An electric dipole is placed on $x$-axis in proximity to a line charge of linear charge density $3.0 \times 10^{-6} \mathrm{C} / \mathrm{m}$. Line charge is placed on $\mathrm{z}$-axis and positive and negative charge of dipole is at a distance of $10 \mathrm{~mm}$ and $12 \mathrm{~mm}$ from the origin respectively. If total force of $4 \mathrm{~N}$ is exerted on the dipole, find out the amount of positive or negative charge of the dipole.
Correct Option: , 4
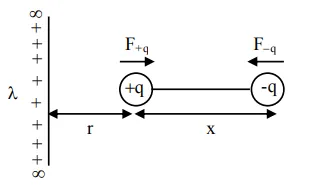
$\mathrm{r}=10 \mathrm{~mm}, \mathrm{x}=2$
$\left|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{\mathrm{q}}\right|=\frac{2 \mathrm{k} \lambda}{\mathrm{r}} \cdot \mathrm{q}$
$\left|\overrightarrow{\mathrm{F}}_{-\mathrm{q}}\right|=\frac{2 \mathrm{k} \lambda}{\mathrm{r}+\mathrm{x}} \cdot \mathrm{q}$
$\Rightarrow \quad\left|\vec{F}_{\text {net }}\right|=\frac{2 k \lambda q}{r}-\frac{2 k \lambda q}{r+x}$
$\left|\vec{F}_{\text {net }}\right|=\frac{2 k \lambda q \cdot x}{r(r+x)}$
$4=\frac{2 \times 9 \times 10^{9} \times 3 \times 10^{-6} \times \mathrm{q} \times 2 \mathrm{~mm}}{10 \mathrm{~mm} .12 \mathrm{~mm}}$
$\Rightarrow \quad q=4.44 \mu C$
