Let $A=\{2,3,4,5\}$ and $B=\{7,9,11,13\}$, and
let $f=\{(2,7),(3,9),(4,11),(5,13)\} .$
Show that $f$ is invertible and find $f^{-1}$.
To Show: that $\mathrm{f}$ is invertible
To Find: Inverse of $f$
[NOTE: Any functions is invertible if and only if it is bijective functions (i.e. one-one and onto)]
one-one function: A function $\mathrm{f}: \mathrm{A} \rightarrow \mathrm{B}$ is said to be a one-one function or injective mapping if different
elements of $A$ have different images in $B$. Thus for $\left.x_{1}, x_{2} \in A \& f\left(x_{1}\right), f\left(x_{2}\right) \in B, f(x)\right)=f(x 2) \leftrightarrow x_{1}=x_{2}$ or $x_{1} \neq$ $x_{2} \leftrightarrow f(x 1) \neq f(x 2)$
onto function: If range $=$ co-domain then $f(x)$ is onto functions.
So, We need to prove that the given function is one-one and onto.
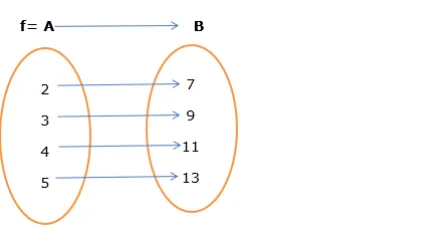
As we see that inthe above figure ( 2 is mapped with 7), ( 3 is mapped with 9$),$ (4 is mapped with 11 ),
(5 is mapped with 13)
So it is one-one functions.
Now elements of $B$ are known as co-domain. Also, a range of a function is also the elements of $B$ (by definition)
So it is onto functions.
Hence Proved that $f$ is invertible.
Now, We know that if $f: A \rightarrow B$ then $f^{-1}: B \rightarrow A$ (if it is invertible)
So,
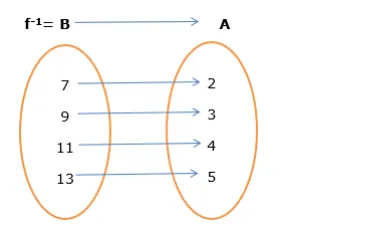
So $f^{-1}=\{(7,2),(9,3),(11,4),(13,5)\}$
