JEE Advanced Previous Year Questions of Chemistry with Solutions are available at eSaral. Practicing JEE Advanced Previous Year Papers Questions of Chemistry will help the JEE aspirants in realizing the question pattern as well as help in analyzing weak & strong areas.
Simulator
Previous Years JEE Advance Questions
Paragraph for questions 1 to 3
Copper is the most nobel of the first row transition metals and occurs in small deposits in several
countries. Ores of copper include chalcanthite $\left(\mathrm{CuSO}_{4}, 5 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right),$ atacamite $\left(\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{Cl}(\mathrm{OH})_{3}\right),$ cuprite $\left(\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right),$ copper glance (Cu.S) and malachite $\left(\mathrm{Cu}_{2}(\mathrm{OH})_{2} \mathrm{CO}_{3}\right) .$ However, $80 \%$ of the world copper production comes from the ore chalcopyrite (CuFeS_{2} ) . \text { The extraction of copper from chalcopyrite involves partial roasting, removal of iron and self-reduction.
Q. Partial roasting of chalcopyrite produces :-
(A) $\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{S}$ and $\mathrm{FeO}$
(B) $\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ and FeO
(C) $\mathrm{CuS}$ and $\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$
(D) $\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$
[JEE-2010]
Ans. (A)
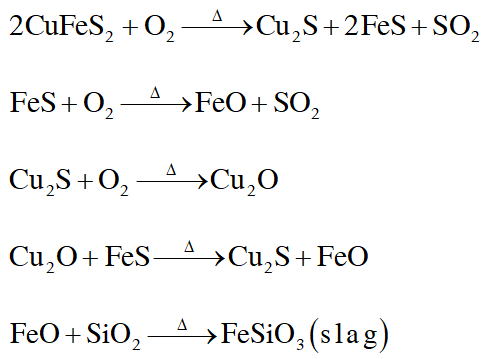
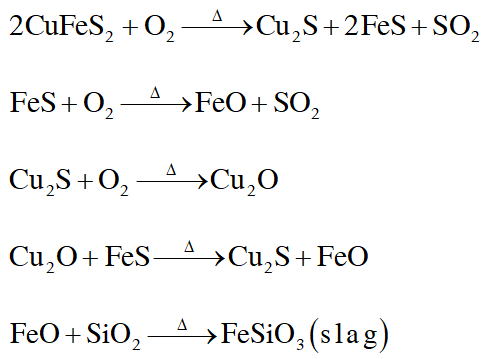
Q. Iron is removed from chalcopyrite as :-
(A) FeO
(B) FeS
(C) $\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$
(D) FeSiO $_{3}$
[JEE-2010]
Ans. (D)
Q. In self-reduction, the reducing species is :-
(A) S
(B) $\mathrm{O}^{2-}$
(C) $\mathrm{S}^{2-}$
(D) $\mathrm{SO}_{2}$
[JEE-2010]
Ans. (C)
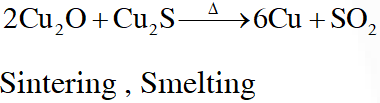
Q. Extraction of metal from the ore cassiterite involves –
(A) carbon reduction of an oxide ore
(B) self-reduction of a sulphide ore
(C) removal of copper impurity
(D) removal of iron impurity
[JEE-2011]
Ans. (A,C,D)
$\mathrm{SnO}_{2}+2 \mathrm{C} \rightarrow \mathrm{Sn}+2 \mathrm{CO}$
Cassetrite contains impurity of Wolframite (FeWO,), Which is a ferro magnatic.
Q. Oxidation states of the metal in the minerals haematite and magnetite, respectively, are –
(A) II, III in haematite and III in magnetite
(B) II, III in haematite and II in magnetite
(C) II in haematite and II, III in magnetite
(D) III in haematite and II, III in magnetite
[JEE-2011]
Ans. (D)
Haematite Ore $\Rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3} ;$ Oxidation state $(+3)$ magnetite ore $\Rightarrow \mathrm{Fe}_{3} \mathrm{O}_{4}\left(\mathrm{FeO}+\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}\right)=$ Oxidation
state of $(+2 \&+3)$
Q. In the cyanide extraction process of silver from argentite ore, the oxidizing and reducing agents used are :
(A) $\mathrm{O}_{2}$ and CO respectively.
