A line perpendicular to the line segment joining the points (1, 0) and (2, 3) divides it in the ratio 1 : 2. Find the equation of the line.
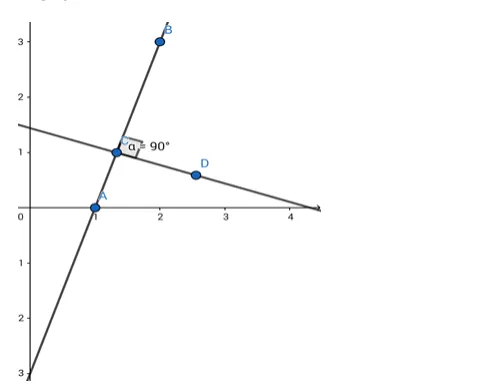
Given: A line perpendicular to the line segment joining the points $(1,0)$ and $(2,3)$ divides it in the ratio $1: 2$.
Formula to be used: If $(a, b)$ and $(c, d)$ are two points then the equation of the line passing through them is
$\frac{\mathrm{y}-\mathrm{b}}{\mathrm{x}-\mathrm{a}}=\frac{\mathrm{b}-\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{a}-\mathrm{c}}$
If $\left(a_{1}, b_{1}\right)$ and $\left(a_{2}, b_{2}\right)$ be two points, then the co - ordinates of the point dividing their join in the ratio $a: b$ is given by
$\mathrm{x}-\mathrm{co}$ ordinate $=\left(\frac{\mathrm{a}_{1} \mathrm{Xb}+\mathrm{a}_{2} \mathrm{Xa}}{\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}}\right)$
$\mathrm{y}-\mathrm{co}$ ordinate $=\left(\frac{\mathrm{b}_{1} \mathrm{Xb}+\mathrm{b}_{2} \mathrm{Xa}}{\mathrm{a}+\mathrm{b}}\right)$
The equation of the line joining points (1,0) and (2,3) is
$\frac{y-0}{x-1}=\frac{0-3}{1-2}$
or, $\frac{y}{x-1}=\frac{-3}{-1}=3$
or,
$y=3 x-3$ or, $3 x-y=3$
i.e. the given line is 3x - y = 3.
Accordingly, the required co - ordinates of the point dividing the join of $(1,0)$ and $(2,3)$ in the ratio $1: 2$ are
$\left(\left(\frac{1 X 2+2 X 1}{1+2}\right),\left(\frac{0 X 2+3 X 1}{1+2}\right)\right)=\left(\frac{4}{3}, 1\right)$
The given line is $3 x-y=3$.
The slope of this line is 3 .
$\therefore$ the slope of the perpendicular line $=\frac{-1}{3}=-\frac{1}{3}$.
The equation of the line can be written in the form $\mathrm{y}=-\frac{1}{3} \mathrm{x}+\mathrm{c}$
( $c$ is the $y$-intercept)
This line will pass through $\left(\frac{4}{3}, 1\right)$.
$\therefore 1=-\frac{1}{3} \mathrm{X} \frac{4}{3}+\mathrm{c}$ or, $\mathrm{c}=1+\frac{4}{9}=\frac{13}{9}$
The required equation is $y=-\frac{1}{3} x+\frac{13}{9}$
i.e. $3 x+9 y=13$
