JEE Main Previous Year Question of Math with Solutions are available at eSaral. Practicing JEE Main Previous Year Papers Questions of mathematics will help the JEE aspirants in realizing the question pattern as well as help in analyzing weak & strong areas.
eSaral helps the students in clearing and understanding each topic in a better way. eSaral is providing complete chapter-wise notes of Class 11th and 12th both for all subjects.
Besides this, eSaral also offers NCERT Solutions, Previous year questions for JEE Main and Advance, Practice questions, Test Series for JEE Main, JEE Advanced and NEET, Important questions of Physics, Chemistry, Math, and Biology and many more.
Download eSaral app for free study material and video tutorials.
Paragraph for Question 7 and 8
Let PQ be a focal chord of the parabolas $\mathrm{y}^{2}=4 \mathrm{ax} .$ The tangents to the parabola at $\mathrm{P}$ and $\mathrm{Q}$ meet at a point lying on the line $\mathrm{y}=2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{a}>0 .$
Paragraph For Questions 11 and 12
Let a,r,s, t be nonzero real numbers. Let $P\left(a t^{2}, 2 a t\right), Q, R\left(a r^{2}, 2 a r\right)$ and $S\left(a s^{2}, 2 a s\right)$ be distinct points on the parabola $y^{2}=4 a x .$ Suppose that $P Q$ is the focal chord and lines $Q R$ and $P K$ are parallel, where $K$ is the point $(2 a, 0) .$
The value of $r$ is-
Q. The tangent PT and the normal PN to the parabola $y^{2}$ = 4ax at a point P on it meet its axis at points T and N, respectively. The locus of the centroid of the triangle PTN is a parabola whose
(A) vertex is $\left(\frac{2 \mathrm{a}}{3}, 0\right)$
(B) directrix is x = 0
(C) latus rectum is $\frac{2 \mathrm{a}}{3}$
(D) focus is (a, 0)
[JEE 2009, 4]
Ans. (A,D)
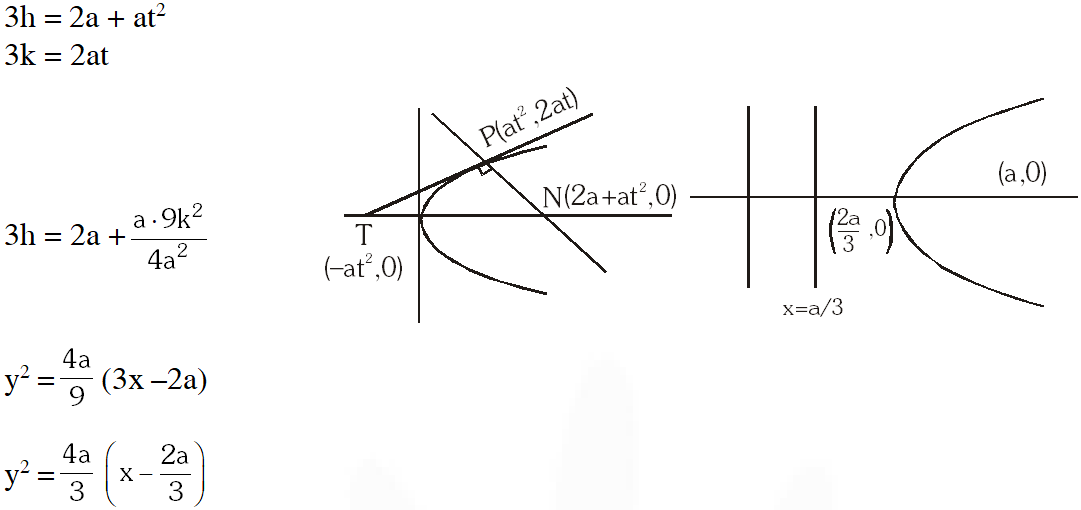
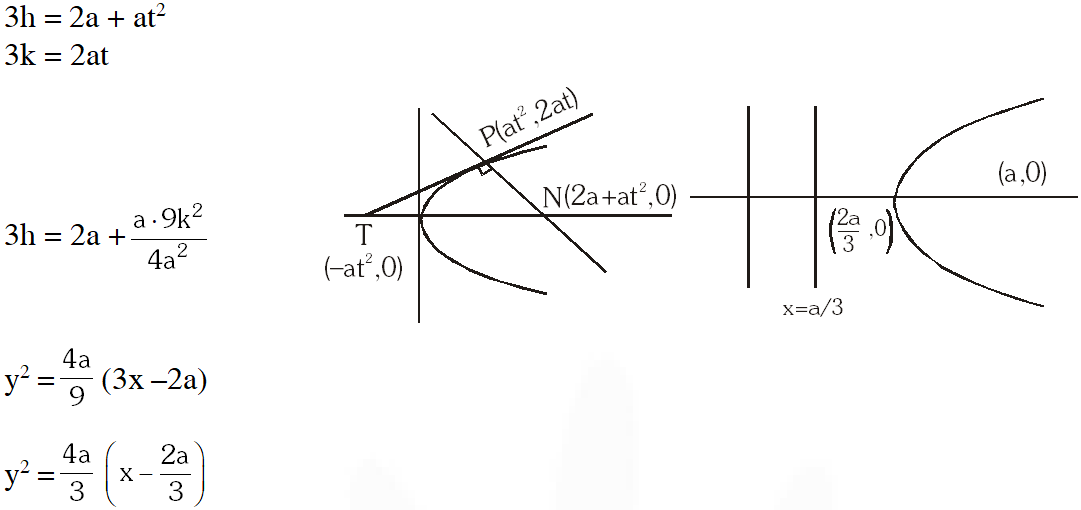
Q. Let A and B be two distinct point on the parabola $y^{2}$ = 4x. If the axis of the parabola touches a circle of radius r having AB as its diameter, then the slope of the line joining A and B can be –
(A) $\frac{-1}{\mathrm{r}}$
(B) $\frac{1}{\mathrm{r}}$
(C) $\frac{2}{\mathrm{r}}$
(D) $\frac{-2}{\mathrm{r}}$
[JEE 2010,3]
Ans. (C,D)
$\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}=\mathrm{r}$
$\frac{2}{\mathrm{r}}=\frac{2}{\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}}$
similarly $-\frac{2}{\mathrm{r}}$ is
also possible
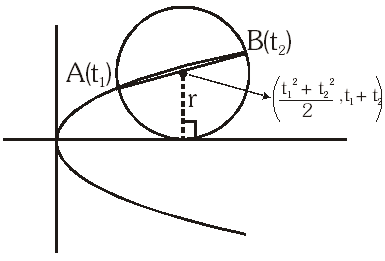
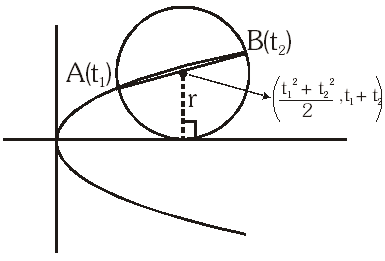
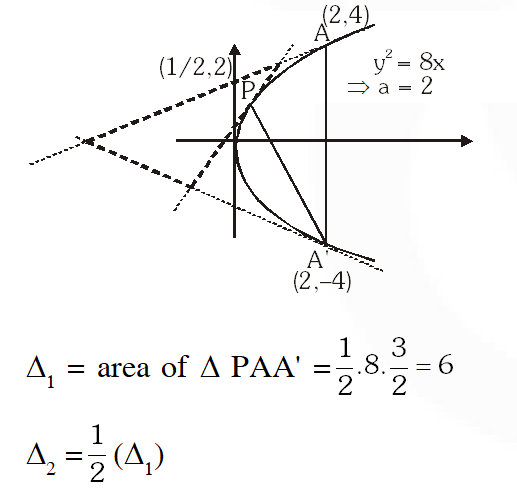
