_{2} \mathrm{is}=2.34 \mathrm{N}$ along $\mathrm{AM}$
Q. (a) Consider an arbitrary electrostatic field configuration. A small test charge is placed at a point (i.e., where E = 0) of the configuration. Show that equilibrium of test charge is necessarily unstable. (b) Verify this result for the simple configuration of two charges of the same magnitude and sign placed a certain distance apart. [NCERT]
Ans. (a)Suppose the equilibrium is stable ; then the test charge displaced slightly in any in any direction will experience a restoring force towards the -point. That is, all field lines near the -point should be directed inwards towards the -point. That is, there is a net inward flux of electric field through a closed surface around the -point. But by Gauss’s law, the flux of electric field through a surface, not enclosing any charge, must be zero. Hence, the equilibrium cannot be stable. (b) The mid-point of the line joining the two charges is a -point. Displace a test charge from the -point slightly along the line. There is a restoring force. But displace it say, normal to the line. You will see that the net force takes it away from the -point. Remember, stability of equilibrium needs restoring force in all direction
Q. The discharging current in the atmosphere due to small conductivity of air is known to be 1800 A on an average over the globe. Why then does the atmosphere not dischrge itself completely in due course and become electrically neutral ? [NCERT]
Ans. This is because the atmosphere of earth is also being charged by thunder storms and lightning all over the globe approximately at the same rate of 1800 ampere. That is why atmosphere cannot become electrically neutral
Q. A spherical conducting shell of inner radius $r_{1}$ and outer radius $r_{2}$ has a charge Q. [NCERT] a) A charge q is placed at the centre of the shell. What is the surface charge density on the inner and outer surfaces of the shell. (b) Is the electric field inside a cavity (with no charge) zero, even if the shell is not spherical, but has any irregular shape? Explain.
Ans. (a) +
q charge placed at the centre of the shell induces –
q charge on the inner surface of the shell and +
q of the outer surface. Thus surface charge on inner surface is $\sigma=-\frac{q}{4 \pi r_{1}^{2}}$
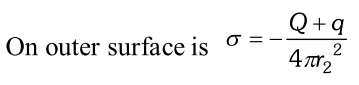
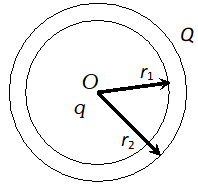
(b) By Gauss’ law, the net charge on the inner surface enclosing the cavity (not having any charge) must be zero. For a cavity of arbitrary shape, this is not enough to claim that electric field inside must be zero. The cavity may have positive and negative charges with total charge zero. In order to clear this point, we take a closed loop, part of which is inside the cavity along a field line and remaining part inside the conductor. Since, field inside the conductor is zero. A certain amount of work is done by the field in carrying a test charge over the closed loop. As this is not possible for an electrostatic field, no field lines are there inside the cavity (
i.e., no field). Thus, we conclude that there will be no charge on the inner surface of the conductor, whatever be its shape.
Q. A conducting sphere of radius 10cm has an unknown charge. If the electric field 20cm from the centre of the sphere is $1.5 \times 10^{3} N / C$ and points radially inward, what is the value of the point charge ? [NCERT]
Ans. Since the electric field is radially inward so charge on sphere will be negative
i.e., Electric field at the surface of

Q. An infinite line charge produces a field of $9 \times 10^{4} N / C$ at a distance of 2cm. Calculate the linear charge density. [NCERT]
Ans. 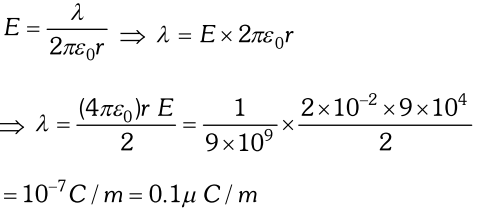
Q. A point charge causes an electric flux of $-1.0 \times 10^{3} N m^{2} / C$ to pass through a spherical Gausian surface of 10.0cm radius centred on the charge. (a) If the radius of the Gausian surface were doubled, how much flux would pass through the surface ? (b) What is the value of the point charge? [NCERT]
Ans. (a) As same charge is enclosed by the Gausian surface, electric flux remains unchanged $i e .$$-10^{3} \mathrm{Nm}^{2} / \mathrm{C}$
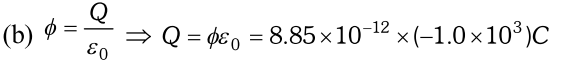
$\Rightarrow Q=-8.8 \times 10^{-9} C$
Q. A point charge $+10 \mu C$ is a distance $5 \mathrm{cm}$ directly above the centre of square of side $10 \mathrm{cm}$ as shown in Fig. What is the magnitude of the electric flux through the square ? [NCERT]
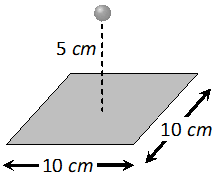
Ans. As we can imagine that given square is one of the faces of a cube of side 10
cm.
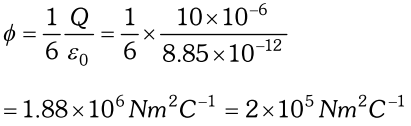
Q. (i) Calculate the potential at a point P due to charge of $4 \times 10^{-7} C$ located 9cm away. (ii) Hence, obtain the work done in bringing a charge of $2 \times 10^{-9} C$ from infinity to the point P. Does the answer depend on the path along which the charge is brought? [NCERT]
Ans. 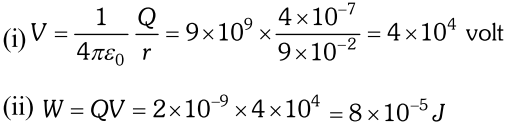
As electric field is conservative, work done does not depend upon path.
