Show that $A B=B A$ in each of the following cases:
$A=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \theta & -\sin \theta \\ \sin \theta & \cos \theta\end{array}\right]$ and $B=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \phi & -\sin \phi \\ \sin \phi & \cos \phi\end{array}\right]$
Given : $A=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \theta & -\sin \theta \\ \sin \theta & \cos \theta\end{array}\right]$ and $B=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \phi & -\sin \phi \\ \sin \phi & \cos \phi\end{array}\right]$
Matrix $A$ is of order $2 \times 2$ and Matrix $B$ is of order $2 \times 2$
To show : matrix $A B=B A$
Formula used:
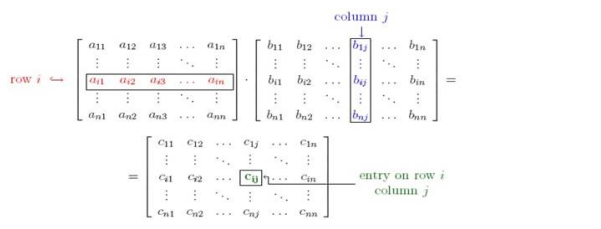
Where $c_{i j}=a_{i 1} b_{1 j}+a_{i 2} b_{2 j}+a_{i 3} b_{3 j}+\ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots \ldots .+a_{i n} b_{n j}$
If $A$ is a matrix of order $a \times b$ and $B$ is a matrix of order $c \times d$, then matrix $A B$ exists and is of order $a \times d$, if and only if $b=$ $C$
If $A$ is a matrix of order $a \times b$ and $B$ is a matrix of order $c \times d$, then matrix $B A$ exists and is of order $c \times b$, if and only if $d=$ a
For matrix $A B, a=2, b=c=2, d=2$, thus matrix $A B$ is of order $2 \times 2$
Matrix $A B=$
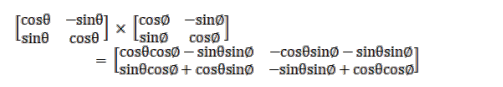
Matrix $A B=\left[\begin{array}{ll}\cos \theta \cos \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset & -\cos \theta \sin \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset \\ \sin \theta \cos \emptyset+\cos \theta \sin \emptyset & -\sin \theta \sin \emptyset+\cos \theta \cos \emptyset\end{array}\right]$
Matrix $A B=\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \theta \cos \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset & -\cos \theta \sin \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset \\ \sin \theta \cos \emptyset+\cos \theta \sin \emptyset & -\sin \theta \sin \emptyset+\cos \theta \cos \emptyset\end{array}\right]$
For matrix $\mathrm{BA}, \mathrm{a}=2, \mathrm{~b}=\mathrm{c}=2, \mathrm{~d}=2$, thus matrix $\mathrm{BA}$ is of order $2 \times 2$
Matrix $\mathrm{BA}=$
$\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \emptyset & -\sin \emptyset \\ \sin \emptyset & \cos \emptyset\end{array}\right] \times\left[\begin{array}{cc}\cos \theta & -\sin \theta \\ \sin \theta & \cos \theta\end{array}\right]$
$=\left[\begin{array}{ll}\cos \emptyset \cos \theta-\sin \emptyset \sin \theta & -\cos \emptyset \sin \theta-\sin \emptyset \cos \theta \\ \sin \emptyset \cos \theta+\cos \emptyset \sin \theta & -\sin \emptyset \sin \theta+\cos \emptyset \cos \theta\end{array}\right]$
Matrix BA $=\left[\begin{array}{ll}\cos \theta \cos \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset & -\cos \theta \sin \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset \\ \sin \theta \cos \emptyset+\cos \theta \sin \emptyset & -\sin \theta \sin \emptyset+\cos \theta \cos \emptyset\end{array}\right]$
Matrix BA = Matrix $A B=\left[\begin{array}{ll}\cos \theta \cos \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset & -\cos \theta \sin \emptyset-\sin \theta \sin \emptyset \\ \sin \theta \cos \emptyset+\cos \theta \sin \emptyset & -\sin \theta \sin \emptyset+\cos \theta \cos \emptyset\end{array}\right]$
Thus Matrix $\mathrm{AB}=\mathrm{BA}$
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