Q. Consider the parabola $\mathrm{y}^{2}=8 \mathrm{x}$. Let $\Delta_{1}$ be the area of the triangle formed by the end points of its latus rectum and the point $\mathrm{P}\left(\frac{1}{2}, 2\right)$ on the parabola, and $\Delta_{2}$ be the area of the triangle formed by drawing tangents at $\mathrm{P}$ and at the end points of the latus rectum. Then $\frac{\Delta_{1}}{\Delta_{2}}$ is
[JEE 2011,4]
Ans. 2

Q. Let (x,y) be any point on the parabola $\mathrm{y}^{2}$ = 4x. Let P be the point that divides the line segment from (0,0) to (x,y) in the ratio 1 : 3. Then the locus of P is-
(A) $x^{2}=y$
(B) $\mathrm{y}^{2}=2 \mathrm{x}$
(C) $\mathrm{y}^{2}=\mathrm{x}$
(D) $x^{2}=2 y$
[JEE 2011,3]
Ans. (C)
Let P be (h, k)
on using section formula $\mathrm{P}\left(\frac{x}{4}, \frac{y}{4}\right)$
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{h}=\frac{x}{4}$ and $\mathrm{k}=\frac{y}{4}$
$\Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{x}=4 \mathrm{h}$ and $\mathrm{y}=4 \mathrm{k}$
$\because \quad(\mathrm{x}, \mathrm{y})$ lies on $\mathrm{y}^{2}=4 \mathrm{x}$
$\therefore \quad 16 \mathrm{k}^{2}=16 \mathrm{h} \quad \Rightarrow \mathrm{k}^{2}=\mathrm{h}$
Locus of point $\mathrm{P}$ is $\mathrm{y}^{2}=\mathrm{x}$
Q. Let L be a normal to the parabola $\mathrm{y}^{2}=4 \mathrm{x} .$ If $\mathrm{L}$ passes through the point $(9,6),$ then $\mathrm{L}$ is given by $-$
(A) y – x + 3 =0
(B) y + 3x – 33 = 0
(C) y + x – 15 = 0
(D) y – 2x + 12 = 0
[JEE 2011,3]
Ans. (A,B,D)
Equation of normal is $\mathrm{y}=\mathrm{mx}-2 \mathrm{m}-\mathrm{m}^{3}$
It passes through the point $(9,6)$ then
$6=9 \mathrm{m}-2 \mathrm{m}-\mathrm{m}^{3}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{m}^{3}-7 \mathrm{m}+6=0$
$\Rightarrow(\mathrm{m}-1)(\mathrm{m}-2)(\mathrm{m}+3)=0$
$\Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{m}=1,2,-3$
Equations of normals are
$\mathrm{y}-\mathrm{x}+3=0, \mathrm{y}+3 \mathrm{x}-33=0$
& $\quad \mathrm{y}-2 \mathrm{x}+12=0$
Q. Let S be the focus of the parabola $y^{2}=8 x \&$ let PQ be the common chord of the circle $x^{2}+y^{2}-2 x-4 y$ $=0$ and the given parabola. The area of the triangle PQS is
[JEE 2012, 4M]
Ans. 4


Q. If chord PQ subtends an angle $\theta$ at the vertex of $y^{2}=4 a x,$ then $\tan \theta=$
(A) $\frac{2}{3} \sqrt{7}$
(B) $\frac{-2}{3} \sqrt{7}$
(C) $\frac{2}{3} \sqrt{5}$
(D) $\frac{-2}{3} \sqrt{5}$
[JEE(Advanced) 2013, 3, (–1)]
Ans. (D)
Single tangent at the extrimities of a focal
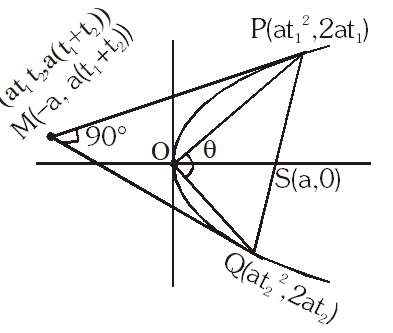 chord will intersect on directrix.
