A track consists of two circular parts $A B C$ and CDE of equal radius $100 \mathrm{~m}$ and joined smoothly as shown in figure (7-E1). Each part subtends a right angle at its centre. A cycle weighing $100 \mathrm{~kg}$ together with the rider travels at a constant speed of $18 \mathrm{~km} / \mathrm{h}$ on the track. (a) Find the normal contact force by the road on the cycle when it is at $B$ and at $D$. (b) Find the force of friction exerted by the track on the tyres when the cycle is at $B, C$ and $D$. (c) Find the normal force between the road and the cycle just before and just after the cycle crosses C. (d) What should be the minimum friction coefficient between the road and the tyre, which will ensure that the cyclist can move with constant speed? Take $\mathrm{g}=10 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}$.
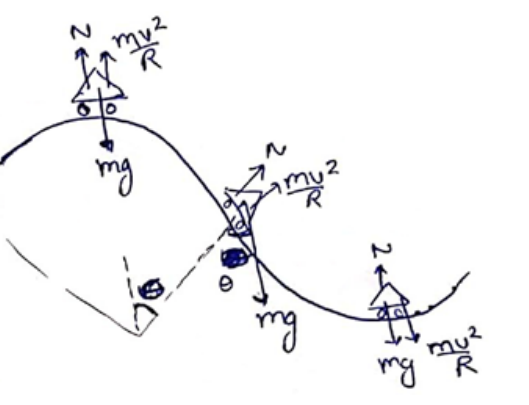
(a)
Velocity of cyclist $=\frac{(18 \times 5)}{18}=5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}$
At point B
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{B}}+\frac{m v^{2}}{R}=\mathrm{mg}$
$N_{B}=(100)(10)-\frac{(100)(5)^{2}}{100}$
$N_{B}=(100)(10)-$
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{B}}=975 \mathrm{~N}$
At point $D$
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{D}}=\mathrm{mg}+\frac{m v^{2}}{R}$
$N_{D}=(100)(10)+\frac{(100)(5)^{2}}{100}$
$N_{D}=1025 \mathrm{~N}$
(b)
No force acts along surface at point B and D
So, $\mathrm{ff}_{\mathrm{B}}=\mathrm{ff}_{\mathrm{D}}=0$
At point $C$,
$\because$ acceleration $=0$
$\mathrm{So}, \mathrm{ffc}=\mathrm{mg} \sin \theta$
$f f c=(100)(10) \sin 450$
$f f c=707 N$
(C)
Before C,
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{c}}+\frac{m V^{2}}{R}=\operatorname{mgcos} 45^{\circ}$
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{c}}=(100)(10)\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)-\frac{(100)(5)^{2}}{(100)}$
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{C}}=682 \mathrm{~N}$
After C,
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{m V^{2}}{R}+\mathrm{mg} \cos 45^{\circ}$
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{C}}=\frac{(100)(5)^{2}}{100}+(100)(10)\left(\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\right)$
$\mathrm{N}_{\mathrm{C}}^{\prime}=732 \mathrm{~N}$
(d) $f f=\mu N$
For minimum friction force normal contact should be minimum.
Normal contact is minimum at point just before C.
$\mathrm{ff}=\mathrm{mg} \sin \theta=\mu \mathrm{N}$
$(100)(10) \sin 45^{\circ}=\mu(682)$
$\mu=1.037$
