In $\triangle A B C, \angle A$ is obtuse, $P B \perp A C$ and $Q C \perp A B$. Prove that:
(i) $\mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{AQ}=\mathrm{AC} \times \mathrm{AP}$
(ii) $B C^{2}=(A C \times C P+A B \times B Q)$
Given: ΔABC where ∠BAC is obtuse. PB ⊥AC and QC⊥AB.
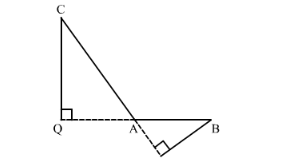
To prove: (i) $\mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{AQ}=\mathrm{AC} \times \mathrm{AP}$ and (ii) $\mathrm{BC}^{2}=\mathrm{AC} \times \mathrm{CP}+\mathrm{AB} \times \mathrm{BQ}$
Proof: In $\triangle \mathrm{ACQ}$ and $\triangle \mathrm{ABP}$,
$\angle C A Q=\angle B A P($ Vertically opposite angles $)$
$\angle Q=\angle P\left(=90^{\circ}\right)$
$\therefore \triangle \mathrm{ACQ} \sim \triangle \mathrm{ABP}[\mathrm{AA}$ similarity test]
$\Rightarrow \frac{\mathrm{CQ}}{\mathrm{BP}}=\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{AB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AQ}}{\mathrm{AP}}$ [Corresponding sides are in the same proportion]
$\frac{\mathrm{AC}}{\mathrm{AB}}=\frac{\mathrm{AQ}}{\mathrm{AP}}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{AQ} \times \mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{AC} \times \mathrm{AP}$.....(1)
In right $\triangle B C Q$,
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=C Q^{2}+Q B^{2}$
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=C Q^{2}+(Q A+A B)^{2}$
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=C Q^{2}+Q A^{2}+A B^{2}+2 Q A \times A B$
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=A C^{2}+A B^{2}+Q A \times A B+Q A \times A B$ [In right $\triangle \mathrm{ACQ}, \mathrm{CQ}^{2}+\mathrm{QA}^{2}=\mathrm{AC}^{2}$ ]
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=A C^{2}+A B^{2}+Q A \times A B+A C \times A P$(Using (1))
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=A C(A C+A P)+A B(A B+Q A)$
$\Rightarrow B C^{2}=A C \times C P+A B \times B Q$
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