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{M}\left(-\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)\right)$
lies on $\mathrm{y}=2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{a}$
$\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)=-2 \mathrm{a}+\mathrm{a} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\quad \& \quad \mathrm{t}_{1} \mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\tan \theta=\left(\frac{\frac{2}{t_{1}}-\frac{2}{t_{2}}}{1+\frac{4}{t_{1} t_{2}}}\right)=\left(\frac{2\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)}{3}\right)$
$\because\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)=\left(t_{2}+t_{1}\right)^{2}-4 t_{1} t_{2}=5$
$t_{2}-t_{1}=\pm \sqrt{5}$
$\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\pm \frac{2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
but $\theta$ is obtuse because $\mathrm{O}$ is the interior point of the circle for which $\mathrm{PQ}$ is diameter. $\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\frac{-2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
chord will intersect on directrix.
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{M}\left(-\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)\right)$
lies on $\mathrm{y}=2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{a}$
$\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)=-2 \mathrm{a}+\mathrm{a} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\quad \& \quad \mathrm{t}_{1} \mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\tan \theta=\left(\frac{\frac{2}{t_{1}}-\frac{2}{t_{2}}}{1+\frac{4}{t_{1} t_{2}}}\right)=\left(\frac{2\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)}{3}\right)$
$\because\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)=\left(t_{2}+t_{1}\right)^{2}-4 t_{1} t_{2}=5$
$t_{2}-t_{1}=\pm \sqrt{5}$
$\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\pm \frac{2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
but $\theta$ is obtuse because $\mathrm{O}$ is the interior point of the circle for which $\mathrm{PQ}$ is diameter. $\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\frac{-2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
 chord will intersect on directrix.
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{M}\left(-\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)\right)$
lies on $\mathrm{y}=2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{a}$
$\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)=-2 \mathrm{a}+\mathrm{a} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\quad \& \quad \mathrm{t}_{1} \mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\tan \theta=\left(\frac{\frac{2}{t_{1}}-\frac{2}{t_{2}}}{1+\frac{4}{t_{1} t_{2}}}\right)=\left(\frac{2\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)}{3}\right)$
$\because\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)=\left(t_{2}+t_{1}\right)^{2}-4 t_{1} t_{2}=5$
$t_{2}-t_{1}=\pm \sqrt{5}$
$\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\pm \frac{2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
but $\theta$ is obtuse because $\mathrm{O}$ is the interior point of the circle for which $\mathrm{PQ}$ is diameter. $\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\frac{-2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
chord will intersect on directrix.
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{M}\left(-\mathrm{a}, \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)\right)$
lies on $\mathrm{y}=2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{a}$
$\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)=-2 \mathrm{a}+\mathrm{a} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\quad \& \quad \mathrm{t}_{1} \mathrm{t}_{2}=-1$
$\tan \theta=\left(\frac{\frac{2}{t_{1}}-\frac{2}{t_{2}}}{1+\frac{4}{t_{1} t_{2}}}\right)=\left(\frac{2\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)}{3}\right)$
$\because\left(t_{2}-t_{1}\right)=\left(t_{2}+t_{1}\right)^{2}-4 t_{1} t_{2}=5$
$t_{2}-t_{1}=\pm \sqrt{5}$
$\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\pm \frac{2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
but $\theta$ is obtuse because $\mathrm{O}$ is the interior point of the circle for which $\mathrm{PQ}$ is diameter. $\therefore \quad \tan \theta=\frac{-2 \sqrt{5}}{3}$
Q. Length of chord PQ is
(A) 7a (B) 5a (C) 2a (D) 3a
[JEE(Advanced) 2013, 3, (–1)]
Ans. (B)
$\begin{aligned} \text { Length of focal chord } \\ \mathrm{PQ} &=\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}-\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)^{2} \\ &=\mathrm{a}\left[\left(\mathrm{t}_{1}+\mathrm{t}_{2}\right)^{2}-4 \mathrm{t}_{1} \mathrm{t}_{2}\right] \\ &=\mathrm{a}[1+4]=5 \mathrm{a} \end{aligned}$
Q. A line L: $y=m x+3$ meets $y-$ axis at $E(0,3)$ and the arc of the parabola $y^{2}=16 x, 0 \leq y$
$\leq 6$ at the point $F\left(x_{0}, y_{0}\right)$. The tangent to the parabola at $F\left(x_{0}, y_{0}\right)$ intersects the $y$ -axis at $G\left(0, y_{1}\right) .$
The slope $m$ of the line $L$ is chosen such that the area of the triangle EFG has a local maximum.
Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the lists.
 [JEE(Advanced) 2013, 3, (–1)]
[JEE(Advanced) 2013, 3, (–1)]
 [JEE(Advanced) 2013, 3, (–1)]
[JEE(Advanced) 2013, 3, (–1)]
Ans. (A )
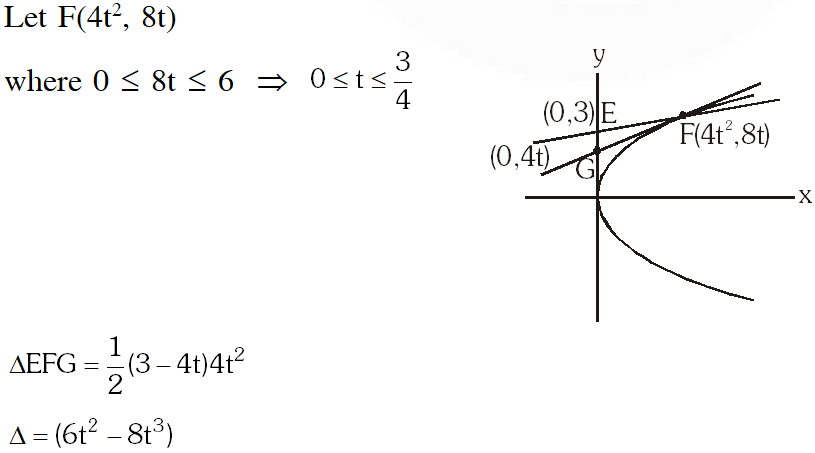
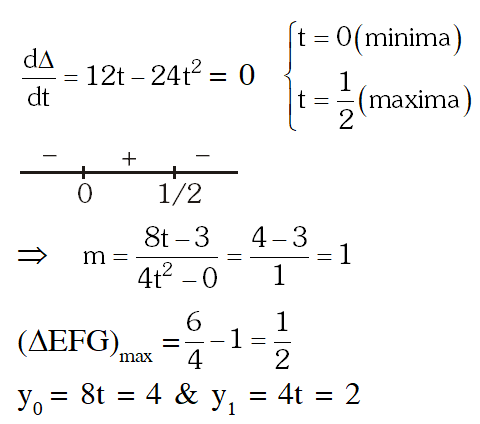
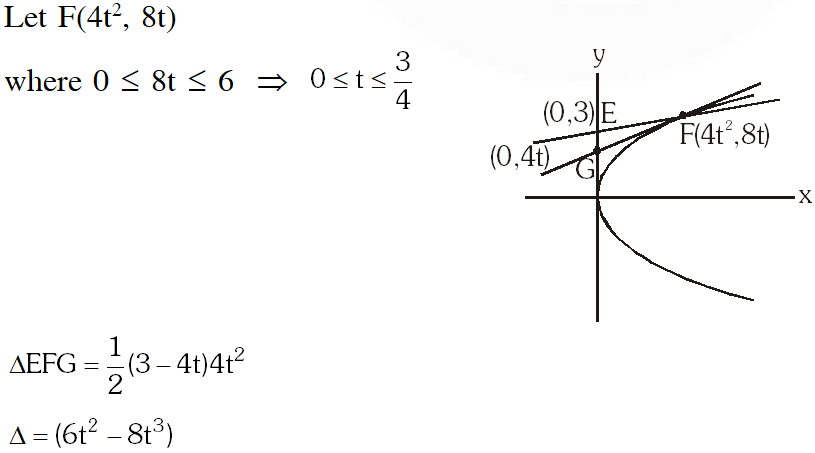
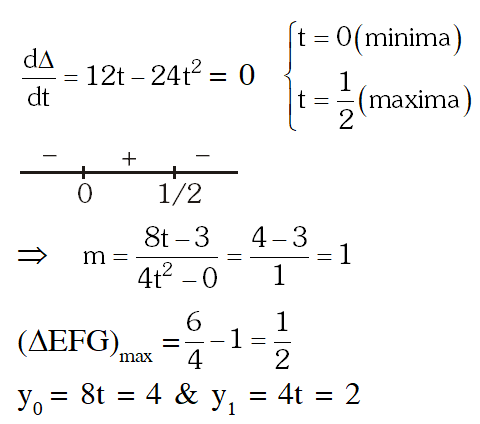
Q. The common tangents to the circle $\mathrm{x}^{2}+\mathrm{y}^{2}=2$ and the parabola $\mathrm{y}^{2}=8 \mathrm{x}$ touch the circle at the point $\mathrm{P}, \mathrm{Q}$ and the parabola at the points $\mathrm{R}, \mathrm{S}$. Then the area of the quadrilateral PQRS
is –
(A) 3 (B) 6 (C) 9 (D) 15
[JEE(Advanced)-2014, 3(–1)]
Ans. (D)
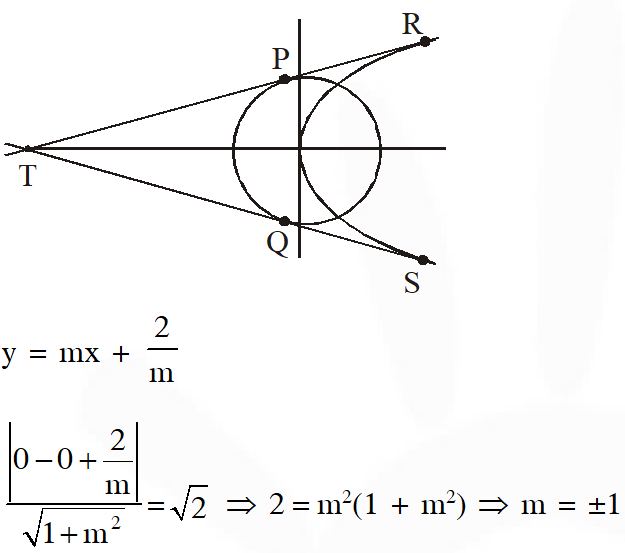
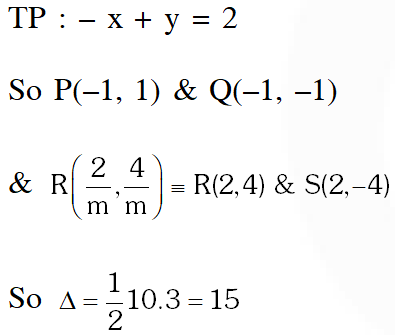
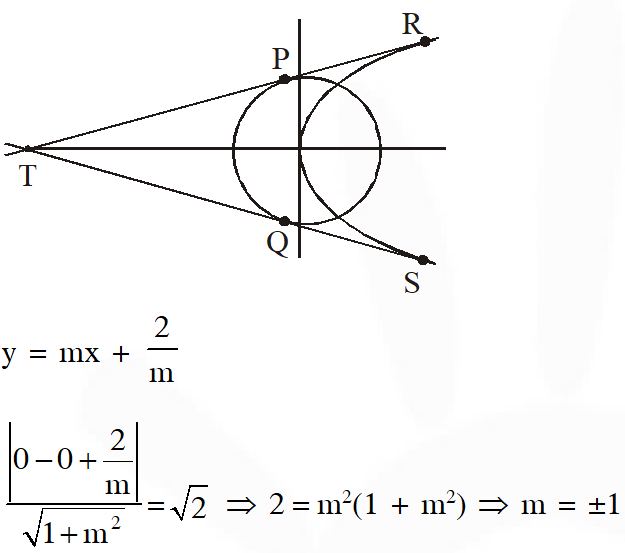
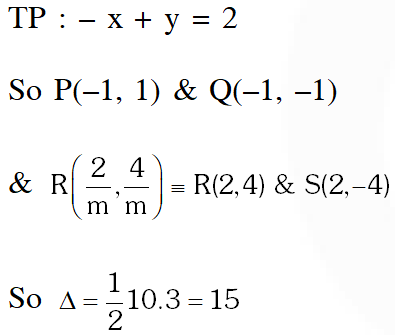
Q. The value of r is-
(A) $-\frac{1}{\mathfrak{t}}$
(B) $\frac{t^{2}+1}{t}$
(C) $\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}$
(D) $\frac{\mathfrak{t}^{2}-1}{\mathfrak{t}}$
[JEE(Advanced)-2014, 3(–1)]
Ans. (D)
$\because \mathrm{PQ}$ is a focal chord
$\therefore$ co-ordinates of point $\mathrm{Q}$ are $=\left(\frac{\mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}},-\frac{2 \mathrm{a}}{\mathrm{t}}\right)$
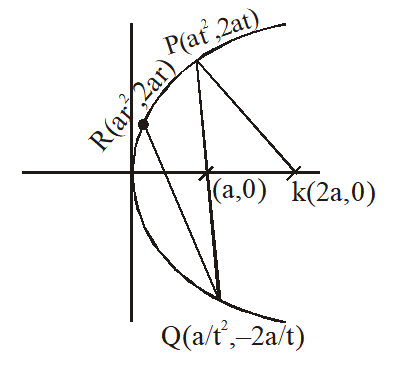 $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}^{2}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}^{2}}\right)}=\frac{2}{\left(\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}$
$\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{at}-0}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}-2\right)}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}$
Given $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{2}{\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{t}-\frac{2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-1}{\mathrm{t}}$
$\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}^{2}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}^{2}}\right)}=\frac{2}{\left(\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}$
$\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{at}-0}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}-2\right)}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}$
Given $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{2}{\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{t}-\frac{2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-1}{\mathrm{t}}$
