Factorise:<br/><br/>(i) $x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2$ <br/><br/>(ii) $x^{3}+3 x^{2}-9 x-5$<br/><br/>(iii) $x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20$<br/><br/> (iv) $2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$
Solution:
(i) Let $p(x)=x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2$
All the factors of 2 have to be considered. These are $\pm 1, \pm 2$
By trial method
$p(-1)=(-1)^{3}-2(-1)^{2}-(-1)+2$
$=-1-2+1+2=0$
Therefore, $(x+1)$ is factor of polynomial $p(x)$.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2$ by $x+1$.
By long division,
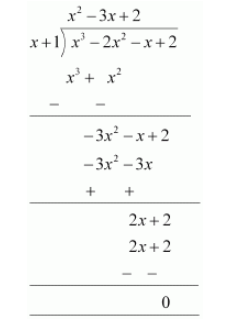
It is known that,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$\therefore x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2=(x+1)\left(x^{2}-3 x+2\right)+0$
$=(x+1)\left[x^{2}-2 x-x+2\right]$
$=(x+1)[x(x-2)-1(x-2)]$
$=(x+1)(x-1)(x-2)$
$=(x-2)(x-1)(x+1)$
(ii) Let $p(x)=x^{3}-3 x^{2}-9 x-5$
All the factors of 5 have to be considered. These are $\pm 1, \pm 5$.
By trial method,
$p(-1)=(-1)^{3}-3(-1)^{2}-9(-1)-5$
$=-1-3+9-5=0$
Therefore, $x+1$ is a factor of this polynomial.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $x^{3}+3 x^{2}-9 x-5$ by $x+1$
By long division,
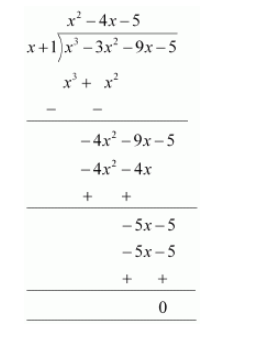
It is known that,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$\therefore x^{3}-3 x^{2}-9 x-5=(x+1)\left(x^{2}-4 x-5\right)+0$
$=(x+1)\left(x^{2}-5 x+x-5\right)$
$=(x+1)[(x(x-5)+1(x-5)]$
$=(x+1)(x-5)(x+1)$
$=(x-5)(x+1)(x+1)$
(iii) Let $p(x)=x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20$
All the factors of 20 have to be considered. Some of them are $\pm 1$, $\pm 2, \pm 4, \pm 5 \ldots \ldots$
By trial method,
$p(-1)=(-1)^{3}+13(-1)^{2}+32(-1)+20$
$=-1+13-32+20$
$=33-33=0$
As $p(-1)$ is zero, therefore, $x+1$ is a factor of this polynomial $p(x)$.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20$ by $(x+1)$
By long division,
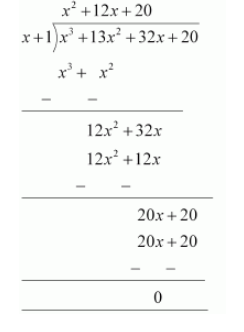
It is known that,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20=(x+1)\left(x^{2}+12 x+20\right)+0$
$=(x+1)\left(x^{2}+10 x+2 x+20\right)$
$=(x+1)[x(x+10)+2(x+10)]$
$=(x+1)(x+10)(x+2)$
$=(x+1)(x+2)(x+10)$
(iv) Let $p(y)=2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$
By trial method,
$p(1)=2(1)^{3}+(1)^{2}-2(1)-1$
$=2+1-2-1=0$
Therefore, $y-1$ is a factor of this polynomial.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$ by $y-1$.
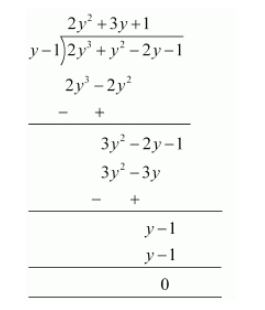
$p(y)=2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$
$=(y-1)\left(2 y^{2}+3 y+1\right)$
$=(y-1)\left(2 y^{2}+2 y+y+1\right)$
$=(y-1)[2 y(y+1)+1(y+1)]$
$=(y-1)(y+1)(2 y+1)$
(i) Let $p(x)=x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2$
All the factors of 2 have to be considered. These are $\pm 1, \pm 2$
By trial method
$p(-1)=(-1)^{3}-2(-1)^{2}-(-1)+2$
$=-1-2+1+2=0$
Therefore, $(x+1)$ is factor of polynomial $p(x)$.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2$ by $x+1$.
