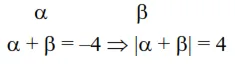Let $y=y(x)$ be the solution of the differential equation $\left((x+2) e^{\left(\frac{y+1}{x+2}\right)}+(y+1)\right) d x=(x+2) d y$ $y(1)=1$. If the domain of $y=y(x)$ is an open interval $(\alpha, \beta)$, then $|\alpha+\beta|$ is equal to
$\mathrm{y}+1=\mathrm{Y} \Rightarrow \mathrm{dy}=\mathrm{d} \mathrm{Y}$
$x+2=X \Rightarrow d x=d X$
$\Rightarrow\left(X e^{\frac{Y}{X}}+Y\right) d X=X d Y$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{Xd} \mathrm{Y}-\mathrm{YdX}=\mathrm{Xe}^{\mathrm{Y} / \mathrm{x}} \mathrm{dX}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{d}\left(\frac{\mathrm{Y}}{\mathrm{X}}\right) \mathrm{e}^{-\frac{\mathrm{Y}}{\mathrm{X}}}=\frac{\mathrm{dX}}{\mathrm{X}}$
$-\mathrm{e}^{-\mathrm{Y} / \mathrm{x}}=\ell|\mathrm{X}|+\mathrm{c}$
$(3,2) \rightarrow-\mathrm{e}^{-2 / 3}=\ell|3|+\mathrm{c}$
$-e^{-\frac{Y}{X}}=\ell n|X|-e^{-\frac{2}{3}}-\ell n 3$
$e^{-\frac{Y}{X}}=e^{2 / 3}+\ln 3-\ell n|X|>0$
$\ell \mathrm{n}|\mathrm{X}|<\left(\mathrm{e}^{2 / 3}+\ell \mathrm{n} 3\right)$
$\operatorname{Let} \lambda=\left(e^{2 / 3}+\ell n 3\right)$
$|x+2| $-\mathrm{e}^{\lambda}<\mathrm{x}+2<\mathrm{e}^{\lambda}$ $-\mathrm{e}^{\lambda}-2<\mathrm{x}<\mathrm{e}^{\lambda}-2$ Although $x=-2$ should be excluded from domain but according to the given problem it will the most appropriate solution.