 $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}^{2}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}^{2}}\right)}=\frac{2}{\left(\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}$
$\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{at}-0}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}-2\right)}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}$
Given $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{2}{\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{t}-\frac{2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-1}{\mathrm{t}}$
$\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{r}^{2}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}^{2}}\right)}=\frac{2}{\left(\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}\right)}$
$\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{at}-0}{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}-2\right)}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}$
Given $\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{QR}}=\mathrm{m}_{\mathrm{PK}}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{2}{\mathrm{r}-\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}}=\frac{2 \mathrm{t}}{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\mathrm{t}-\frac{2}{\mathrm{t}}+\frac{1}{\mathrm{t}} \Rightarrow \mathrm{r}=\frac{\mathrm{t}^{2}-1}{\mathrm{t}}$
Q. If st = 1, then the tangent at P and the normal at S to the parabola meet at a point whose ordinate is-
(A) $\frac{\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}+1\right)^{2}}{2 \mathrm{t}^{3}}$
(B) $\frac{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}+1\right)^{2}}{2 \mathrm{t}^{3}}$
(C) $\frac{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}+1\right)^{2}}{\mathrm{t}^{3}}$
(D) $\frac{\mathrm{a}\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}+2\right)^{2}}{\mathrm{t}^{3}}$
[JEE(Advanced)-2014, 3(–1)]
Ans. (B)
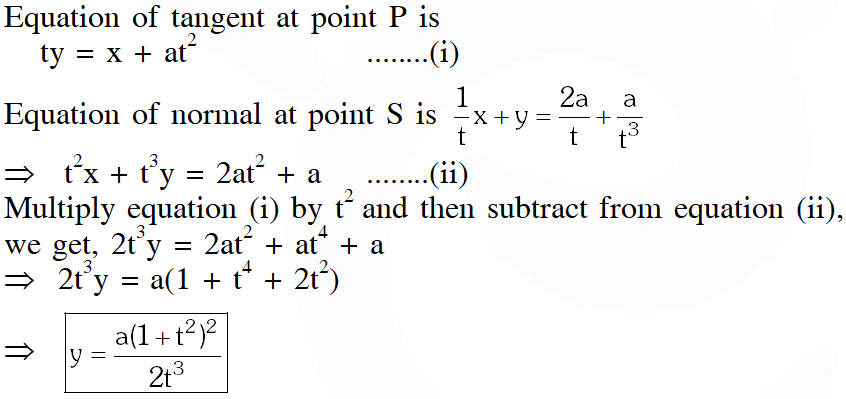
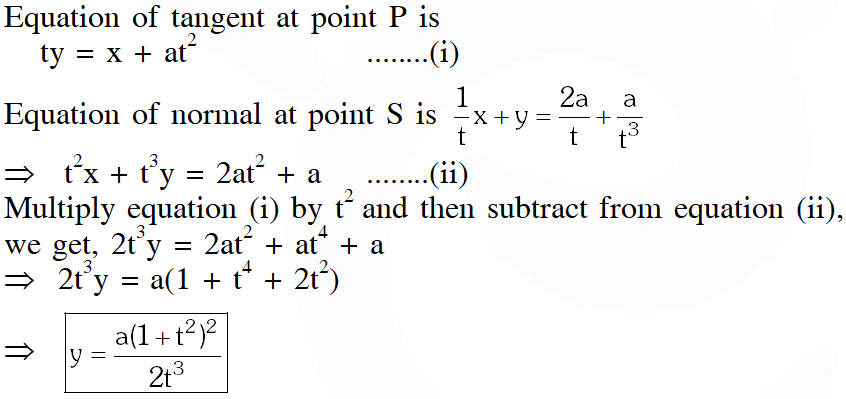
Q. If the normals of the parabola $y^{2}=4 x$ drawn at the end points of its latus rectum are tangents to the circle $(x-3)^{2}+(y+2)^{2}=r^{2},$ then the value of $r^{2}$ is
[JEE 2015, 4M, –0M]
Ans. 2

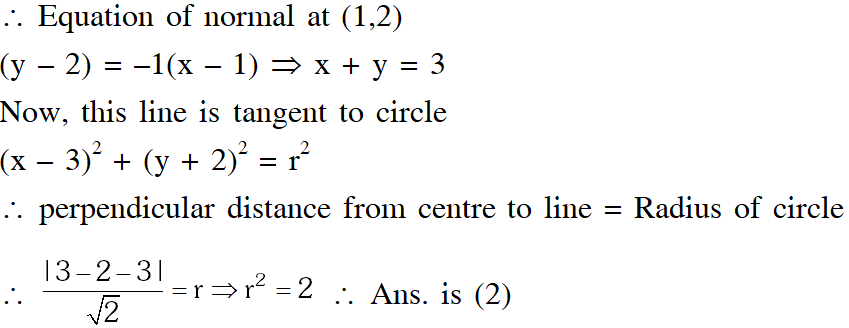

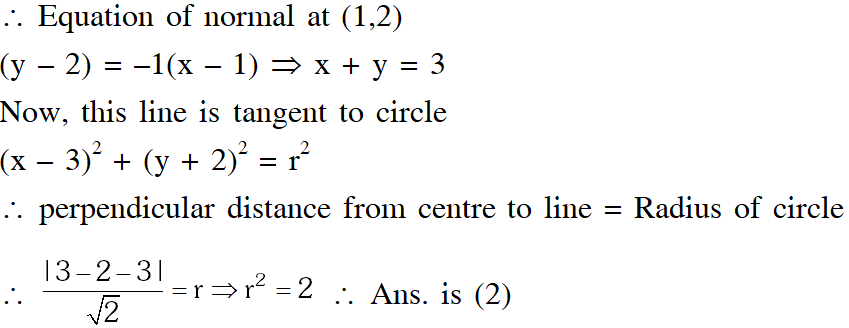
Q. Let the curve $C$ be the mirror image of the parabola $y^{2}=4 x$ with respect to the line $x+y+4=0 .$ If $A$ and $B$ are the points of intersection of $C$ with the line $y=-5$, then the distance between A and $B$ is