Q. (i) Determine the electrostatic potential energy of a system containing two charges $7 \mu C$ and $-2 \mu C$separated by a distance of 18cm. (ii) How much work is required to separate the two charges infinitely away from each other? [NCERT]
Ans. 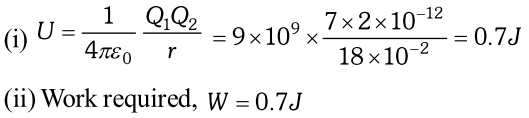
Q. A charge of $8 m C$ is located at the origin. Calculated the work done is taking a small charge of $-20 \times 10^{-9} C$ from a point $A(0,0,3 \mathrm{cm})$ to a point $B(0,4 \mathrm{cm}, 0),$ via point $C(0,6 \mathrm{cm}, 9 \mathrm{cm})$. [NCERT]
Ans. Here $Q=8 \times 10^{-3} C, Q_{0}=2 \times 10^{-9} C, r_{1}=3 \mathrm{cm}$ and $r_{2}=4 \mathrm{cm}$
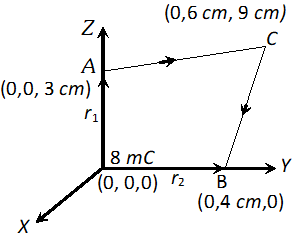
Electric potential energies at points
A and
B are
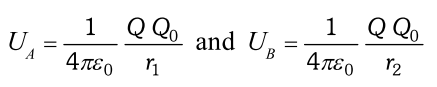
Hence, work done in taking the charge from point
A to
B 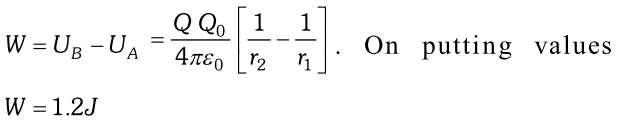
Q. If one of the two electrons from a $H_{2}$ molecule is removed, we get hydrogen molecular ion $\left(H_{2}^{+}\right)$. In the ground state of a , the two protons are separated by roughly , and the electron is roughly from each proton. Determine the potential energy of the system. Specify your choice of the zero of potential energy. [NCERT]
Ans. 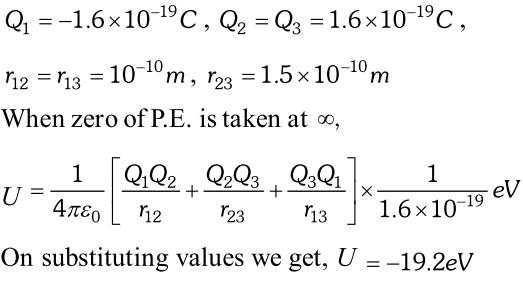
Q. Two charges $2 \mu C$ and $-2 \mu C$ are placed at points A and B 6 cm apart. (i) Identify equipotential surface of the system. (ii) What is the direction of the electric field at every point on this surface ?
Ans. Figure shows two charges of $2 \mu C$ and $-2 \mu C$ located at the points
A and
B, such that
AB = 6
cm.
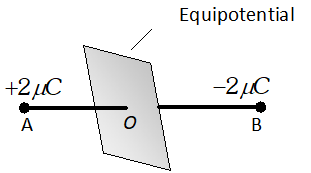
(i) For the given system of two charges, the equipoential surface will be a plane normal to the line
AB joining the two charges and passing through its mid-point
O. On any point on this plane, the potential is zero. (ii) The electric field is in a direction from the point
A to point
B i.e. from the positive charge to negative charge and normal to the equipotential surface.
Q. In a hydrogen atom, the electron and proton are bound at a distance of about $0.53 A1.06 A$ separation ? [NCERT]
Ans. $Q_{1}=-1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}, Q_{2}=+1.6 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}$ When zero of potential energy is taken at infinite separation, potential energy
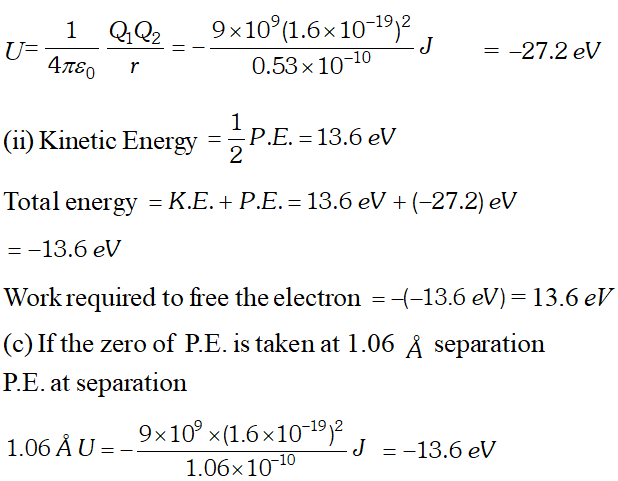
Q. A hollow charged conductor has a tiny hole cut into its surface. Show that the electric field in the hole is $\left(\frac{\sigma}{2 \epsilon_{0}}\right) \hat{n}$ where $\hat{n}$ is the unit vector in the outward normal direction and $\sigma$ is the surface charge density near the hole. [NCERT]
Ans. In case hole is filled up, total electric field outside is $\vec{E}_{1}+\vec{E}_{2}=\frac{\sigma}{\epsilon_{0}} \hat{n}$ …(i)
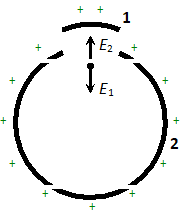
Total field inside the hollow conductor $\vec{E}_{1}+\vec{E}_{2}=0 \cdots$ (ii) Here $\vec{E}_{1}$ is the electric field due to the portion filling up the hole and $\vec{E}_{2}$ is the electric field due to rest of the charged conductor. From relations (i) and (ii) we conclude that
Q. Two large, thin metal plates are parallel and close to each other. On their inner faces, the plates have surface charge densities of opposite signs and of magnitude $17.0 \times 10^{-12} \mathrm{C} / \mathrm{m}^{2}$. What is E : (a) in the outer region of the first plate (b) in the outer region of the second plate, and (c) between the plates [NCERT]
Ans. In the I and II region of the plates, electric field is $E_{I}=E_{I I}=0$ as electric field are equal in magnitude and opposite in directions in region I and II Electric field between the plates
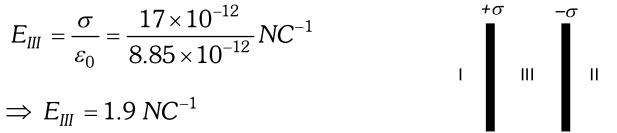
Q. Figure given below shows tracks of three charged particles in a uniform electrostatic field. Give the signs of the three charges. Which particle has the highest charge to mass ratio ? Explain.
