From a point P which is at a distance of 13 cm from the centre 0 of a circle of radius 5 cm, the pair of tangents PQ and PR to the circle is drawn.
Then, the area of the quadrilateral PQOR is
(a) 60 cm2
(b) 65 cm2
(c) 30 cm2
(d) 32.5 cm2
(a) Firstly, draw a circle of radius 5 cm having centre O. P is a point at a distance of 13 cm from O. A pair of tangents PQ and PR are drawn.
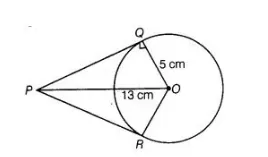
Thus, quadrilateral POOR is formed.
$\because \quad \quad O Q \perp Q P$ [since, AP is a tangent line]
In right angled $\triangle P Q O, \quad O P^{2}=O Q^{2}+Q P^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \quad 13^{2}=5^{2}+Q P^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \quad Q P^{2}=169-25=144$
$\Rightarrow \quad Q P=12 \mathrm{~cm}$
Now, area of $\Delta O Q P=\frac{1}{2} \times Q P \times Q O$
$=\frac{1}{2} \times 12 \times 5=30 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
$\therefore \quad$ Area of quadrilateral $Q O R P=2 \triangle O Q P$
$=2 \times 30=60 \mathrm{~cm}^{2}$
