In an equilateral triangle with side a prove that area $=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^{2}$.
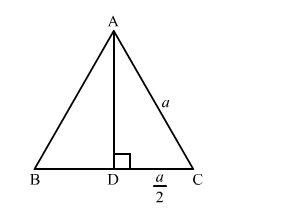
We know that the altitude of an equilateral triangle bisects the side on which it stands and forms right angled triangles with the remaining sides..
Suppose ABC is an equilateral triangle having AB = BC = CA = a.
Suppose AD is the altitude drawn from the vertex A to the side BC.
So, It will bisects the side BC
$\therefore \mathrm{DC}=\frac{1}{2} a$
Now, In right triangle ADC
By using Pythagoras theorem, we have
$\mathrm{AC}^{2}=\mathrm{CD}^{2}+\mathrm{DA}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow a^{2}=\left(\frac{1}{2} a\right)^{2}+\mathrm{DA}^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{DA}^{2}=a^{2}-\frac{1}{4} a^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{DA}^{2}=\frac{3}{4} a^{2}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{DA}=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a$
Now, area $(\triangle \mathrm{ABC})=\frac{1}{2} \times \mathrm{BC} \times \mathrm{AD}$
$=\frac{1}{2} \times a \times \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} a$
$=\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4} a^{2}$
