$f(x)=x^{3}(x-1)^{2}$
Given : $f(x)=x^{3}(x-1)^{2}$
$\Rightarrow f^{\prime}(x)=3 x^{2}(x-1)^{2}+2 x^{3}(x-1)$
For a local maximum or a local minimum, we must have
$f^{\prime}(x)=0$
$\Rightarrow 3 x^{2}(x-1)^{2}+2 x^{3}(x-1)=0$
$\Rightarrow x^{2}(x-1)\{3 x-3+2 x\}=0$
$\Rightarrow x^{2}(x-1)(5 x-3)=0$
$\Rightarrow x=0,1, \frac{3}{5}$
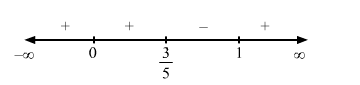
Since $f^{\prime}(x)$ changes from negative to positive when $x$ increases through $1, x=1$ is the point of local minima. The local minimum value of $f(x)$ at $x=1$ is given by
$(1)^{3}(1-1)^{2}=0$
Since $f^{\prime}(x)$ changes from positive to negative when $x$ increases through $\frac{3}{5}, x=\frac{3}{5}$ is the point of local maxima. The local minimum value of $f(x)$ at $x=\frac{3}{5}$ is given by
$\left(\frac{3}{5}\right)^{3}\left(\frac{3}{5}-1\right)^{2}=\frac{27}{125} \times \frac{4}{25}=\frac{108}{3125}$
Since $f^{\prime}(x)$ does not change from positive as $x$ increases through $0, x=0$ is a point of inflexion.
Disclaimer: The solution in the book is incorrect. The solution here is created according to the question given in the book.
