Roohi travels 300 km to her home partly by train and partly by bus. She takes 4 hours if she travels 60 km by train and the remaining by bus. If she travels 100 km by train and the remaining by bus, she takes 10 minutes longer. Find the speed of the train and the bus separately.
Let the speed of the train be x km/hour that of the bus be y km/hr, we have the following cases
Case I: When Roohi travels 300 Km by train and the rest by bus
Time taken by Roohi to travel $60 \mathrm{Km}$ by train $=\frac{60}{x} h r s$
Time taken by Roohi to travel $(300-60)=240 \mathrm{Km}$ by bus $=\frac{240}{y} h r s$
Total time taken by Roohi to cover $300 \mathrm{Km}=\frac{60}{x}+\frac{240}{y}$
It is given that total time taken in 4 hours
$\frac{60}{x}+\frac{240}{y}=4$
$60\left(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{4}{y}\right)=4$
$\left(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{4}{y}\right)=\frac{4}{60}$
$\frac{1}{x}+\frac{4}{y}=\frac{1}{15} \cdots(i)$
Case II: When Roohi travels 100 km by train and the rest by bus
Time taken by Roohi to travel $100 \mathrm{Km}$ by train $=\frac{100}{x} h r s$
Time taken by Roohi to travel $(300-100)=200 \mathrm{Km}$ by bus $=\frac{200}{y} h r s$
In this case total time of the journey is 4 hours 10 minutes
$\frac{100}{x}+\frac{200}{y}=4 h r s 10 \mathrm{~min}$ utes
$\frac{100}{x}+\frac{200}{y}=4 \frac{10}{60}$
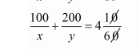
$\frac{100}{x}+\frac{200}{y}=\frac{25}{6}$
$100\left(\frac{1}{x}+\frac{2}{y}\right)=\frac{25}{6}$
$\frac{1}{x}+\frac{2}{y}=\frac{25}{6} \times \frac{1}{100}$
$\frac{1}{x}+\frac{2}{y}=\frac{1}{24}$$\ldots$ (i)
Putting $\frac{1}{x}=u$ and $\frac{1}{y}=u$, the equations $(i)$ and $(i i)$ reduces to
$1 u+4 v=\frac{1}{15} \cdots(i i i)$
$1 u+2 v=\frac{1}{24} \cdots(i v)$
Subtracting equation (iv) from (iii)we get
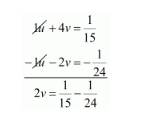
$2 v=\frac{24-15}{360}$
$2 v=\frac{9}{360}$
$2 v=\frac{9}{360}$
$v=\frac{1}{40} \times \frac{1}{2}$
$v=\frac{1}{80}$
Putting $v=\frac{1}{80}$ in equation (iii), we get
$1 u+4 v=\frac{1}{15}$
$1 u+4 \times \frac{1}{80}=\frac{1}{15}$
$1 u+\frac{4}{80}=\frac{1}{15}$
$1 u=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{4}{80}$
$1 u=\frac{1}{15}-\frac{1}{20}$
$1 u=\frac{20-15}{300}$
$1 u=\frac{5}{300}$
$u=\frac{1}{60}$
Now
$u=\frac{1}{60}$
$\frac{1}{x}=\frac{1}{60}$
$x=60$
and
$v=\frac{1}{80}$
$\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{80}$
$y=80$
Hence, the speed of the train is $60 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{hr}$,
The speed of the bus is $80 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{hr}$
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
