Draw the graphs of x − y + 1 = 0 and 3x + 2y − 12 = 0. Determine the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle formed by these lines and x-axis and shade the triangular area. Calculate the area bounded by these lines and x-axis.
The given equations are
$x-y+1=0$...$.(i )$
$3 x+2 y-12=0$$...(i i)$
Putting $x=0$ in equation $(i)$, we get:
$\Rightarrow 0-y=-1$
$\Rightarrow y=1$
$x=0, \quad y=1$
Putting $y=0$ in equation (i) we get:
$\Rightarrow x-0=-1$
$\Rightarrow x=-1$
$x=-1, \quad y=0$
Use the following table to draw the graph.

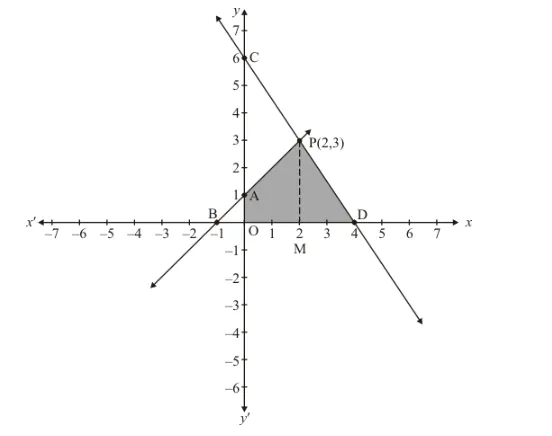
Draw the graph by plotting the two points $A(0,1), B(-1,0)$ from table.
$3 x+2 y=12$....(ii)
Putting $x=0$ in equation (ii) we get:
$\Rightarrow 3 \times 0+2 y=12$
$\Rightarrow y=6$
$x=0, \quad y=6$
Putting $y=0$ in equation $(i i)$. We get:
$\Rightarrow 3 x+2 \times 0=12$
$\Rightarrow x=4$
$x=4, \quad y=0$
Use the following table to draw the graph.

Draw the graph by plotting the two points $C(0,6), D(4,0)$ from table.
The two lines intersect at $P(2,3)$.
Now, Required area = Area of shaded region
$\Rightarrow$ Required area $=$ Area of PBD
$\Rightarrow$ Required area $=1 / 2$ (basexheight)
$\Rightarrow$ Required area $=1 / 2(B D \times P M)$
$\Rightarrow$ Required area $=1 / 2(5 \times 3)$ sq. units
Hence the area $=7.5$ sq.units
