Magnetism and Matter Class 12 Notes will help you in your Exam Preparation and will also help in scoring good! The property of any object by virtue of which it can attract a piece of iron or steel is called magnetism.
Natural Magnet
A natural magnet is an ore of iron (Fe3O4), which attracts small pieces of iron, cobalt and nickel towards it.
Magnetite or lode stone is a natural magnet.
Artificial Magnet
A magnet which is prepared artificially is called an artificial magnet, e.g., a bar magnet, an electromagnet, a magnetic needle, a horse-shoe magnet etc.
According to molecular theory, every molecular of magnetic substance (whether magnetised or not) is a complete magnet itself.
The phenomenon of attracting magnetic substances like iron, cobalt nickel etc is called magnetism. A body possessing the property of magnetism is called magnet.
Historical facts :
(1) The word magnet is derived from the name of an island in Greece called magnesia where magnetic ore deposits were found.
(2) Thales of Miletus knew that pieces of lodestone or magnetite (black iron oxide $Fe _{2} O _{3}$) could attract small pieces of iron.
(3) The Chinese discovered that a linear piece of lodestone when suspended freely pointed in north and south direction. That is why name lodestone which is given to magnetite means leading stone.
(4) The Chinese are credited with making technological use of this directional property for navigation of ships.
(5) In 1600 BC William Gilbert published a book De Magnete which gave an account of then known facts of magnetism.
(6) Due to their irregular shapes and weak attracting power natural magnets are rarely used.
(7) Lodestone or magnetite is naaaatural magnet. Earth is also a natural magnet.
Artificial magnets :
 2. The temporary artificial magnet like electromagnets are prepared by passing current through coil wound on soft iron core.
These cannot retain its attracting power for a long time.
2. The temporary artificial magnet like electromagnets are prepared by passing current through coil wound on soft iron core.
These cannot retain its attracting power for a long time.
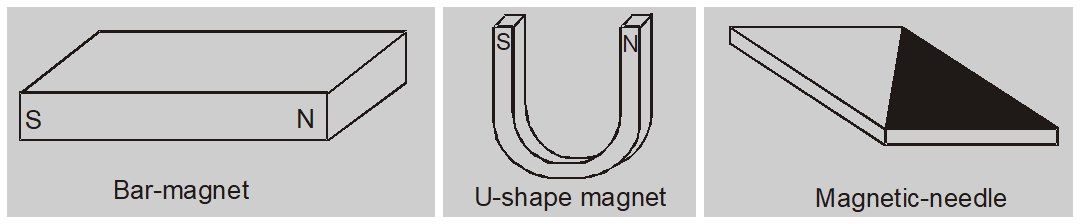
- The permanent artificial magnets are made of some metals and alloys like carbon-steel, Alnico, Platinum-cobalt, Alcomax, Ticonal. The permanent magnets are made of ferromagnetic substances with large coercivity and retentivity and can have desired shape like bar-magnet, U shaped magnet or magnetic needle etc. These magnet retain its attracting power for a long time.
 2. The temporary artificial magnet like electromagnets are prepared by passing current through coil wound on soft iron core.
These cannot retain its attracting power for a long time.
2. The temporary artificial magnet like electromagnets are prepared by passing current through coil wound on soft iron core.
These cannot retain its attracting power for a long time.
About eSaral At eSaral we are offering a complete platform for IIT-JEE & NEET preparation. The main mission behind eSaral is to provide education to each and every student in India by eliminating the Geographic and Economic factors, as a nation’s progress and development depends on the availability of quality education to each and every one. With the blend of education & technology, eSaral team made the learning personalized & adaptive for everyone.
