An arch is in the form of a semi-ellipse. It is 8 m wide and 2 m high at the centre. Find the height of the arch at a point 1.5 m from one end.
An arch is in the form of a semi-ellipse. It is 8 m wide and 2 m high at the centre. Find the height of the arch at a point 1.5 m from one end.
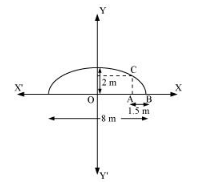
Since the height and width of the arc from the centre is 2 m and 8 m respectively, it is clear that the length of the major axis is 8 m, while the length of the semi-minor axis is 2 m.
The origin of the coordinate plane is taken as the centre of the ellipse, while the major axis is taken along the x-axis. Hence, the semi-ellipse can be diagrammatically represented as
The equation of the semi-ellipse will be of the form $\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}=1, y \geq 0$, where $a$ is the semi-major axis
Accordingly, $2 a=8 \Rightarrow a=4$
b = 2
Therefore, the equation of the semi-ellipse is $\frac{x^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1, y \geq 0$ (1)
Let A be a point on the major axis such that AB = 1.5 m.
Draw $A C \perp O B$.
OA = (4 – 1.5) m = 2.5 m
The x-coordinate of point C is 2.5.
On substituting the value of x with 2.5 in equation (1), we obtain
$\frac{(2.5)^{2}}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1$
$\Rightarrow \frac{6.25}{16}+\frac{y^{2}}{4}=1$
$\Rightarrow y^{2}=4\left(1-\frac{6.25}{16}\right)$
$\Rightarrow y^{2}=4\left(\frac{9.75}{16}\right)$
$\Rightarrow y^{2}=2.4375$
$\Rightarrow y=1.56 \quad$ (approx.)
$\therefore A C=1.56 \mathrm{~m}$
Thus, the height of the arch at a point 1.5 m from one end is approximately 1.56 m.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
