The area of a rectangle remains the same if the length is increased by 7 meters and the breadth is decreased by 3 meters.
The area of a rectangle remains the same if the length is increased by 7 meters and the breadth is decreased by 3 meters. The area remains unaffected if the length is decreased by 7 meters and breadth in increased by 5 meters. Find the dimensions of the rectangle.
Let the length and breadth of the rectangle be $x$ and $y$ units respectively
Then, area of rectangle $=x y$ square units
If length is increased by 7 meters and breadth is decreased by 3 meters when the area of a rectangle remains the same
Therefore,
$x y=(x+7)(y-3)$
$x y=x y+7 y-3 x-21$
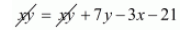
$3 x-7 y+21=0 \cdots(i)$
If the length is decreased by 7 meters and breadth is increased by 5 meters when the area remains unaffected, then
$x y=(x-7)(y+5)$
$x y=x y-7 y+5 x-35$
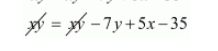
$0=5 x-7 y-35 \cdots(i i)$
Thus we get the following system of linear equation
$3 x-7 y+21=0$
$5 x-7 y-35=0$
By using cross-multiplication, we have
$\frac{x}{(-7 \times-35)-(-7 \times 21)}=\frac{-y}{(3 \times-35)-(5 \times 21)}=\frac{1}{(3 \times-7)-(5 \times-7)}$
$\frac{x}{245+147}=\frac{-y}{-105-105}=\frac{1}{-21+35}$
$\frac{x}{392}=\frac{-y}{-210}=\frac{1}{14}$
$x=\frac{392}{14}$
$x=28$
and
$y=\frac{210}{14}$
$y=15$
Hence, the length of rectangle is 28 meters
The breadth of rectangle is 15 meters
