Question:
In figure, CD ∥ AE and CY ∥ BA.
(i) Name a triangle equal in area of ΔCBX
(ii) Prove that ar(ΔZDE) = ar(ΔCZA)
(iii) Prove that ar(BCZY) = ar(ΔEDZ)
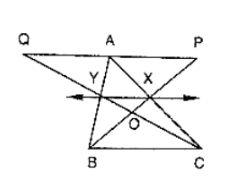
Solution:
Since, triangle BCA and triangle BYA are on the same base BA and between same parallel s BA and CY.
Then ar(ΔBCA) = ar(ΔBYA)
⇒ ar(ΔCBX) + ar(ΔBXA) = ar(ΔBXA) + ar(ΔAXY)
⇒ ar(ΔCBX) = ar(ΔAXY) ⋅⋅⋅⋅ (1)
Since, triangles ACE and ADE are on the same base AE and between same parallels CD and AE
Then, ar(ΔACE) = ar(ΔADE)
ar(ΔCZA) + ar(ΔAZE) = ar(ΔAZE) + ar(ΔDZE)
ar(ΔCZA) = ar(ΔDZE) ⋅⋅⋅ (2)
Adding ar(ΔCYG) on both sides , we get
⇒ ar(ΔCBX) + ar(ΔCYZ) = ar(ΔCAY) + ar(ΔCYZ)
⇒ ar(BCZY) = ar(ΔCZA) ⋅⋅⋅ (3)
Compare equation 2 and 3
⇒ ar(BCZY) = ar(ΔDZE)
