$f(x)=2 \sin x-x,-\frac{\pi}{2}<\leq x \leq \frac{\pi}{2}$
Given : $f(x)=2 \sin x-x$
$\Rightarrow f^{\prime}(x)=2 \cos x-1$
For a local maximum or a local minimum, we must have
$f^{\prime}(x)=0$
$\Rightarrow 2 \cos x-1=0$
$\Rightarrow \cos x=\frac{1}{2}$
$\Rightarrow x=\frac{\pi}{3}$ or $\frac{-\pi}{3}$
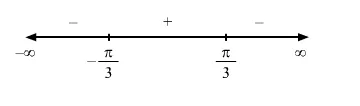
Since $f^{\prime}(x)$ changes from positive to negative when $x$ increases through $\frac{\pi}{3}, x=\frac{\pi}{3}$ is the point of local maxima. The local maximum value of $f(x)$ at $x=\frac{\pi}{3}$ is given by
$2 \sin \left(\frac{\pi}{3}\right)-\frac{\pi}{3}=\sqrt{3}-\frac{\pi}{3}$
Since $f^{\prime}(x)$ changes from negative to positive when $x$ increases through $-\frac{\pi}{3}, x=-\frac{\pi}{3}$ is the point of local minima.
The local minimum value of $f(x)$ at $x=-\frac{\pi}{3}$ is given by
$2 \sin \left(\frac{-\pi}{3}\right)+\frac{\pi}{3}=\frac{\pi}{3}-\sqrt{3}$
