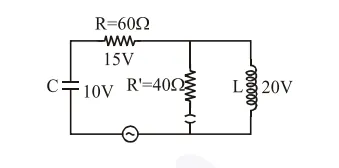
The angular frequency of alternating current in a L-C-R circuit is $100 \mathrm{rad} / \mathrm{s}$. The components connected are shown in the figure. Find the value of inductance of the coil and capacity of condenser.
Correct Option: , 2
Current through $60 \Omega$ resistance $=\frac{15}{60}=\frac{1}{4} \mathrm{~A}$
thus capacitor current $=\frac{1}{4} \mathrm{~A}$
$\because \quad \mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{C}}=\mathrm{I} \mathrm{X}_{\mathrm{C}}$
$10=\frac{1}{4} \times \frac{1}{\omega C}$
$\therefore \mathrm{C}=\frac{1}{40 \omega}=\frac{1}{4000}=250 \mu \mathrm{F}$
Now,
current through $40 \Omega$ resistance $=\frac{20}{40}=\frac{1}{2} \mathrm{~A}$
thus current through inductor $=\frac{1}{2}-\frac{1}{4}=\frac{1}{4} \mathrm{~A}$
$\mathrm{V}_{\mathrm{L}}=\mathrm{IX}_{\mathrm{L}}=\frac{1}{4} \times \omega \mathrm{L}$
$20=\frac{1}{4} \times 100 \times \mathrm{L}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{L}=0.8 \mathrm{H}$
