Find the equation of the line passing through ( - 3, 5) and perpendicular to the line through the points (2, 5) and ( - 3, 6).
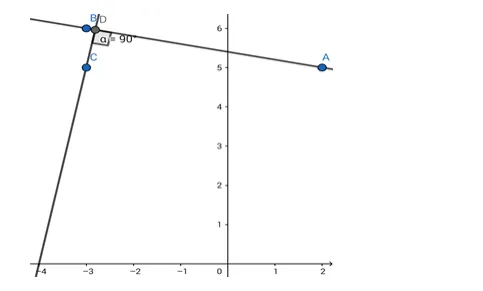
Given: The line perpendicular to the line passing through $(2,5)$ and $(-3,6)$ passes through $(-3,5)$.
Formula to be used: If $(a, b)$ and $(c, d)$ are two points then the equation of the line passing through them is
$\frac{y-b}{x-a}=\frac{b-d}{a-c}$
Product of slopes of two perpendicular lines $=-1$
The equation of the line joining points $(2,5)$ and $(-3,6)$ is
$\frac{y-5}{x-2}=\frac{5-6}{2-(-3)}$
or, $\frac{y-5}{x-2}=\frac{-1}{5}$
Or, $5 y-25=-x+2$
i.e. the given line is x + 5y = 27.
The slope of this line is $-1 / 5$.
$\therefore$ the slope of the perpendicular line =
$\frac{-1}{-1 / 5}=5$
The equation of the line can be written in the form y = 5x + c
(c is the y - intercept)
This line passes through ( - 3,5).
Hence, 5 = 5x( - 3) + c or, c = 20
The required equation of the line will be y = 5x + 20
i.e. 5x - y + 20 = 0
