In a cyclic quadrilateral $A B C D, \angle A=(2 x+4)^{\circ}, \angle B=(y+3)^{\circ}, \angle C=(2 y+10)^{\circ}, \angle D=(4 x-5)^{\circ}$. Find the four angles.
We know that the sum of the opposite angles of cyclic quadrilateral is $180^{\circ}$ in the cyclic quadrilateral $A B C D$, angles $A$ and $C$ and angles $B$ and $D$ pairs of opposite angles
Therefore $\angle A+\angle C=180^{\circ}$ and $\angle B+\angle D=180^{\circ}$
Taking $\angle A+\angle C=180^{\circ}$
By substituting $\angle A=(2 x+4)^{\circ}$ and $\angle c=(2 y+10)^{\circ}$ we get
$2 x+4+2 y+10=180$
$2 x+2 y+14=180^{\circ}$
$2 x+2 y=180^{\circ}-14^{\circ}$
$2 x+2 y=166 \cdots(i)$
Taking $\angle B+\angle D=180^{\circ}$
By substituting $\angle B=(y+3)^{\circ}$ and $\angle D=(4 x-5)^{\circ}$ we get
$y+3+4 x-5=180^{\circ}$
$4 x+y-5+3=180^{\circ}$
$4 x+y-2=180^{\circ}$
$4 x+y=180^{\circ}+2^{\circ}$
$4 x+y=182^{\circ} \cdots(i i)$
By multiplying equation $($ ii $)$ by 2 we get $8 x+2 y=364 \cdots($ iii $)$
By subtracting equation $(i i i)$ from $(i)$ we get
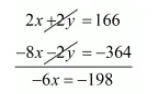
$x=\frac{-198}{-6}$
$x=33^{\circ}$
By substituting $x=33^{\circ}$ in equation $(i i)$ we get
$4 x+y=182$
$4 \times 33+y=182$
$132+y=182$
$y=182-132$
$y=50$
The angles of a cyclic quadrilateral are
$\angle A=2 x+4$
$=2 \times 33+4$
$=66+4$
$=70^{\circ}$
$\angle B=y+3$
$=50+3$
$=53^{\circ}$
$\angle C=2 y+10^{\circ}$
$=2 \times 50+10$
$=100+10$
$=110^{\circ}$
$\angle D=4 x-5$
$=4 \times 33-5$
$=132-5$
$=127^{\circ}$
Hence, the angles of cyclic quadrilateral $\mathrm{ABCD}$ are $\angle A=70^{\circ}, \angle B=53^{\circ}, \angle C=110^{\circ}, \angle D=127^{\circ}$