[NCERT] 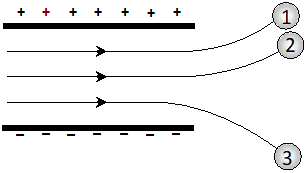
Ans. As charged particles deflect towards oppositely charged plates therefore particles 1, 2 are negatively charged and particle 3 is positively charged.
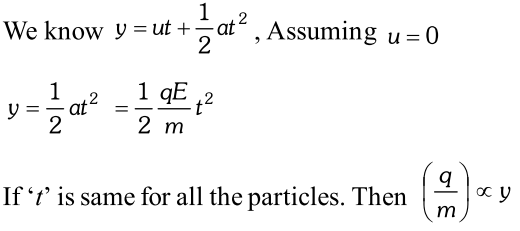
Thus, particle 3 having maximum deflection along vertical direction will be having the highest charge to mass ratio.
Q. An oil drop of 12 excess electrons is held stationary under a constant electric field of $2.55 \times 10^{-4} N C^{-1}$ oil drop experiment. The density of the oil is $1.26 g \mathrm{cm}^{-1}$. Estimate the radius of the drop . $\left(g=9.81 m s^{-2}, e=1.60 \times 10^{-19} \mathrm{C}\right)$ [NCERT]
Ans. 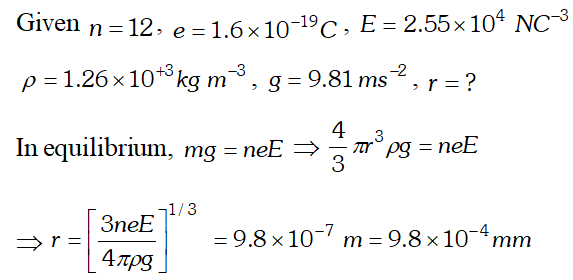
Q. (i) Two insulated charged copper spheres A and B have their centres separated by distance of 50cm. What is the mutual force of electrostatic repulsion if the charge on each is $6.5 \times 10^{-7} \mathrm{C}$ ? The radii of A and B are negligible compared to the distance of separation. (ii) What is the force of repulsion if each sphere is charged double the above amount, and the distance between them is halved ? [NCERT]
Ans. 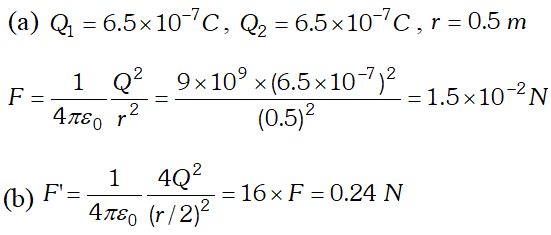
Q. Suppose the spheres A and B in the above question have identical sizes. A third sphere of the same size but uncharged is brought in contact with the first, then brought in contact with the second, and finally removed from both. What is the new force of repulsion between A and B ? [NCERT]
Ans. 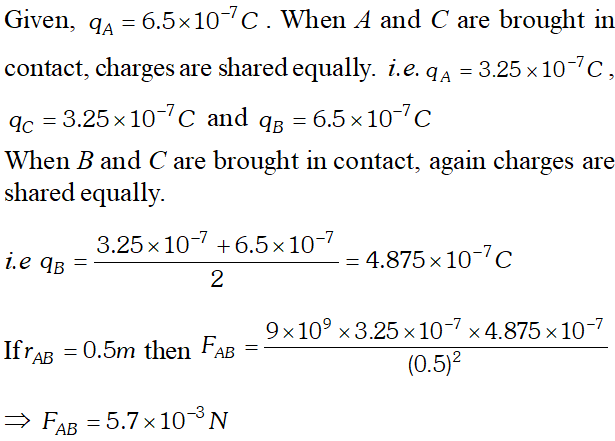
Q. A plastic comb run through one’s dry hairs attracts small bits of paper. Why? What happens if the hairs are wet or if it is raining ? [NCERT]
Ans. A plastic comb run through dry hairs acquires a negative charge by friction. When it is brought near a bit of paper*, the electrons in each atom of the paper are repelled away resulting in a charge separation within each atom. As the positive charge of each atom is now closer to the comb than the negative charge (which has been repelled away), the force of attraction between the comb and the positive charge of the atom exceeds the force of repulsion between the comb and the negative charge of the atom. Thus the net force on the paper is attractive. If the hairs are wet, friction between the comb and the hairs is much reduced and so the comb does not acquire enough charge to attract bits of paper. If it is raining, the air becomes some what conducting and the comb fails to acquire charge. Hence it does not attract bits of paper.
Q. A glass rod rubbed with silk is brought close to two uncharged metallic spheres
A and
B touching each other. The rod induces charges on
A and
B, as shown. State what happens when : (i)
A and
B are slightly separated, (ii) the glass rod is then taken away, and finally (iii)
A and
B are separated far apart.
