In figure, if PQR is the tangent to a circle at Q whose centre is 0, AB is a chord parallel to PR and ∠BQR = 70°, then ∠AQB is equal to
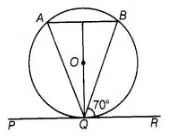
(a) 20°
(b) 40°
(c) 35°
(d) 45°
(b) Given. $A B \| P R$
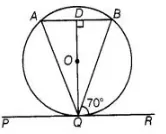
$\therefore$$\angle A B Q=\angle B Q R=70^{\circ}$ [alternate angles]
$\triangle \operatorname{lon} O D$ is nernendicular to $A B$ and $Q D$ bisects $A B$.
In $\triangle Q D A$ and $\triangle Q D B, \quad \angle Q D A=\angle Q D B$ [each $90^{\circ}$ ]
$A D=B D$
$Q D=Q D$ [common side]
$\therefore$ $\triangle A D Q \cong \triangle B D Q$ [by SAS similarity criterion]
Then $\angle Q A D=\angle Q B D$ $[\mathrm{CPCT}] \ldots$ (i)
Also $\angle A B Q=\angle B Q R$ [alternate interior angle]
$\therefore$ $\angle A B Q=70^{\circ}$ $\left[\because \angle B Q R=70^{\circ}\right]$
Hence, $\angle Q A B=70^{\circ}$ [from Eq. (i)]
Now, in $\triangle A B Q_{1} \quad \angle A+\angle B+\angle Q=180^{\circ}$
$\Rightarrow$ $\angle Q=180^{\circ}-\left(70^{\circ}+70^{\circ}\right)=40^{\circ}$