[JEE 2015, 4M, –0M]
Ans. 4
Let there be a point $\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}, 2 \mathrm{t}\right)$ on $\mathrm{y}^{2}=4 \mathrm{x}$
Clearly its reflection in $\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}+4=0$ is given by
$$
\frac{\mathrm{x}-\mathrm{t}^{2}}{1}=\frac{\mathrm{y}-2 \mathrm{t}}{1}=\frac{-2\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}+2 \mathrm{t}+4\right)}{2}
$$
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{x}=-(2 \mathrm{t}+4) \quad \& \mathrm{y}=-\left(\mathrm{t}^{2}+4\right)$
Now, $\mathrm{y}=-5 \quad \Rightarrow \quad \mathrm{t}=\pm 1$
$\therefore \quad \mathrm{x}=-6 \quad$ or $\quad \mathrm{x}=-2$
$\therefore \quad$ Distance between $\mathrm{A} \& \mathrm{B}=4$
Q. Let $P$ and $Q$ be distinct points on the parabola $y^{2}=2 x$ such that a circle with $P Q$ as diameter passes through the vertex $O$ of the parabola. If $P$ lies in the first quadrant and the area of the triangle $\Delta O P Q$ is $3 \sqrt{2},$ then which of the following is (are) the coordinates of $P ?$
(A) $(4,2 \sqrt{2})$
(B) $(9,3 \sqrt{2})$
(C) $\left(\frac{1}{4}, \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)$
(D) $(1, \sqrt{2})$
[JEE 2015, 4M, –2M]
Ans. (A,D)






Q. The circle $C_{1}: x^{2}+y^{2}=3,$ with centre at $O,$ intersects the parabola $x^{2}=2 y$ at the point $P$ in the first quadrant. Let the tangent to the circle $C_{1}$ at $P$ touches other two circles $C_{2}$ and $C_{3}$ at $R_{2}$ and $R_{3},$ respectively. Suppose $C_{2}$ and $C_{3}$ have equal radii $2 \sqrt{3}$ and centres $Q_{2}$ and $Q_{3}$ respectively. If $Q_{2}$ and $Q_{3}$ lie on the y-axis, then-
(A) $\mathrm{Q}_{2} \mathrm{Q}_{3}=12$
(B) $\mathrm{R}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3}=4 \sqrt{6}$
(C) area of the triangle $\mathrm{OR}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3}$ is $6 \sqrt{2}$
(D) area of the triangle $\mathrm{PQ}_{2} \mathrm{Q}_{3}$ is $4 \sqrt{2}$
[JEE (Advanced) 2016]
Ans. (A,B,C)
On solving $\mathrm{x}^{2}+\mathrm{y}^{2}=3$ and $\mathrm{x}^{2}=2 \mathrm{y}$ we get point $\mathrm{P}(\sqrt{2}, 1)$
Equation of tangent at $\mathrm{P}$
$\sqrt{2} \cdot \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}=3$
Let $\mathrm{Q}_{2}$ be $(0, \mathrm{k})$ and radius is $2 \sqrt{3}$
$\therefore\left|\frac{\sqrt{2}(0)+k-3}{\sqrt{2+1}}\right|=2 \sqrt{3}$
$\therefore \mathrm{k}=9,-3$
$\mathrm{Q}_{2}(0,9)$ and $\mathrm{Q}_{3}(0,-3)$