[NCERT] 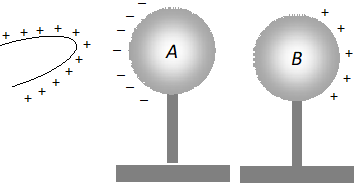
Ans. A glass rod rubbed with silk acquires positive charge. When this rod in brought close to two uncharged metallic spheres
A and
B in contact negative charge in induced on left side of sphere
A and an equal positive charge is induced on right side of sphere
B, as shown in figure (i) When the spheres
A and
B are slightly separated, the right face of
A acquires positive induced charge and the left face of
B acquires negative induced charge, as shown in the figure.
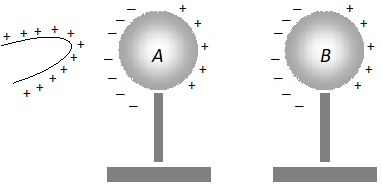
ii) When the glass red rod is removed, the distribution of charges on
A and
B remains the same, because the positive charge on
A and the negative charge on
B are mutually bound. When
A and
B are separated far apart, the negative and positive charges on each re-unite and both
A and
B become uncharged.
Q. Consider a uniform electric field $E=3 \times 10^{3} \hat{i} N / C$ (a) What is the flux of this through a square of 10cm on a side whose plane is parallel to the y-z plane ? (b) What is the flux through the same square if the normal to its plane makes a 30° angle with the x-axis [NCERT]
Ans. 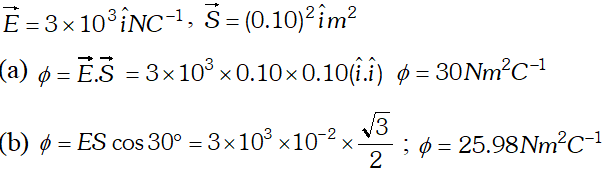
Q. Derive an expression for the magnitude of electric field intensity at any point along the equatorial line of a short electric dipole. Give the direction of electric field intensity at that point. For a short dipole what is the ratio of electric field intensities at two equidistant points from the centre of dipole. One along the axial line and another on the equatorial line.
Ans. Let an electric dipole
AB of charge
q and separation between them 2
l, 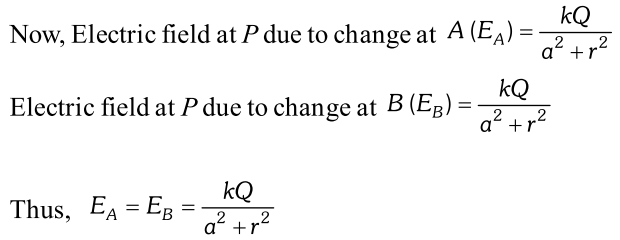
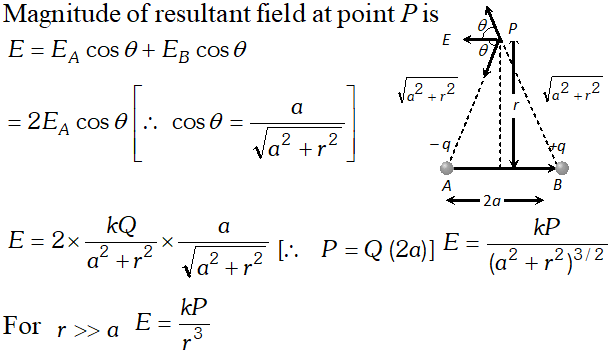
The direction of electric field $\vec{E}$ isopposite to that of dipole moment $\vec{p} .$ Electric field on axial line is double of the electric field on equitorial line for a short dipole a two equidistant points from the centre of dipole. i.e. $E_{\text {axial }}: E_{\text {eqn }}:: 2: 1$
Q. In a certain region of space, electric field is along the z-direction throughout. The magnitude of electric field is, however, not constant but increases uniformly along the positive z-direction, at the rate of $10^{5} N C^{-1}$ per meter. What are the force and total dipole moment equal to $10^{-7} \mathrm{Cm}$ in the negative z-direction? [NCERT]
Ans. 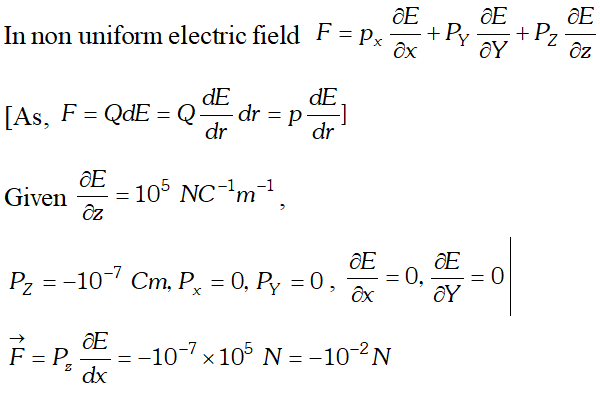
Here –
ve sign indicates that force is directed along –
ve z-axis. As both $\vec{P}$ and $\vec{E}$ are along $z$ -axis, in apposite direction $\sin \theta=180^{\circ}$ $\therefore \tau=p E \sin \theta=0$
Q. A molecule of a substance has permanent electric dipole moment equal to $10^{-29} C \times m$ . A mole of this substance is polarised (at low temperature) by applying a strong electrostatic field of the magnitude $\left(10^{6} \mathrm{Vm}^{-1}\right)$ . The direction of the field is suddenly changed by an angle of 60°. Estimate the heat released by the substance in aligning its dipoles along the new direction of the field. For simplicity, assume 100% polarisation of sample. [NCERT]
Ans. 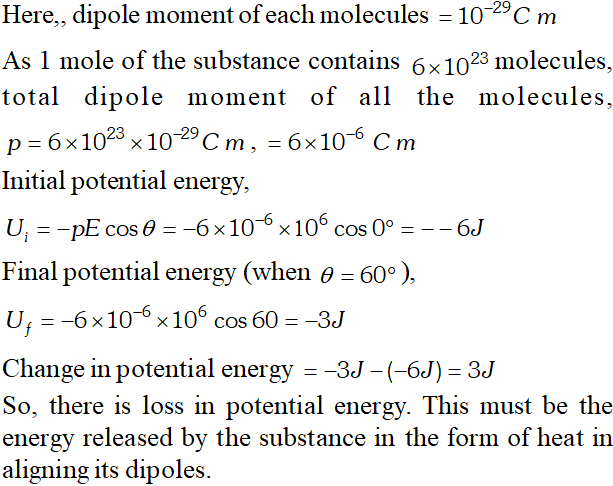
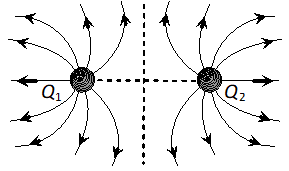
Q. Figures (a) and (b) show the field lines of a single positive and negative charge respectively :
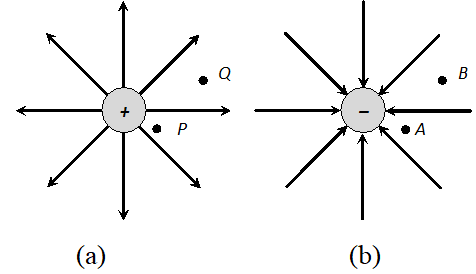 (i) Give the sign of the potential difference $V_{P}-V_{Q}$ and $V_{B}-V_{A}$ (ii) Give the sign of the potential energy difference of a small negative charge between the point Q and P ; A and B. (iii) Give the sign of the work done by the field in moving a small positive charge from point Q to P. (iv) Give the sign of the work done by an external agency in moving a small negative charge from point B to A. (v) Does the kinetic energy of a small negative charge increase or decrease in going from point B to A?
