Show that the semi-vertical angle of the cone of the maximum volume and of given slant height is $\tan ^{-1} \sqrt{2}$.
Let $\theta$ be the semi-vertical angle of the cone.
It is clear that $\theta \in\left[0, \frac{\pi}{2}\right]$.
Let $r, h$, and $/$ be the radius, height, and the slant height of the cone respectively.
The slant height of the cone is given as constant.
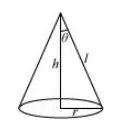
Now, $r=I \sin \theta$ and $h=I \cos \theta$
The volume (V) of the cone is given by,
$\begin{aligned} V &=\frac{1}{3} \pi r^{2} h \\ &=\frac{1}{3} \pi\left(l^{2} \sin ^{2} \theta\right)(l \cos \theta) \\ &=\frac{1}{3} \pi l^{3} \sin ^{2} \theta \cos \theta \\ \Rightarrow \frac{d V}{d \theta} &=\frac{l^{3} \pi}{3}\left[\sin ^{2} \theta(-\sin \theta)+\cos \theta(2 \sin \theta \cos \theta)\right] \\ &=\frac{l^{3} \pi}{3}\left[-\sin ^{3} \theta+2 \sin \theta \cos ^{2} \theta\right] \\ \Rightarrow \frac{d^{2} V}{d \theta^{2}} &=\frac{l^{3} \pi}{3}\left[-3 \sin ^{2} \theta \cos \theta+2 \cos ^{3} \theta-4 \sin ^{2} \theta \cos \theta\right] \\ &=\frac{l^{3} \pi}{3}\left[2 \cos ^{3} \theta-7 \sin ^{2} \theta \cos \theta\right] \end{aligned}$
Now, $\frac{d V}{d \theta}=0$
$\Rightarrow \sin ^{3} \theta=2 \sin \theta \cos ^{2} \theta$
$\Rightarrow \tan ^{2} \theta=2$
$\Rightarrow \tan \theta=\sqrt{2}$
$\Rightarrow \theta=\tan ^{-1} \sqrt{2}$
Now, when $\theta=\tan ^{-1} \sqrt{2}$, then $\tan ^{2} \theta=2$ or $\sin ^{2} \theta=2 \cos ^{2} \theta$.
Then, we have:
$\frac{d^{2} V}{d \theta^{2}}=\frac{l^{3} \pi}{3}\left[2 \cos ^{3} \theta-14 \cos ^{3} \theta\right]=-4 \pi l^{3} \cos ^{3} \theta<0$ for $\theta \in\left[0, \frac{\pi}{2}\right]$
$\therefore$ By second derivative test, the volume $(V)$ is the maximum when $\theta=\tan ^{-1} \sqrt{2}$.
Hence, for a given slant height, the semi-vertical angle of the cone of the maximum volume is $\tan ^{-1} \sqrt{2}$.