hence $\mathrm{Q}_{2} \mathrm{Q}_{3}=12$
$\mathrm{R}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3}$ is internal common tangent of circle $\mathrm{C}_{2}$ and $\mathrm{C}_{3}$
$\begin{aligned} \therefore \mathrm{R}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3} &=\sqrt{\left(\mathrm{Q}_{2} \mathrm{Q}_{3}\right)^{2}-(2 \sqrt{3}+2 \sqrt{3})^{2}} \\ &=\sqrt{12^{2}-48}=\sqrt{96}=4 \sqrt{6} \end{aligned}$
Perpendicular distance of origin $\mathrm{O}$ from $\mathrm{R}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3}$ is equal to radius of circle $\mathrm{C}_{1}=\sqrt{3}$
Hence area of $\Delta \mathrm{OR}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3}=\frac{1}{2} \times\left(\mathrm{R}_{2} \mathrm{R}_{3}\right) \sqrt{3}=\frac{1}{2} \cdot 4 \sqrt{6} \cdot \sqrt{3}=6 \sqrt{2}$
Perpendicular Distance of $\mathrm{P}$ from $\mathrm{Q}_{2} \mathrm{Q}_{3}=\sqrt{2}$
$\therefore$ Area of $\Delta \mathrm{PQ}_{2} \mathrm{Q}_{3}=\frac{1}{2} \times 12 \times \sqrt{2}=6 \sqrt{2}$


Q. Let $P$ be the point on the parabola $y^{2}=4 x$ which is at the shortest distance from the center Sof the circle $x^{2}+y^{2}-4 x-16 y+64=0$. Let $Q$ be the point on the circle dividing the line segment SP internally. Then-
(A) $\mathrm{SP}=2 \sqrt{5}$
(B) $\mathrm{SQ}: \mathrm{QP}=(\sqrt{5}+1): 2$
(C) the $\mathrm{x}$ -intercept of the normal to the parabola at $\mathrm{P}$ is 6
(D) the slope of the tangent to the circle at $\mathrm{Q}$ is $\frac{1}{2}$
[JEE (Advanced) 2016]
Ans. (A,C,D)
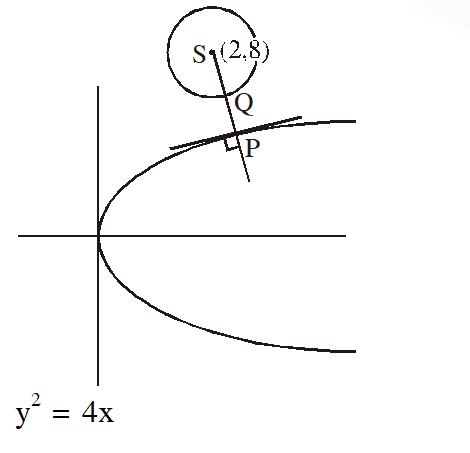 point $P$ lies on normal to parabola passing through centre of circle
$y+t x=2 t+t^{3}$
$8+2 t=2 t+t^{3}$
$t=2$
$t=2$
$P(4,4)$
$S P=\sqrt{(4-2)^{2}+(4-8)^{2}}$
$S P=2 \sqrt{5}$
$\mathrm{SQ}=2$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{PQ}=2 \sqrt{5}-2$
$\frac{\mathrm{SQ}}{\mathrm{QP}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}$
To find $\mathrm{x}$ intercept
put $\mathrm{y}=0 \mathrm{in}(\mathrm{i})$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{x}=2+\mathrm{t}^{2}$
$\because=6$
$\because \quad$ Slope of common normal $=-\mathrm{t}=-2$
$\therefore \quad$ Slope of tangent $=\frac{1}{2}$
point $P$ lies on normal to parabola passing through centre of circle
$y+t x=2 t+t^{3}$
$8+2 t=2 t+t^{3}$
$t=2$
$t=2$
$P(4,4)$
$S P=\sqrt{(4-2)^{2}+(4-8)^{2}}$
$S P=2 \sqrt{5}$
$\mathrm{SQ}=2$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{PQ}=2 \sqrt{5}-2$
