In Fig. 4.60, check whether AD is the bisector of ∠A of ∆ABC in each of the following:
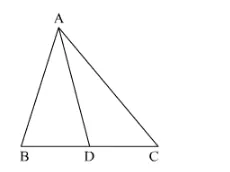
(i) AB = 5 cm, AC = 10 cm, BD = 1.5 cm and CD = 3.5 cm
(ii) AB = 4 cm, AC = 6 cm, BD = 1.6 cm and CD = 2.4 cm
(iii) AB = 8 cm, AC = 24 cm, BD = 6 cm and BC = 24 cm
(iv) AB = 6 cm, AC = 8 cm, BD = 1.5 cm and CD = 2 cm
(v) AB = 5 cm, AC = 12 cm, BD = 2.5 cm and BC = 9 cm
(i) It is given that $A B=5 \mathrm{~cm}, A C=10 \mathrm{~cm}, B D=1.5 \mathrm{~cm}$ and $C D=3.5 \mathrm{~cm}$.
We have to check whether $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
First we will check proportional ratio between sides.
Now
ABAC=510=12
BDCD=1.53.5=37
Since ABAC\neqBDCD
Hence $A D$ is not the bisector of $\angle A$.
(ii) It is given that, $A B=4 \mathrm{~cm}, A C=6 \mathrm{~cm}, B D=1.6 \mathrm{~cm}$ and $C D=2.4 \mathrm{~cm}$.
We have to check whether $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
First we will check proportional ratio between sides.
So $\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{B D}{D C}$
$\Rightarrow 46=1.62 .4 \Rightarrow 23=23$
(It is proportional)
Hence, $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
(iii) It is given that, $A B=8 \mathrm{~cm}, A C=24 \mathrm{~cm}, B D=6 \mathrm{~cm}$ and $B C=24 \mathrm{~cm}$.
We have to check whether $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
First we will check proportional ratio between sides.
Now
$D C=B C-B D$
$D C=24-6$
$=18$
So $\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{B D}{D C}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{8}{24}=\frac{6}{18}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{1}{3}=\frac{1}{3}$
(It is proportional)
Hence, $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
(iv) It is given that, AB = 6 cm, AC = 8 cm, BD = 1.5 cm and CD = 2 cm.
We have to check whether $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
First we will check proportional ratio between sides.
So $\frac{A B}{A C}=\frac{B D}{D C}$
⇒68=1.52⇒34=34
(It is proportional)
Hence $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
(v) It is given that AB = 5 cm, AC = 12 cm, BD = 2.5 cm and BC = 9 cm
We have to check whether $A D$ is bisector of $\angle A$.
First we will check proportional ratio between sides.
Now
ABAC=512
BDCD=2.59=518
Since ABAC\neqBDCD
Hence $A D$ is not the bisector of $\angle A$.
