Represent $\sqrt{6}, \sqrt{7}, \sqrt{8}$ on the number line.
We are asked to represent $\sqrt{6}, \sqrt{7}$ and $\sqrt{8}$ on the number line
We will follow certain algorithm to represent these numbers on real line
We will consider point A as reference point to measure the distance
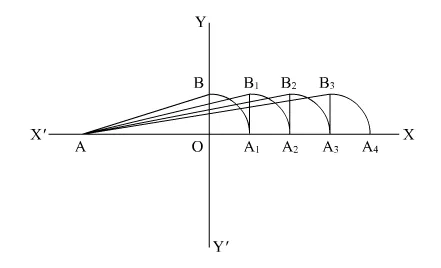
(1) First of all draw a line AX and YY’ perpendicular to AX
(2) Consider $A O=2$ unit and $O B=1$ unit, so
$A B=\sqrt{2^{2}+1^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{5}$
(3) Take A as center and AB as radius, draw an arc which cuts line AX at A1
(4) Draw a perpendicular line A1B1 to AX such that ![]() and
and
(5) Take A as center and AB1 as radius and draw an arc which cuts the line AX at A2.
Here
$A B_{1}=A A_{2}$
$=\sqrt{A A_{1}{ }^{2}+A_{1} B_{1}{ }^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{(\sqrt{5})^{2}+1}$
$=\sqrt{6}$ unit
So $A A_{2}=\sqrt{6}$ unit
So $A_{2}$ is the representation for $\sqrt{6}$
(1) Draw line A2B2 perpendicular to AX
(2) Take A center and AB2 as radius and draw an arc which cuts the horizontal line at A3 such that
$A B_{2}=A A_{3}$
$=\sqrt{A A_{2}^{2}+A_{2} B_{2}^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{(\sqrt{6})^{2}+1}$
$=\sqrt{7}$ unit
So point $A 3$ is the representation of $\sqrt{7}$
(3) Again draw the perpendicular line $A_{3} B_{3}$ to $A X$
(4) Take $A$ as center and $A B 3$ as radius and draw an arc which cuts the horizontal line at $A 4$
Here;
$A B_{3}=A A_{4}$
$=\sqrt{A A_{3}^{2}+A_{3} B_{3}^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{(\sqrt{7})^{2}+1^{2}}$
$=\sqrt{8}$ unit
$A 4$ is basically the representation of $\sqrt{8}$
