If the equation of the base of an equilateral triangle is x + y = 2 and the vertex is (2, – 1), then find the length of the side of the triangle.
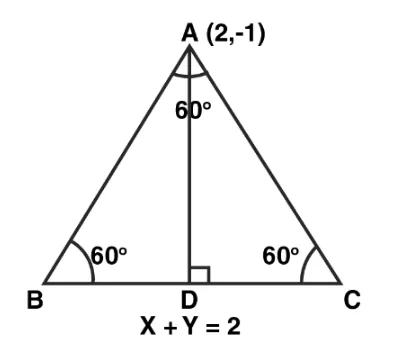
Let $\triangle \mathrm{ABC}$ be an equilateral triangle.
Given equation of the base $B C$ is $x+y=2$
We know that, in an equilateral triangle all angles are of $60^{\circ}$
So, in $\triangle \mathrm{ABD}$
$\sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{AB}}$\
$\Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}=\frac{\mathrm{AD}}{\mathrm{AB}}\left[\because \sin 60^{\circ}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\right]$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{AD}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \mathrm{AB}$
We know that, the distance $d$ of a point $P\left(x_{0}, y_{0}\right)$ from the line $A x+B y+C=0$ is given by
$d=\left|\frac{A x_{0}+B y_{0}+C}{\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}}}\right|$
Now, length of perpendicular from vertex $A(2,-1)$ to the line $x+y=2$ is
$\mathrm{AD}=\left|\frac{1 \times 2+1 \times(-1)-2}{\sqrt{(1)^{2}+(1)^{2}}}\right|$
$\Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \mathrm{AB}=\left|\frac{2-1-2}{\sqrt{2}}\right|$
On simplification we get
$\Rightarrow \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \mathrm{AB}=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}$
Squaring both the sides, we get
$\Rightarrow \frac{3}{4} \mathrm{AB}^{2}=\frac{1}{2}$
On cross multiplication we get
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{AB}^{2}=\frac{4}{3} \times \frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{AB}^{2}=\frac{2}{3}$
$\Rightarrow A B=\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$
Hence, the required length of side is $\sqrt{\frac{2}{3}}$