(B) $\mathrm{O}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{Zn}$ dust respectively.
(C) $\mathrm{HNO}_{3}$ and $\mathrm{Zn}$ dust respectively.
(D) $\mathrm{HNO}_{3}$ and CO respectively.
[JEE-2012]
Ans. (B)
$2 \mathrm{Ag}+4 \mathrm{NaCN}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{O}_{2}(\text { air }) \longrightarrow 2 \mathrm{Na}\left[\mathrm{Ag}(\mathrm{CN})_{2}\right]+2 \mathrm{NaOH},$ Here $\mathrm{O}_{2}$ is oxidising agent $\& \mathrm{Zn}^{-}$
dust act as reducing agent.
Q. Sulfide ores are common for the metals –
(A) Ag, Cu and Pb
(B) Ag, Cu and Sn
(B) Ag, Cu and Sn
(D) Al, Cu and Pb
[JEE-2013]
Ans. (A)
Q. The carbon-based reduction method is NOT used for the extraction of -
(A) $\operatorname{tin}$ from $\mathrm{SnO}_{2}$
(B) Iron from $\mathrm{Fe}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$
(C) aluminium from $\mathrm{Al}_{2} \mathrm{O}_{3}$
(D) magnesium from $\mathrm{MgCO}_{3} . \mathrm{CaCO}_{3}$
[JEE-2013]
Ans. (C,D)
Being a more reactive metal "Al" and "Mg" can be reduced by electrolytic reduction.
Q. Upon heating with $\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{S},$ the reagent(s) that give copper metal is/are
(A) CuFeS $_{2}$
(B) CuO
(C) $\mathrm{Cu}_{2} \mathrm{O}$
(D) $\mathrm{CuSO}_{4}$
[JEE Adv. 2015]
Ans. (A,C,D)
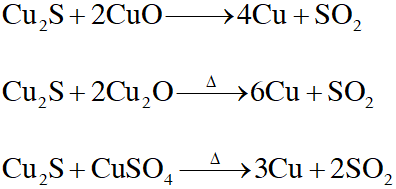
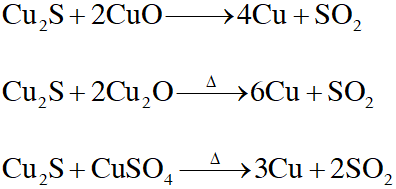
Q. Copper is purified by electrolytic refining of blister copper. The correct statement(s) about this process is (are) -
(A) Impure Cu strip is used as cathode
(B) Acidified aqueuous $\mathrm{CuSO}_{4}$ is used as electrolyte
(C) Pure Cu deposits at cathode
(D) Impurities settle as anode-mud
[JEE Adv. 2015]
Ans. (B,C,D)
Impure "Cu" act as a Anode . While " Pure thin strips of Cu act as cathode and aqueous solution of $\mathrm{CuSO}_{4}$ act as electrolyte.
Q. Match the anionic species given in Column-I that are present in the ore(s) given in
Column-II –
 [JEE Adv. 2015]
[JEE Adv. 2015]
 [JEE Adv. 2015]
[JEE Adv. 2015]
Ans. $(A \rightarrow P, Q, S, B \rightarrow T, C \rightarrow Q, R, D \rightarrow R)$
Name of ores & their metals.