(i) Give the sign of the potential difference $V_{P}-V_{Q}$ and $V_{B}-V_{A}$ (ii) Give the sign of the potential energy difference of a small negative charge between the point Q and P ; A and B. (iii) Give the sign of the work done by the field in moving a small positive charge from point Q to P. (iv) Give the sign of the work done by an external agency in moving a small negative charge from point B to A. (v) Does the kinetic energy of a small negative charge increase or decrease in going from point B to A? Ans. (i) In Figure (a), as the field is due to positive charge, $V_{P}-V_{Q}>0$ In Figure (b), as the field is due to negative charge, $\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{A}}-\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{B}}<0$ or $\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{B}}-\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{A}}>0$ (ii) The potential energy of a negative charge at point
Q will be negative and at point
P, it will be still more negative. Therefore, For similar reasons, $(P . E .)_{A}-(P . E .)_{B}>0$ (iii) A small positive charge will tend to move from point
P to
Q and the work done by the field in moving the charge from point
P to
Q will be positive. Therefore, work done by electric field in moving a small positive charge from point
Q to
P will be negative. (iv) For the reasons as given in (iii), work done by external agency in moving a small negative charge from
B to
A will be positive. (v) As the potential energy of the negative charge increases, kinetic energy of the negative charge decreases in going from point
B to
A.
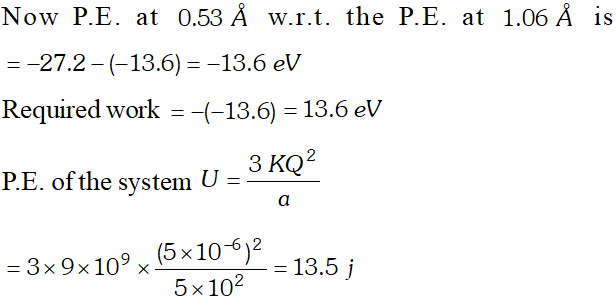
Click Here for Detailed Notes of any chapter.
eSaral provides you complete edge to prepare for Board and Competitive Exams like JEE, NEET, BITSAT, etc. We have transformed classroom in such a way that a student can study anytime anywhere. With the help of AI we have made the learning Personalized, adaptive and accessible for each and every one. Visit eSaral Website to download or view free study material for JEE & NEET. Also get to know about the strategies to Crack Exam in limited time period.

 \
\ 

 (ii) Again the equipotential surface are planes parallel to the x – y plane but they become closer together as the field increases,
(ii) Again the equipotential surface are planes parallel to the x – y plane but they become closer together as the field increases,  (iii) Concentric spheres with centre at the origin.
(iii) Concentric spheres with centre at the origin.  Short Answer (2 Marks)
Short Answer (2 Marks) 
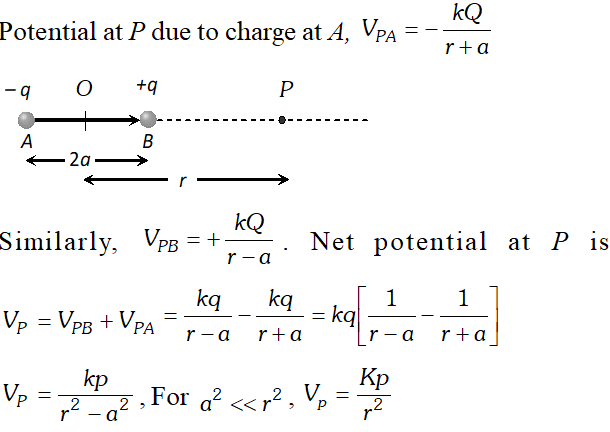
 Force on charge $+q$ at $B$ is $F=q E,$ along the direction of $\vec{E}$ force on charge $-q$ at $A$ is also in opposite direction of . Since, these two forces are parallel and equal and also acting at different points so they will form a couple which rotates the dipole in clockwise direction. Draw a line , perpendicular distance between the forces = $A C=A B \sin \theta=2 l \sin \theta$ As torque $\tau=$ force $\times$ perpendicular distance between forces $\Rightarrow \tau=(q E) \times 2 l \sin \theta \Rightarrow \tau=(q \times 2 l) E \sin \theta=p E \sin \theta$ In vector form $\vec{\tau}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}$ (ii) Since two equal and opposite forces are acting on dipole so net force on it is zero i.e. it will not execute translatory motion.
