If $\sec \theta=\frac{13}{5}$, show that $\frac{2 \sin \theta-3 \cos \theta}{4 \sin \theta-9 \cos \theta}=3$.
Given:
$\sec \theta=\frac{13}{5}$
To show that $\frac{2 \sin \theta-3 \cos \theta}{4 \sin \theta-9 \cos \theta}=3$
Now, we know that $\cos \theta=\frac{1}{\sec \theta}$
Therefore,
$\cos \theta=\frac{1}{\frac{13}{5}}$
Therefore,
$\cos \theta=\frac{5}{13}$...(1)
Now, we know that
$\cos \theta=\frac{\text { Base side adjacent to } \angle \theta}{\text { Hypotenuse }}$....(2)
Now, by comparing equation (1) and (2)
We get,
Base side adjacent to $\angle \theta=5$
And
Hypotenuse = 13
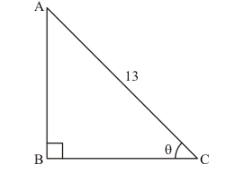
Therefore from above figure
Base side $B C=5$
Hypotenuse $A C=13$
Side AB is unknown, It can be determined by using Pythagoras theorem
Therefore by applying Pythagoras theorem
We get,
$A C^{2}=A B^{2}+B C^{2}$
Therefore by substituting the values of known sides
We get,
$13^{2}=A B^{2}+5^{2}$
Therefore,
$A B^{2}=13^{2}-5^{2}$
$A B^{2}=169-25$
$A B^{2}=144$
$A B=\sqrt{144}$
Therefore,
$A B=12 \ldots \ldots(3)$
Now, we know that
$\sin \theta=\frac{\text { Perpendicular side opposite to } \angle \theta}{\text { Hypotenuse }}$
Now from figure (a)
We get,
$\sin \theta=\frac{A B}{A C}$
Therefore,
$\sin \theta=\frac{12}{4}$...(4)
Now L.H.S. of the equation to be proved is as follows
L.H.S. $=\frac{2 \sin \theta-3 \cos \theta}{4 \sin \theta-9 \cos \theta}$
Substituting the value of $\cos \theta$ and $\sin \theta$ from equation (1) and (4) respectively
We get,
$L . H . S .=\frac{2\left(\frac{12}{13}\right)-3\left(\frac{5}{13}\right)}{4\left(\frac{12}{13}\right)-9\left(\frac{5}{13}\right)}$
Therefore,
L.H.S. $=\frac{2 \times 12-3 \times 5}{4 \times 12-9 \times 5}$
L.H.S. $=\frac{24-15}{48-45}$
$L . H . S .=\frac{9}{3}$
$L . H . S .=3$
Hence proved that,
$\frac{2 \sin \theta-3 \cos \theta}{4 \sin \theta-9 \cos \theta}=3$
