Find k, so that x2 + 2x + k is a factor of 2x4 + x3 – 14x2 + 5x + 6. Also, find all the zeroes of the two polynomials.
Given that, x2 + 2x+ k is a factor of 2x4 + x3 -14x2 + 5x+ 6, then we apply division algorithm,
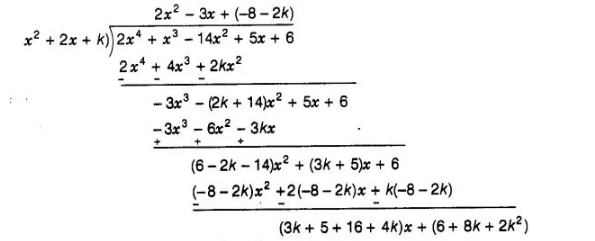
Since, $\left(x^{2}+2 x+k\right)$ is a factor of $2 x^{4}+x^{3}-14 x^{2}+5 x+6$
So, when we apply division algorithm remainder should be zero.
$\therefore \quad(7 k+21) x+\left(2 k^{2}+8 k+6\right)=0 \cdot x+0$
$\Rightarrow \quad 7 k+21=0$ and $2 k^{2}+8 k+6=0$
$\Rightarrow \quad k=-3$ or $k^{2}+4 k+3=0$
$\Rightarrow \quad k^{2}+3 k+k+3=0 \quad$ [by splitting middle term]
$\Rightarrow \quad k(k+3)+1(k+3)=0$
$\Rightarrow \quad(k+1)(k+3)=0$
$\Rightarrow \quad k=-1$ or $-3$
Here, if we take $k=-3$, then remainder will be zero.
Thus, the required value of $k$ is $-3$.
Now,
Dividend $=$ Divisor $\times$ Quotient $+$ Remainder
$\Rightarrow \quad 2 x^{4}+x^{3}-14 x^{2}+5 x+16=\left(x^{2}+2 x-3\right)\left(2 x^{2}-3 x-2\right)$
Using factorisation method,
$=\left(x^{2}+3 x-x-3\right)\left(2 x^{2}-4 x+x-2\right)$ [by splitting middle term]
$=\{x(x+3)-1(x+3)\}\{2 x(x-2)+1(x-2)\}$
$=(x-1)(x+3)(x-2)(2 x+1)$
Hence, the zeroes of $x^{2}+2 x-3$ are $1,-3$ and the zeroes of $2 x^{4}+x^{3}-14 x^{2}+5 x+6$
are $1,-3,2, \frac{-1}{2}$