Force on charge $+q$ at $B$ is $F=q E,$ along the direction of $\vec{E}$ force on charge $-q$ at $A$ is also in opposite direction of . Since, these two forces are parallel and equal and also acting at different points so they will form a couple which rotates the dipole in clockwise direction. Draw a line , perpendicular distance between the forces = $A C=A B \sin \theta=2 l \sin \theta$ As torque $\tau=$ force $\times$ perpendicular distance between forces $\Rightarrow \tau=(q E) \times 2 l \sin \theta \Rightarrow \tau=(q \times 2 l) E \sin \theta=p E \sin \theta$ In vector form $\vec{\tau}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{p}} \times \overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}$ (ii) Since two equal and opposite forces are acting on dipole so net force on it is zero i.e. it will not execute translatory motion. 
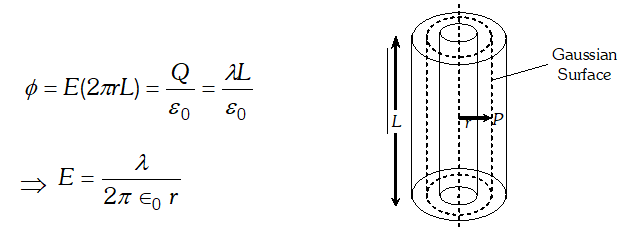


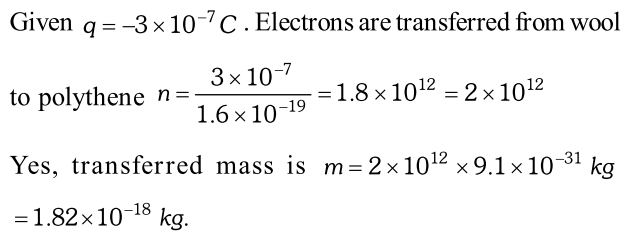

![]() Force exerted on charge by charge at $C$$=1.35 \mathrm{N}$ along $\mathrm{A} C$ The resultant force of $\mathrm{F}_{1}$ and $\mathrm{F}_{2} \mathrm{is}=2.34 \mathrm{N}$ along $\mathrm{AM}$
Force exerted on charge by charge at $C$$=1.35 \mathrm{N}$ along $\mathrm{A} C$ The resultant force of $\mathrm{F}_{1}$ and $\mathrm{F}_{2} \mathrm{is}=2.34 \mathrm{N}$ along $\mathrm{AM}$ 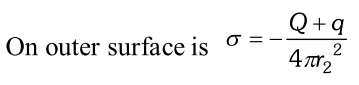
 (b) By Gauss’ law, the net charge on the inner surface enclosing the cavity (not having any charge) must be zero. For a cavity of arbitrary shape, this is not enough to claim that electric field inside must be zero. The cavity may have positive and negative charges with total charge zero. In order to clear this point, we take a closed loop, part of which is inside the cavity along a field line and remaining part inside the conductor. Since, field inside the conductor is zero. A certain amount of work is done by the field in carrying a test charge over the closed loop. As this is not possible for an electrostatic field, no field lines are there inside the cavity (i.e., no field). Thus, we conclude that there will be no charge on the inner surface of the conductor, whatever be its shape.
(b) By Gauss’ law, the net charge on the inner surface enclosing the cavity (not having any charge) must be zero. For a cavity of arbitrary shape, this is not enough to claim that electric field inside must be zero. The cavity may have positive and negative charges with total charge zero. In order to clear this point, we take a closed loop, part of which is inside the cavity along a field line and remaining part inside the conductor. Since, field inside the conductor is zero. A certain amount of work is done by the field in carrying a test charge over the closed loop. As this is not possible for an electrostatic field, no field lines are there inside the cavity (i.e., no field). Thus, we conclude that there will be no charge on the inner surface of the conductor, whatever be its shape. 
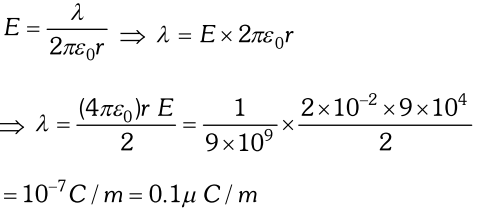
![]() $\Rightarrow Q=-8.8 \times 10^{-9} C$
$\Rightarrow Q=-8.8 \times 10^{-9} C$ 
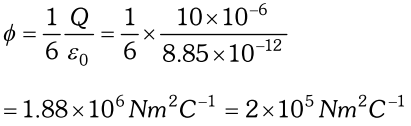
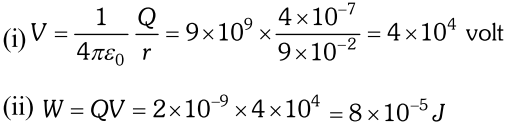 As electric field is conservative, work done does not depend upon path.
