If O is the centre of the circle, find the value of x in each of the following figures.
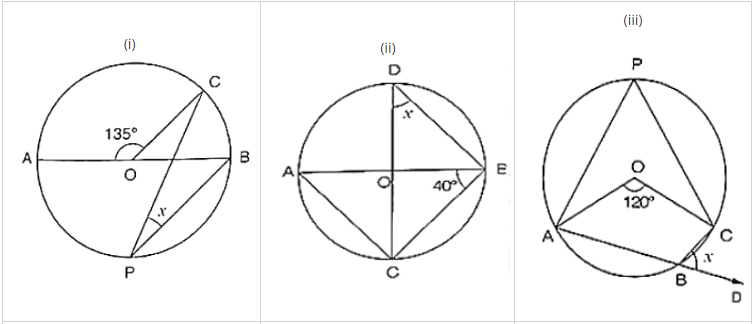
(i) ∠AOC = 135°
∴ ∠AOC + ∠BOC = 180° [Linear pair of angles]
⇒ 135° + ∠BOC = 180°
⇒ ∠BOC = 180° − 135°
⇒ ∠BOC = 45°
By degree measure theorem
∠BOC = 2∠CPB
⇒ 45° = 2x
⇒ x = 45°/2 = 22½°
(ii) We have ∠ABC = 40°
∠ACB = 90° [Angle in semi circle]
In ΔABC, by angle sum property
∠CAB + ∠ACB + ∠ABC = 180°
⇒ ∠CAB + 90° + 40° = 180°
⇒ ∠CAB = 180° − 90° − 40°
⇒ ∠CAB = 50°
Now, ∠CDB = ∠CAB [Angle is same in segment]
⇒ x = 50°
(iii) We have
∠AOC = 120° By degree measure theorem.
∠AOC = 2∠APC
⇒ 120° = 2∠APC
⇒ ∠APC = 120°/2 = 60°
∠APC + ∠ABC = 180° [Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilaterals]
⇒ 60° + ∠ABC = 180°
⇒ ∠ABC = 180° − 60°
⇒ ∠ABC = 120°
∴ ∠ABC + ∠DBC = 180° [Linear pair of angles]
⇒ 120 + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° − 120° = 60°
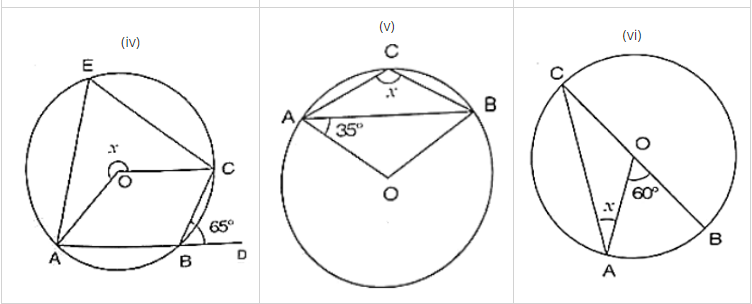
(iv) We have
∠CBD = 65°
∴ ∠ABC + ∠CBD = 180° [Linear pair of angles]
⇒ ∠ABC = 65° = 180°
⇒ ∠ABC = 180° − 65° = 115°
∴ reflex ∠AOC = 2∠ABC [By degree measure theorem]
⇒ x = 2 × 115°
⇒ x = 230°
(v) We have
∠OAB = 35° Then,
∠OBA = ∠OAB = 35° [Angles opposite to equal radii]
In ΔAOB, by angle sum property
⇒∠AOB + ∠OAB + ∠OBA = 180°
⇒ ∠AOB + 35° + 35° = 180°
⇒ ∠AOB = 180° −35° − 35° = 110°
∴ ∠AOB + reflex ∠AOB = 360° [Complexangle]
⇒ 110° + reflex ∠AOB = 360°
⇒ reflex ∠AOB = 360° − 110° = 250°
By degree measure theorem reflex
∠AOB = 2∠ACB
⇒ 250° = 2x
⇒ x = 250°/2 = 125°
(vi) We have
∠AOB = 60° By degree measure theorem reflex
∠AOB = 2∠ACB
⇒ 60° = 2∠ACB
⇒ ∠ACB = 60°/2 = 30° [Angles opposite to equal radii]
⇒ x = 30°.
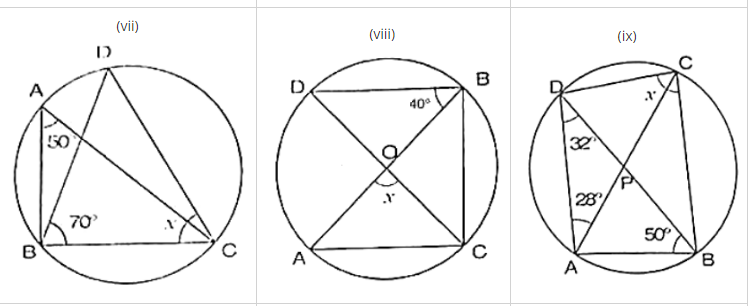
(vii) We have
∠BAC = 50° and ∠DBC = 70°
∴ ∠BDC = ∠BAC = 50° [Angle in same segment]
In ΔBDC, by angle sum property
∠BDC + ∠BCD + ∠DBC = 180°
⇒ 50° + x + 70° = 180°
⇒ x = 180° − 50° − 70° = 60°
(viii) We have
∠DBO = 40° and ∠DBC = 90° [Angle in a semicircle]
⇒ ∠DBO + ∠OBC = 90°
⇒ 40° + ∠OBC = 90°
⇒ ∠OBC = 90° − 40° = 50° By degree measure theorem
∠AOC = 2∠OBC
⇒ x = 2 × 50° = 100°
(ix) In ΔDAB, by angle sum property
∠ADB + ∠DAB + ∠ABD = 180°
⇒ 32° + ∠DAB + 50° = 180°
⇒ ∠DAB = 180° − 32° − 50°
⇒ ∠DAB = 98°
Now, ∠OAB + ∠DCB = 180° [Opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral]
⇒ 98° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° − 98° = 82°
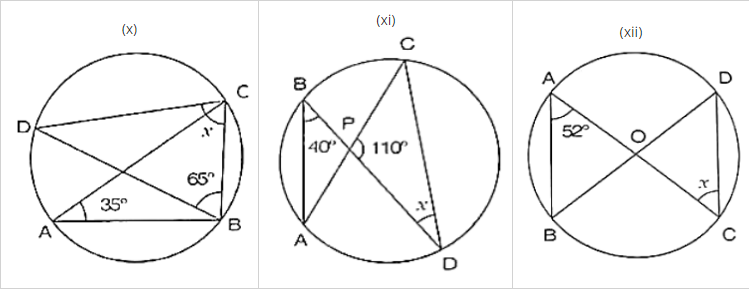
(x) We have,
∠BAC = 35°
∠BDC = ∠BAC = 35° [Angle in same segment]
In ΔBCD, by angle sum property
∠BDC + ∠BCD + ∠DBC = 180°
⇒ 35° + x + 65° = 180°
⇒ x = 180° − 35° − 65° = 80°
(xi) We have
∠ABD = 40°
∠ACD = ∠ABD = 40° [Angle in same segment]
In ΔPCD, by angle sum property
∠PCD + ∠CPO + ∠PDC = 180°
⇒ 40° + 110° + x = 180°
⇒ x = 180° − 150°
⇒ x = 30°
(xii) Given that,
∠BAC = 52°
Then ∠BDC = ∠BAC = 52° [Angle in same segment]
Since OD = OC
Then ∠ODC = ∠OCD [Opposite angle to equal radii]
⇒ x = 52°
