Find the area of a parallelogram $A B C D$ if three of its vertices are $A(2,4), B(2+\sqrt{3}, 5)$ and $C(2,6)$.
It is given that $\mathrm{A}(2,4), \mathrm{B}(2+\sqrt{3}, 5)$ and $\mathrm{C}(2,6)$ are the vertices of the parallelogram $\mathrm{ABCD}$.
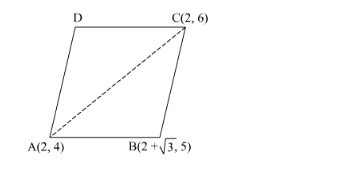
We know that the diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into two triangles having equal area.
$\therefore$ Area of the parallogram $\mathrm{ABCD}=2 \times$ Area of the $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}$
Now,
$\operatorname{ar}(\Delta \mathrm{ABC})=\frac{1}{2}\left|x_{1}\left(y_{2}-y_{3}\right)+x_{2}\left(y_{3}-y_{1}\right)+x_{3}\left(y_{1}-y_{2}\right)\right|$
$=\frac{1}{2}|2(5-6)+(2+\sqrt{3})(6-4)+2(4-5)|$
$=\frac{1}{2}|-2+4+2 \sqrt{3}-2|$
$=\frac{1}{2} \times 2 \sqrt{3}$
$=\sqrt{3}$ square units
$\therefore$ Area of the parallooram $A B C D=2 \times$ Area of the $\triangle A B C=2 \times \sqrt{3}=2 \sqrt{3}$ square units
Hence, the area of given parallelogram is $2 \sqrt{3}$ square units.