By long division,
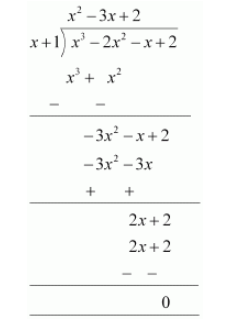
It is known that,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$\therefore x^{3}-2 x^{2}-x+2=(x+1)\left(x^{2}-3 x+2\right)+0$
$=(x+1)\left[x^{2}-2 x-x+2\right]$
$=(x+1)[x(x-2)-1(x-2)]$
$=(x+1)(x-1)(x-2)$
$=(x-2)(x-1)(x+1)$
(ii) Let $p(x)=x^{3}-3 x^{2}-9 x-5$
All the factors of 5 have to be considered. These are $\pm 1, \pm 5$.
By trial method,
$p(-1)=(-1)^{3}-3(-1)^{2}-9(-1)-5$
$=-1-3+9-5=0$
Therefore, $x+1$ is a factor of this polynomial.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $x^{3}+3 x^{2}-9 x-5$ by $x+1$
By long division,
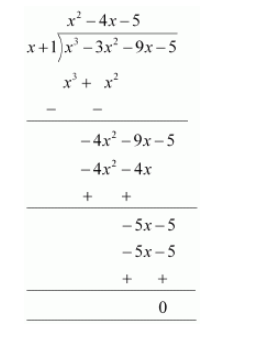
It is known that,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$\therefore x^{3}-3 x^{2}-9 x-5=(x+1)\left(x^{2}-4 x-5\right)+0$
$=(x+1)\left(x^{2}-5 x+x-5\right)$
$=(x+1)[(x(x-5)+1(x-5)]$
$=(x+1)(x-5)(x+1)$
$=(x-5)(x+1)(x+1)$
(iii) Let $p(x)=x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20$
All the factors of 20 have to be considered. Some of them are $\pm 1$, $\pm 2, \pm 4, \pm 5 \ldots \ldots$
By trial method,
$p(-1)=(-1)^{3}+13(-1)^{2}+32(-1)+20$
$=-1+13-32+20$
$=33-33=0$
As $p(-1)$ is zero, therefore, $x+1$ is a factor of this polynomial $p(x)$.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20$ by $(x+1)$
By long division,
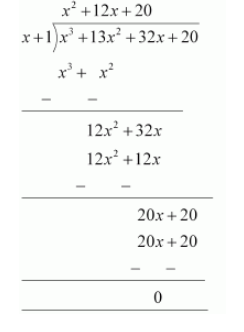
It is known that,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$x^{3}+13 x^{2}+32 x+20=(x+1)\left(x^{2}+12 x+20\right)+0$
$=(x+1)\left(x^{2}+10 x+2 x+20\right)$
$=(x+1)[x(x+10)+2(x+10)]$
$=(x+1)(x+10)(x+2)$
$=(x+1)(x+2)(x+10)$
(iv) Let $p(y)=2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$
By trial method,
$p(1)=2(1)^{3}+(1)^{2}-2(1)-1$
$=2+1-2-1=0$
Therefore, $y-1$ is a factor of this polynomial.
Let us find the quotient on dividing $2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$ by $y-1$.
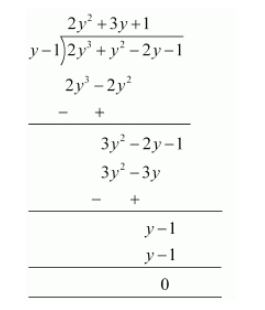
$p(y)=2 y^{3}+y^{2}-2 y-1$
$=(y-1)\left(2 y^{2}+3 y+1\right)$
$=(y-1)\left(2 y^{2}+2 y+y+1\right)$
$=(y-1)[2 y(y+1)+1(y+1)]$
$=(y-1)(y+1)(2 y+1)$
