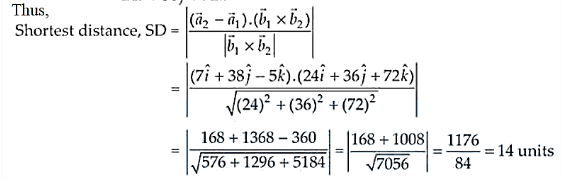Find the shortest distance between the lines given by
$\vec{r}=(8+3 \lambda \hat{i}-(9+16 \lambda) \hat{j}+(10+7 \lambda) \hat{k}$ and
$\vec{r}=15 \hat{i}+29 \hat{j}+5 \hat{k}+\mu(3 \hat{i}+8 \hat{j}-5 \hat{k})$
Given equations of lines are
$\ddot{r}=(8+3 \lambda) \hat{i}-(9+16 \lambda) \hat{j}+(10+7 \lambda) \hat{k}$ ......(i)
and $\quad \vec{r}=15 \hat{i}+29 \hat{j}+5 \hat{k}+\mu(3 \hat{i}+8 \hat{j}-5 \hat{k})$ .............(ii)
Equation (i) can be re-written as
$\vec{r}=8 \hat{i}-9 \hat{j}+10 \hat{k}+\lambda(3 \hat{i}-16 \hat{j}+7 \hat{k})$ ......(iii)
Here, $\quad \vec{a}_{1}=8 \hat{i}-9 \hat{j}+10 \hat{k}$ and $\vec{a}_{2}=15 \hat{i}+29 \hat{j}+5 \hat{k}$
$\vec{b}_{1}=3 \hat{i}-16 \hat{j}+7 \hat{k}$ and $\vec{b}_{2}=3 \hat{i}+8 \hat{j}-5 \hat{k}$
$\vec{a}_{2}-\vec{a}_{1}=7 \hat{i}+38 \hat{j}-5 \hat{k}$
$\vec{b}_{1} \times \vec{b}_{2}=\left|\begin{array}{rrr}\hat{i} & \hat{j} & \hat{k} \\ 3 & -16 & 7 \\ 3 & 8 & -5\end{array}\right|$
$=\hat{i}(80-56)-\hat{j}(-15-21)+\hat{k}(24+48)$
$=24 \hat{i}+36 \hat{j}+72 \hat{k}$