$\frac{\mathrm{SQ}}{\mathrm{QP}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}$
To find $\mathrm{x}$ intercept
put $\mathrm{y}=0 \mathrm{in}(\mathrm{i})$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{x}=2+\mathrm{t}^{2}$
$\because=6$
$\because \quad$ Slope of common normal $=-\mathrm{t}=-2$
$\therefore \quad$ Slope of tangent $=\frac{1}{2}$
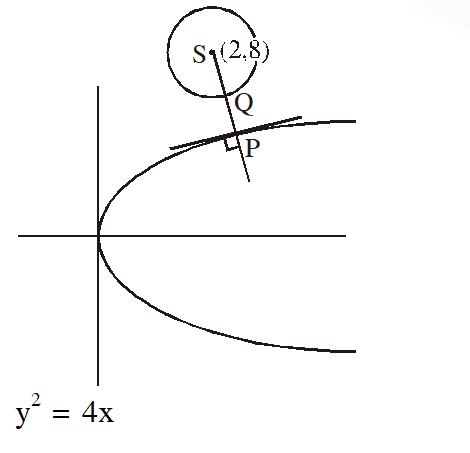 point $P$ lies on normal to parabola passing through centre of circle
$y+t x=2 t+t^{3}$
$8+2 t=2 t+t^{3}$
$t=2$
$t=2$
$P(4,4)$
$S P=\sqrt{(4-2)^{2}+(4-8)^{2}}$
$S P=2 \sqrt{5}$
$\mathrm{SQ}=2$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{PQ}=2 \sqrt{5}-2$
$\frac{\mathrm{SQ}}{\mathrm{QP}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}$
To find $\mathrm{x}$ intercept
put $\mathrm{y}=0 \mathrm{in}(\mathrm{i})$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{x}=2+\mathrm{t}^{2}$
$\because=6$
$\because \quad$ Slope of common normal $=-\mathrm{t}=-2$
$\therefore \quad$ Slope of tangent $=\frac{1}{2}$
point $P$ lies on normal to parabola passing through centre of circle
$y+t x=2 t+t^{3}$
$8+2 t=2 t+t^{3}$
$t=2$
$t=2$
$P(4,4)$
$S P=\sqrt{(4-2)^{2}+(4-8)^{2}}$
$S P=2 \sqrt{5}$
$\mathrm{SQ}=2$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{PQ}=2 \sqrt{5}-2$
$\frac{\mathrm{SQ}}{\mathrm{QP}}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{5}-1}=\frac{\sqrt{5}+1}{4}$
To find $\mathrm{x}$ intercept
put $\mathrm{y}=0 \mathrm{in}(\mathrm{i})$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{x}=2+\mathrm{t}^{2}$
$\because=6$
$\because \quad$ Slope of common normal $=-\mathrm{t}=-2$
$\therefore \quad$ Slope of tangent $=\frac{1}{2}$
Q. If a chord, which is not a tangent, of the parabola $y^{2}=16 x$ has the equation $2 x+y=p,$ and midpoint $(h, k),$ then which of the following is (are) possible value(s) of $p, h$ and $k ?$
(A) p = 5, h = 4, k = –3
(B) p = –1, h = 1, k = –3
(C) p = –2, h = 2, k = –4
(D) p = 2, h = 3, k = –4
[JEE (Advanced) 2017]
Ans. (D)
Equation of chord with mid point $(\mathrm{h}, \mathrm{k}):$
$\mathrm{k} \cdot \mathrm{y}-16\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{h}}{2}\right)=\mathrm{k}^{2}-16 \mathrm{h}$
$\Rightarrow 8 \mathrm{x}-\mathrm{ky}+\mathrm{k}^{2}-8 \mathrm{h}=0$
Comparing with $2 \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{y}-\mathrm{p}=0,$ we get
$\mathrm{k}=-4 ; 2 \mathrm{h}-\mathrm{p}=4$
only (D) satisfies above relation.
Comments
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