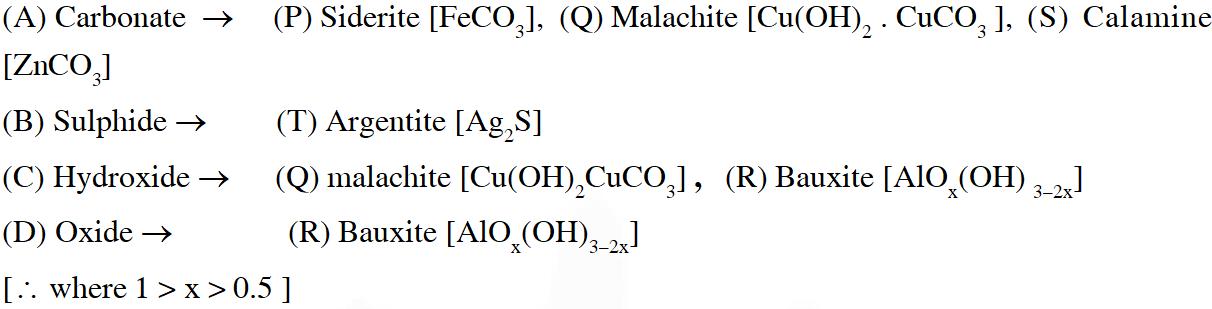
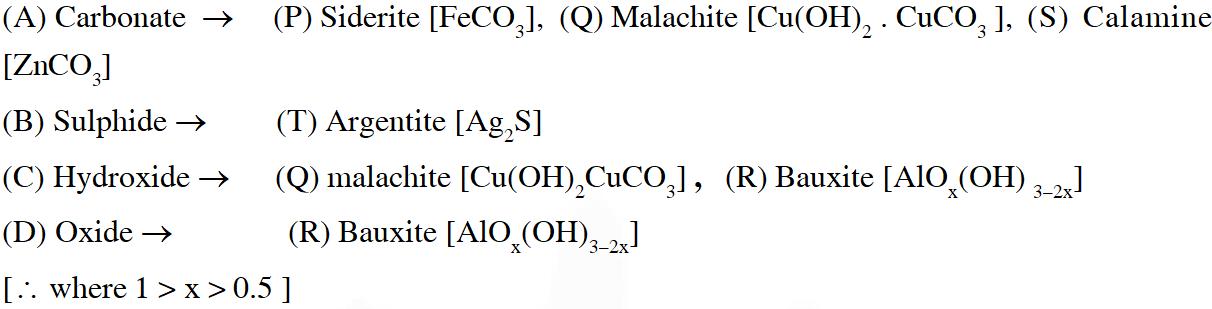
Q. Galena (an ore) is partially oxidized by passing air through it at high temperature. After some time, the passage of air is stopped, but the heating is continued in a closed furnance such that the contents undergo self-reduction. The weight (in kg) of Pb produced per kg of $\mathrm{O}_{2}$ consumed is ______ .
(Atomic weights in $\left.\mathrm{g} \text { mol }^{-1}: \mathrm{O}=16, \mathrm{S}=32, \mathrm{Pb}=207\right)$
[JEE Adv. 2018]
Ans. 6.47
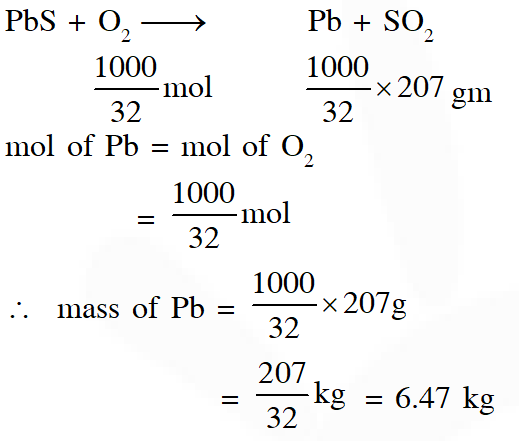
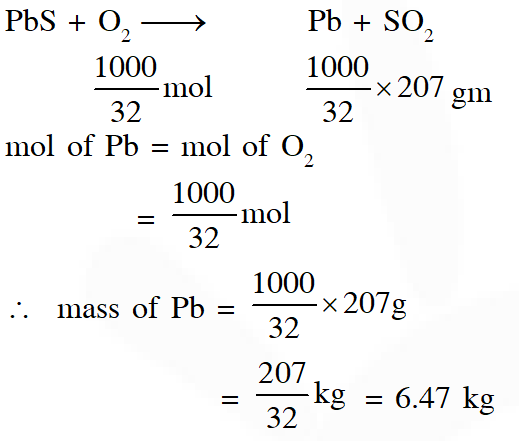
Comments
Divya
Aug. 20, 2022, 10:31 a.m.
Thank you sir, it will be more helpful if you upload some more questions
