If $f(x)=x^{2}+\frac{x^{2}}{1+x^{2}}+\frac{x^{2}}{\left(1+x^{2}\right)}+\ldots+\frac{x^{2}}{\left(1+x^{2}\right)}+\ldots$
then at $x=0, f(x)$
(a) has no limit
(b) is discontinuous
(c) is continuous but not differentiable
(d) is differentiable
(b) is discontinuous
We have,
$f(x)=x^{2}+\frac{x^{2}}{1+x^{2}}+\frac{x^{2}}{\left(1+x^{2}\right)}+\ldots+\frac{x^{2}}{\left(1+x^{2}\right)}+\ldots$
When $x=0$ then $x^{2}=0$
and $\frac{x^{2}}{1+x^{2}}=0$
$\therefore f(0)=0+0+0+0 \ldots \ldots$
$\Rightarrow f(0)=0$
When, $x \neq 0$
Then, $x^{2}>0$
and $1+x^{2}>x^{2}$
$\Rightarrow 0<\frac{x^{2}}{1+x^{2}}<1$
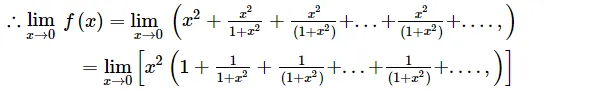
$=\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\left[x^{2}\left(\frac{1}{1-\frac{1}{1+x^{2}}}\right)\right]$ $\left[\right.$ Sum of infinite series where, $\left.r=\frac{1}{1+x^{2}}\right]$
$=\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\left[x^{2}\left(\frac{1+x^{2}}{x^{2}}\right)\right]$
$=\lim _{x \rightarrow 0}\left(1+x^{2}\right)$
$=1$
$\therefore \lim _{x \rightarrow 0} f(x) \neq f(0)$
$\therefore f(x)$ is discontinuous at $x=0$
