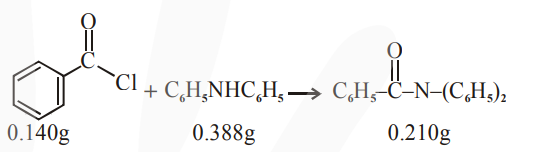
Consider the above reaction. The percentage yield of amide product is (Round off to the Nearest Integer).
(Given : Atomic mass : $\mathrm{C}: 12.0 \mathrm{u}, \mathrm{H}: 1.0 \mathrm{u}$, $\mathrm{N}: 14.0 \mathrm{u}, \mathrm{O}: 16.0 \mathrm{u}, \mathrm{Cl}: 35.5 \mathrm{u})$
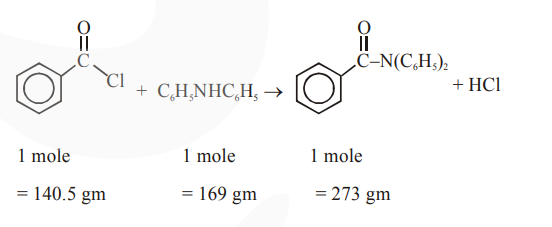
$\therefore 0.140 \mathrm{gm} \quad \frac{169}{140.5} \times 0.140$
$\begin{array}{ll}\text { L.R. } & =0.168 \mathrm{gm}<0.388 \mathrm{gm}\end{array}$
excess
$\therefore$ Theoretical amount of given product formed
$=\frac{273}{140.5} \times 0.140=0.272 \mathrm{gm}$
But its actual amount formed is $0.210 \mathrm{gm}$. Hence, the percentage yield of product.
$=\frac{0.210}{0.272} \times 100=77.20 \approx 77$
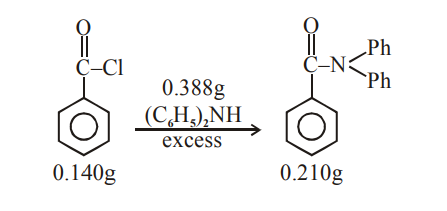
Mole of $\mathrm{Ph}-\mathrm{CoCl}=\frac{0.140}{140}=10^{-3} \mathrm{~mol}$
Mole of $\mathrm{Ph}$  $(\mathrm{Ph})_{2}$, that should be obtained
$(\mathrm{Ph})_{2}$, that should be obtained
by mol-mol analysis $=10^{-3} \mathrm{~mol}$.
Theoritical mass of product $=10^{-3} \times 273=$ $273 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~g}$
Observed mass of product $=210 \times 10^{-3} \mathrm{~g}$
$\%$ yield of product $=\frac{210 \times 10^{-3}}{273 \times 10^{-3}} \times 100=76.9 \%=77$
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
