
JEE Mains is the first phase of JEE and is conducted by NTA (National testing Agency) every year to facilitate admissions into various undergraduate courses offered at NITs, IIITs, and other centrally funded institutes. As it is one of the toughest competitive exams in the world it is obvious that its preparation demands vigorous study.
It is very crucial to know about the syllabus before starting your preparations for JEE. The purpose of this separate article on JEE Mains Physics Syllabus is to let the student know about the content to be studied. Knowing the syllabus beforehand will help in better understanding of the topics relevant to JEE Mains 2018. The Physics Syllabus is itself further subdivided into two sections viz. Section A: 80% weightage (Theory Part) and Section B: 20% weightage (Experimental Skills).
All the chapters of Physics (Section A) are divided into 5 Units as follows: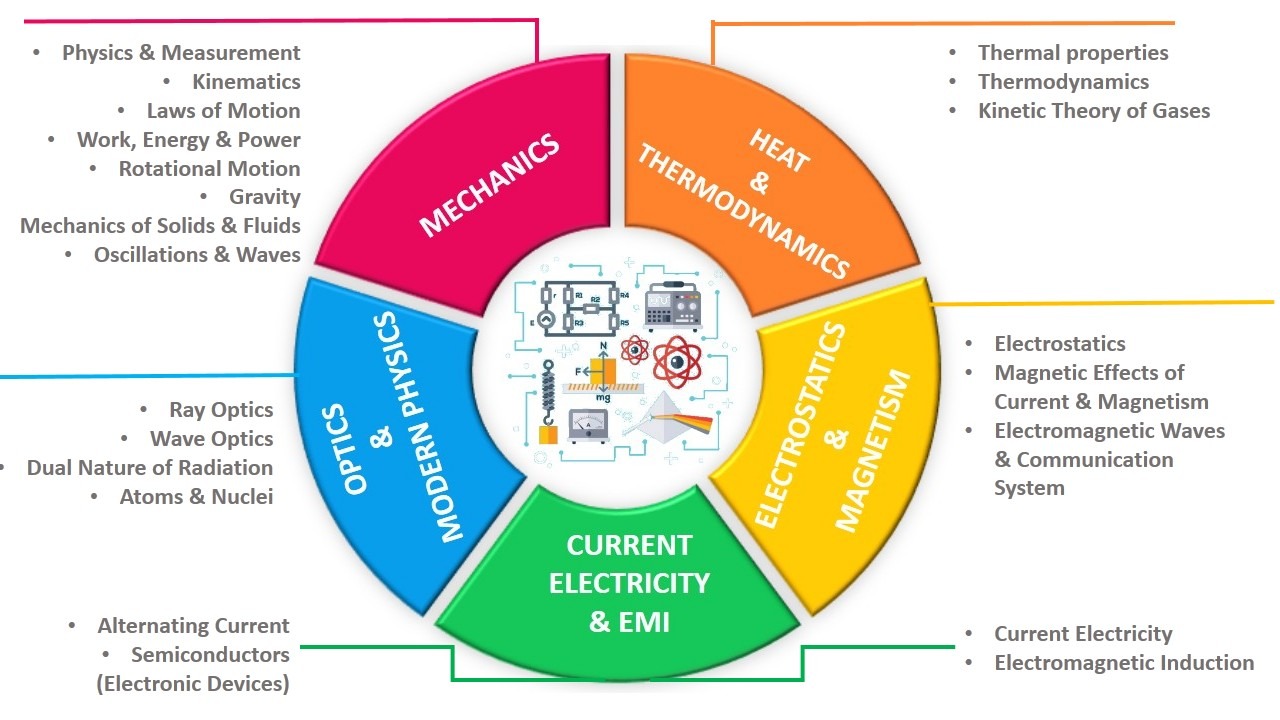
To get Free Learning Videos for JEE Main preparations install the eSaral App.
It is very crucial to know about the syllabus before starting your preparations for JEE. The purpose of this separate article on JEE Mains Physics Syllabus is to let the student know about the content to be studied. Knowing the syllabus beforehand will help in better understanding of the topics relevant to JEE Mains 2018. The Physics Syllabus is itself further subdivided into two sections viz. Section A: 80% weightage (Theory Part) and Section B: 20% weightage (Experimental Skills).
All the chapters of Physics (Section A) are divided into 5 Units as follows:
- MECHANICS
- HEAT & THERMODYNAMICS
- ELECTROSTATICS & MAGNETISM
- CURRENT ELECTRICITY & EMI
- OPTICS & MODERN PHYSICS

JEE Mains Physics Syllabus – Detailed Version
JEE Mains Physics Syllabus: Section A (80% weightage):
| CHAPTER - 1 | Physics & Measurement
|
| CHAPTER - 2 | Kinematics
|
| CHAPTER - 3 | Laws of Motion
|
| CHAPTER - 4 | Work Energy & Power
|
| CHAPTER - 5 | Rotational Motion
|
| CHAPTER - 6 | Gravitation
|
| CHAPTER - 7 | Properties of Solids
|
| CHAPTER - 8 | Thermodynamics
|
| CHAPTER - 9 | Kinetic Theory of Gases
|
| CHAPTER - 10 | Oscillations & Waves
|
| CHAPTER - 11 | Electrostatics
|
| CHAPTER - 12 | Current Electricity
|
| CHAPTER - 13 | Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism
|
| CHAPTER - 14 | Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Currents
|
| CHAPTER - 15 | Electromagnetic Waves
|
| CHAPTER - 16 | Optics
|
| CHAPTER -17 | Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation
|
| CHAPTER - 18 | Atoms & Nuclei
|
| CHAPTER - 19 | Electronic Devices
|
| CHAPTER - 20 | Communication Systems
|
JEE Mains Physics Syllabus: Section B (20% weightage):
| Experimental Skills |
|
All Chapters
- Physics & Measurement
- Kinematics
- Laws of Motion
- Work Energy & Power
- Rotational Motion
- Gravitation
- Properties of Solids
- Thermodynamics
- Kinetic Theory of Gases
- Oscillations & Waves
- Electrostatics
- Current Electricity
- Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism
- Electromagnetic Induction & Alternating Currents
- Electromagnetic Waves
- Optics
- Dual Nature of Matter & Radiation
- Atoms & Nuclei
- Electronic Devices
- Communication Systems
To get Free Learning Videos for JEE Main preparations install the eSaral App.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
