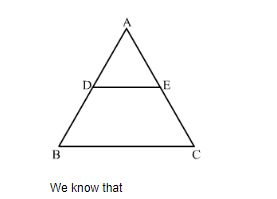
In a ∆ABC, point D is on side AB and point E is on side AC, such that BCED is a trapezium. If DE : BC = 3 : 5, then Area (∆ ADE) : Area (◻BCED) =
In a ∆ABC, point D is on side AB and point E is on side AC, such that BCED is a trapezium. If DE : BC = 3 : 5, then Area (∆ ADE) : Area (◻BCED) =
(a) 3 : 4
(b) 9 : 16
(c) 3 : 5
(d) 9 : 25
Given: In ΔABC, D is on side AB and point E is on side AC, such that BCED is a trapezium. DE: BC = 3:5.
To find: Calculate the ratio of the areas of ΔADE and the trapezium BCED.
In ΔADE and ΔABC,
∠ADE=∠B Corresponding angles∠A=∠A Common∴∆ADE~∆ABC AA Similarity
$\frac{\operatorname{Ar}(\Delta \mathrm{ADE})}{\operatorname{Ar}(\Delta \mathrm{ABC})}=\frac{\mathrm{DE}^{2}}{\mathrm{BC}^{2}}$
$\frac{\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ADE})}{\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ABC})}=\frac{3^{2}}{5^{2}}$
$\frac{\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ADE})}{\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ABC})}=\frac{9}{25}$
Let Area of ΔADE = 9x sq. units and Area of ΔABC = 25x sq. units
$\operatorname{Ar}[\operatorname{trapBCED}]=\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ABC})-\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ADE})$
$=25 x-9 x$
$=16 x \mathrm{sq}$ units
Now ,
$\frac{\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ADE})}{\operatorname{Ar}(\operatorname{trapBCED})}=\frac{9 x}{16 x}$
$\frac{\operatorname{Ar}(\triangle \mathrm{ADE})}{\operatorname{Ar}(\operatorname{trapBCED})}=\frac{9}{16}$
Hence the correct answer is $(b)$.
