Explain structures of diborane and boric acid.
(a) Diborane
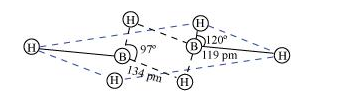
$\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ is an electron-deficient compound. $\mathrm{B}_{2} \mathrm{H}_{6}$ has only 12 electrons $-6 \mathrm{e}^{-}$from $6 \mathrm{H}$ atoms and $3 \mathrm{e}^{-}$each from $2 \mathrm{~B}$ atoms. Thus, after combining with $3 \mathrm{H}$ atoms, none of the boron atoms has any electrons left. X-ray diffraction studies have shown the structure of diborane as:
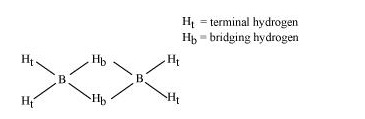
2 boron and 4 terminal hydrogen atoms $\left(H_{t}\right)$ lie in one plane, while the other two bridging hydrogen atoms $\left(H_{b}\right)$ lie in a plane perpendicular to the plane of boron atoms. Again, of the two bridging hydrogen atoms, one $\mathrm{H}$ atom lies above the plane and the other lies below the plane. The terminal bonds are reelentron ( $2 \mathrm{c}-2 \mathrm{e}^{-}$) bonds, while the two bridging (B-H-B) bonds are three-centre two-electron (3c - 2e^-) bonds.
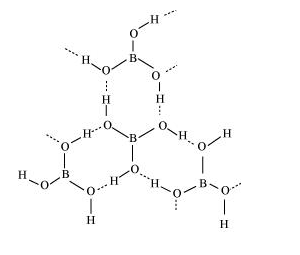
(b) Boric acid
Boric acid has a layered structure. Each planar $\mathrm{BO}_{3}$ unit is linked to one another through $\mathrm{H}$ atoms. The $\mathrm{H}$ atoms form a covalent bond with a $\mathrm{BO}_{3}$ unit, while a hydrogen bond is formed with another $\mathrm{BO}_{3}$ unit. In the given figure, the dotted lines represent hydrogen bonds.