As electric field is conservative, work done does not depend upon path. 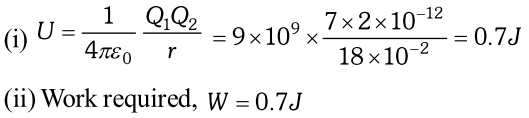
 Electric potential energies at points A and B are
Electric potential energies at points A and B are 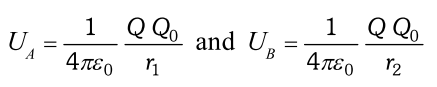 Hence, work done in taking the charge from point A to B
Hence, work done in taking the charge from point A to B 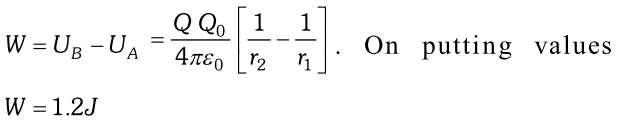
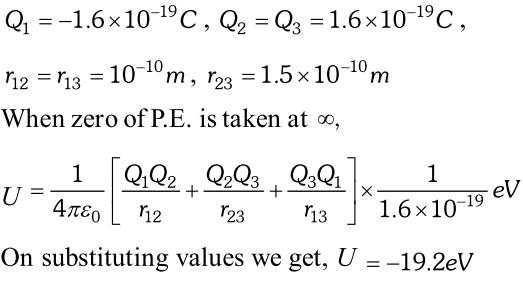
 (i) For the given system of two charges, the equipoential surface will be a plane normal to the line AB joining the two charges and passing through its mid-point O. On any point on this plane, the potential is zero. (ii) The electric field is in a direction from the point A to point B i.e. from the positive charge to negative charge and normal to the equipotential surface.
(i) For the given system of two charges, the equipoential surface will be a plane normal to the line AB joining the two charges and passing through its mid-point O. On any point on this plane, the potential is zero. (ii) The electric field is in a direction from the point A to point B i.e. from the positive charge to negative charge and normal to the equipotential surface. 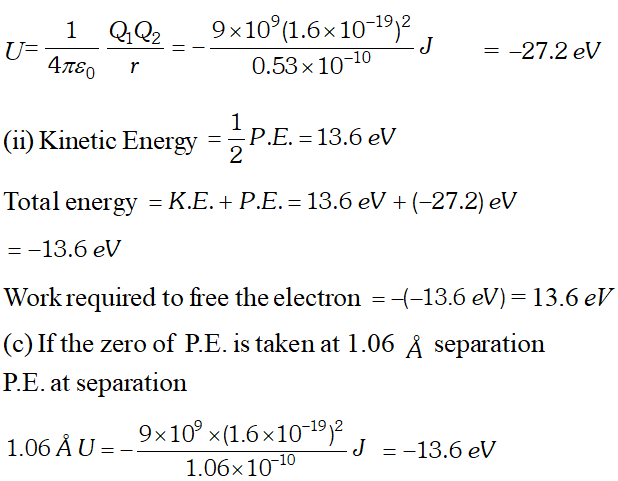
 Total field inside the hollow conductor $\vec{E}_{1}+\vec{E}_{2}=0 \cdots$ (ii) Here $\vec{E}_{1}$ is the electric field due to the portion filling up the hole and $\vec{E}_{2}$ is the electric field due to rest of the charged conductor. From relations (i) and (ii) we conclude that
Total field inside the hollow conductor $\vec{E}_{1}+\vec{E}_{2}=0 \cdots$ (ii) Here $\vec{E}_{1}$ is the electric field due to the portion filling up the hole and $\vec{E}_{2}$ is the electric field due to rest of the charged conductor. From relations (i) and (ii) we conclude that 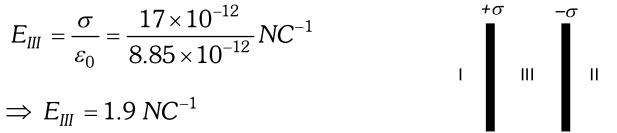

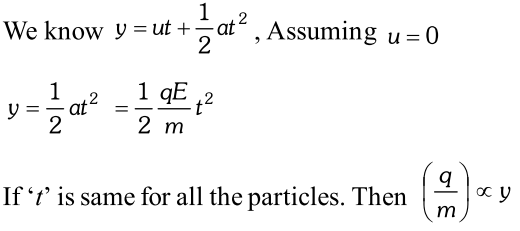 Thus, particle 3 having maximum deflection along vertical direction will be having the highest charge to mass ratio.
Thus, particle 3 having maximum deflection along vertical direction will be having the highest charge to mass ratio. 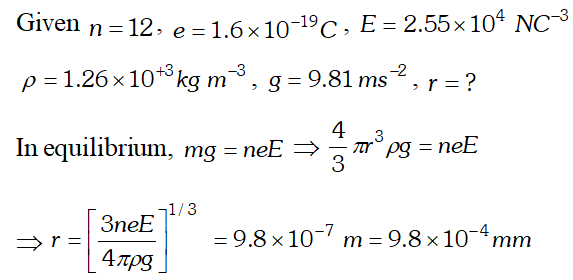
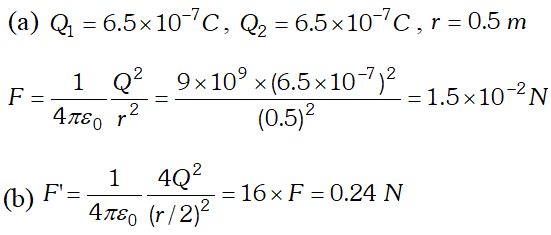
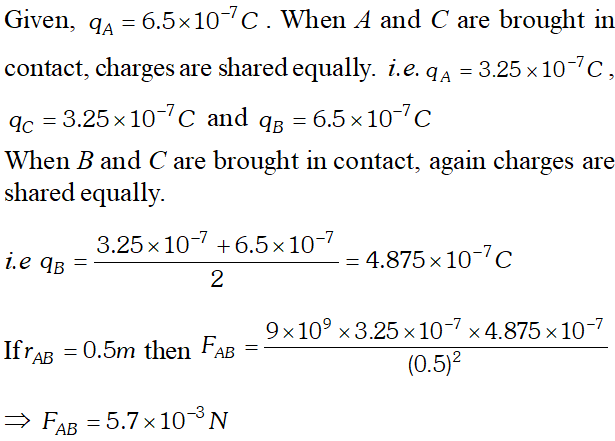

 ii) When the glass red rod is removed, the distribution of charges on A and B remains the same, because the positive charge on A and the negative charge on B are mutually bound. When A and B are separated far apart, the negative and positive charges on each re-unite and both A and B become uncharged.
