At 0°C, the density of a certain oxide of a gas at 2 bar is same as that of dinitrogen at 5 bar. What is the molecular mass of the oxide?
Density (d) of the substance at temperature (T) can be given by the expression,
$d=\frac{M p}{R T}$
Now, density of oxide (d1) is given by,
$d_{1}=\frac{M_{1} p_{1}}{\mathrm{R} T}$
Where, M1 and p1 are the mass and pressure of the oxide respectively.
Density of dinitrogen gas (d2) is given by,
$d_{2}=\frac{M_{2} p_{2}}{R T}$
Where, M2 and p2 are the mass and pressure of the oxide respectively.
According to the given question,
$d_{1}=d_{2}$
$\therefore M_{1} p_{1}=M_{2} p_{2}$
Given,
$p_{1}=2 b a r$
$p_{2}=5 \mathrm{bar}$
Molecular mass of nitrogen, $M_{2}=28 \mathrm{~g} / \mathrm{mol}$
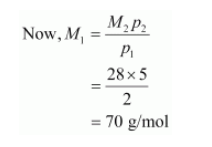
Hence, the molecular mass of the oxide is 70 g/mol.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
