A motorcycle has to move with a constant speed on an overbridge which is in the form of a circular arc of radius $R$ and has a total length $L$. Suppose the motorcycle starts from the highest point. (a) What can its maximum velocity be for which the contact with the road is not broken at the highest point? (b) If the motorcycle goes at speed 1/42 times the maximum found in part (a), where will it lose the contact with the road? (c) What maximum uniform speed can it maintain on the bridge if it does not lose contact anywhere on the bridge?
(a)
At highest point,
$N+\frac{m v^{2}}{R}=m g$
For maximum speed, $\mathrm{N}=0$
$\frac{m v_{\max }^{2}}{R}=m g$
$V_{\max }=\sqrt{(R g)}$
(b)
$V=\frac{V_{\max }}{\sqrt{2}}=\sqrt{\frac{R g}{\sqrt{2}}}$
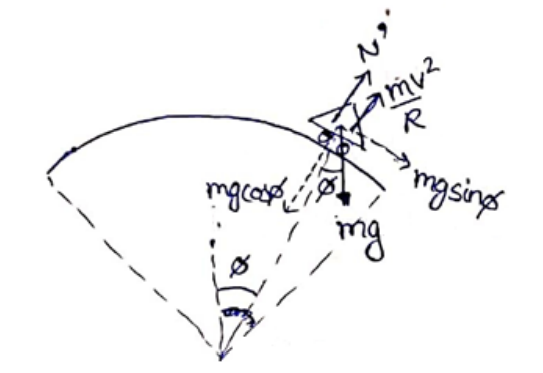
Let at angle $\boldsymbol{\Phi}$ it loses its contact with road
$N^{\prime}=0$
$\operatorname{Cos} \Phi=\frac{1}{2}$
$\Phi=60^{\circ}$ or ${ }^{\frac{\pi}{3}} \mathrm{rad}$
So it loses contact after a distance $\pi R / 3$ along the bridge from the highest point.
(c)
Normal contact at any angle $\boldsymbol{\Phi}$
$\mathrm{N}^{\prime}=\operatorname{mgcos} \boldsymbol{\Phi} \frac{m v^{2}}{R}$
So, as motorcycle moves along the curve $\boldsymbol{\Phi}$ increases, so $\cos \boldsymbol{\Phi}$ decreases and hence N' decreases.
Normal contact will be minimum at the extreme point.
At extreme point
$\boldsymbol{\Phi}=\frac{\theta}{2}=\frac{L}{2 R}=$ and $\mathrm{N}^{\prime}=0$
From equation (1),
$0=\operatorname{mgcos}\left(\frac{L}{2 R}\right)-\frac{m v^{2}}{R}$
$V=\sqrt{\mathrm{g} \operatorname{Rcos}\left(\frac{L}{2 R}\right)}$
$\mathrm{N}^{\prime}+\frac{m V^{2}}{R}=\operatorname{mgcos} \boldsymbol{\Phi}$
