The ionization constant of nitrous acid is $4.5 \times 10^{-4}$ Calculate the $\mathrm{pH}$ of $0.04 \mathrm{M}$ sodium nitrite solution and also its degree of hydrolysis.
NaNO2 is the salt of a strong base (NaOH) and a weak acid (HNO2).
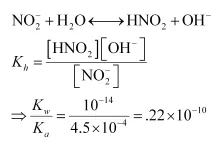
Now, If x moles of the salt undergo hydrolysis, then the concentration of various species present in the solution will be:
$\left[\mathrm{NO}_{2}^{-}\right]=.04-x ; 0.04$
$\left[\mathrm{HNO}_{2}\right]=x$
$\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right]=x$
$K_{h}=\frac{x^{2}}{0.04}=0.22 \times 10^{-10}$
$x^{2}=.0088 \times 10^{-10}$
$x=.093 \times 10^{-5}$
$\therefore\left[\mathrm{OH}^{-}\right]=0.093 \times 10^{-5} \mathrm{M}$
$\left[\mathrm{H}_{3} \mathrm{O}^{+}\right]=\frac{10^{-14}}{.093 \times 10^{-5}}=10.75 \times 10^{-9} \mathrm{M}$
$\Rightarrow \mathrm{pH}=-\log \left(10.75 \times 10^{-9}\right)$
$=7.96$
Therefore, degree of hydrolysis
$=\frac{x}{0.04}=\frac{.093 \times 10^{-5}}{.04}=2.325 \times 10^{-5}$
