Solve the following systems of equations:
$\frac{1}{2(x+2 y)}+\frac{5}{3(3 x-2 y)}=\frac{-3}{2}$
$\frac{5}{4(x+2 y)}-\frac{3}{5(3 x-2 y)}=\frac{61}{60}$
The given equations are:
$\frac{1}{2(x+2 y)}+\frac{5}{3(3 x-2 y)}=-\frac{3}{2}$
$\frac{5}{4(x+2 y)}-\frac{3}{5(3 x-2 y)}=\frac{61}{60}$
Let $\frac{1}{x+2 y}=u$ and $\frac{1}{3 x-2 y}=v$ then equations are
$\frac{1}{2} u+\frac{5}{3} v=-\frac{3}{2} \ldots$$\ldots(i)$
$\frac{5}{4} u-\frac{3}{5} v=\frac{61}{60}$$. .(i i)$
Multiply equation $(i)$ by $\frac{3}{5}$ and equation $(i i)$ by $\frac{5}{3}$ add both equations, we get
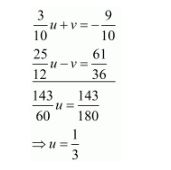
Put the value of $u$ in equation $(i)$, we get
$\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{3}+\frac{5}{3} v=-\frac{3}{2}$
$\Rightarrow \frac{5}{3} v=-\frac{10}{6}$
$\Rightarrow v=-1$
Then
$\frac{1}{x+2 y}=\frac{1}{3}$
$\Rightarrow x+2 y=3$$\ldots(i i i)$
$\frac{1}{3 x-2 y}=-1$
$\Rightarrow 3 x-2 y=-1$...$(i v)$
Add both equations, we get
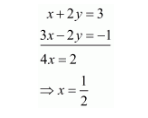
Put the value of $x$ in equation (iii) we get
$\frac{1}{2}+2 y=3$
$\Rightarrow y=\frac{5}{2}$
$\Rightarrow y=\frac{5}{4}$
Hence the value of $x=\frac{1}{2}$ and $y=\frac{5}{4}$.
Click here to get exam-ready with eSaral
For making your preparation journey smoother of JEE, NEET and Class 8 to 10, grab our app now.
