From the choices given below, choose the equation whose graph is given fig:
(i) y = x + 2
(ii) y = x – 2
(iii) y = - x + 2
(iv) x + 2y = 6
We are given co-ordinates (-1, 3) and (2, 0) as the solution of one of the following equations.
We will substitute the value of both co-ordinates in each of the equation and find the equation which satisfies the given co-ordinates.
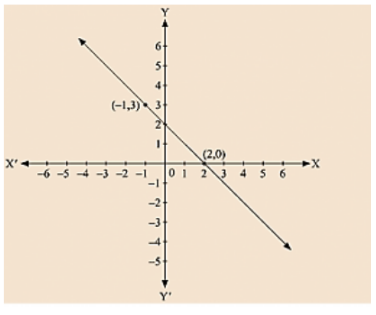
(i) We are given, y=x+2 Substituting x = - 1 and y = 3,
We get 3 ≠ -1+ 2
L.H.S ≠ R.H.S
Substituting x = 2 and y = 0,
We get 0 ≠ 4
L.H.S ≠ R.H.S
Therefore, the given solution does not satisfy this equation.
(ii) We are given, y = x - 2
Substituting x = 1 and y = 3,
We get 3 = - 1 - 2
L.H.S ≠ R.H.S
Substituting x = 2 and y = 0, we get 0 = 0
L.H.S = R.H.S
Therefore, the given solutions does not completely satisfy this equation.
(iii) We are given, y = - x + 2
Substituting x = - 1 and y = 3,
We get 3 = - (-1) + 2
L.H.S = R.H.S
Substituting x = 2 and y = 0, we get 0 = - 2 + 2
0 = 0
L.H.S = R.H.S
Therefore, the given solutions satisfy this equation. Thus, it is the equation whose graph is given.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