ii) When the glass red rod is removed, the distribution of charges on A and B remains the same, because the positive charge on A and the negative charge on B are mutually bound. When A and B are separated far apart, the negative and positive charges on each re-unite and both A and B become uncharged. 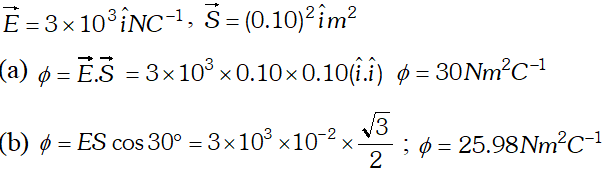
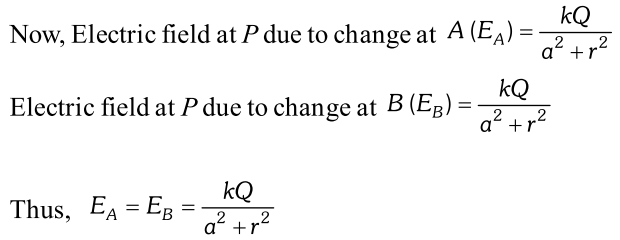
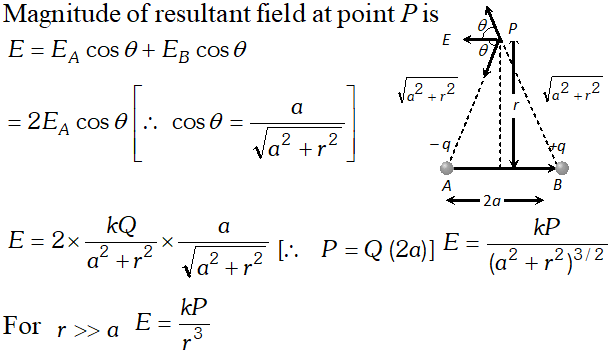 The direction of electric field $\vec{E}$ isopposite to that of dipole moment $\vec{p} .$ Electric field on axial line is double of the electric field on equitorial line for a short dipole a two equidistant points from the centre of dipole. i.e. $E_{\text {axial }}: E_{\text {eqn }}:: 2: 1$
The direction of electric field $\vec{E}$ isopposite to that of dipole moment $\vec{p} .$ Electric field on axial line is double of the electric field on equitorial line for a short dipole a two equidistant points from the centre of dipole. i.e. $E_{\text {axial }}: E_{\text {eqn }}:: 2: 1$ 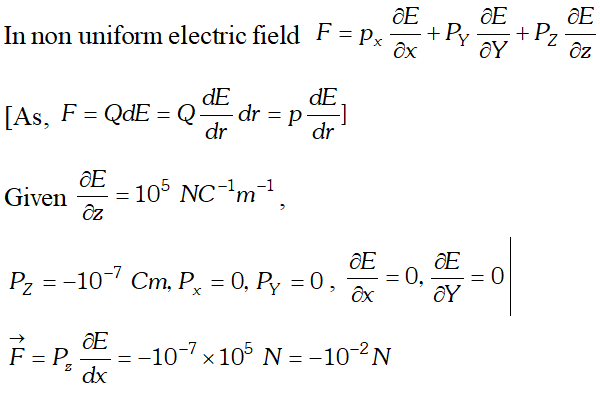 Here –ve sign indicates that force is directed along –ve z-axis. As both $\vec{P}$ and $\vec{E}$ are along $z$ -axis, in apposite direction $\sin \theta=180^{\circ}$ $\therefore \tau=p E \sin \theta=0$
Here –ve sign indicates that force is directed along –ve z-axis. As both $\vec{P}$ and $\vec{E}$ are along $z$ -axis, in apposite direction $\sin \theta=180^{\circ}$ $\therefore \tau=p E \sin \theta=0$ 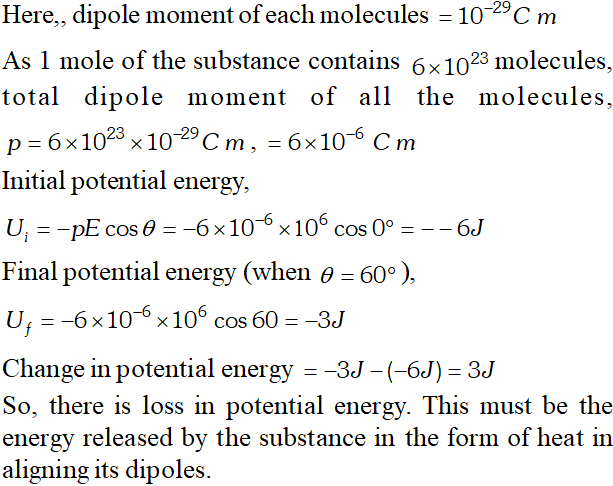
 (i) Give the sign of the potential difference $V_{P}-V_{Q}$ and $V_{B}-V_{A}$ (ii) Give the sign of the potential energy difference of a small negative charge between the point Q and P ; A and B. (iii) Give the sign of the work done by the field in moving a small positive charge from point Q to P. (iv) Give the sign of the work done by an external agency in moving a small negative charge from point B to A. (v) Does the kinetic energy of a small negative charge increase or decrease in going from point B to A?
(i) Give the sign of the potential difference $V_{P}-V_{Q}$ and $V_{B}-V_{A}$ (ii) Give the sign of the potential energy difference of a small negative charge between the point Q and P ; A and B. (iii) Give the sign of the work done by the field in moving a small positive charge from point Q to P. (iv) Give the sign of the work done by an external agency in moving a small negative charge from point B to A. (v) Does the kinetic energy of a small negative charge increase or decrease in going from point B to A?