Question.
The lengths of two parallel chords of a circle are 6 cm and 8 cm. If the smaller chord is at distance 4 cm from the centre, what is the distance of the other chord from the centre?
Solution:
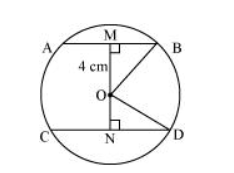
Let AB and CD be two parallel chords in a circle centered at O. Join OB and OD.
Distance of smaller chord AB from the centre of the circle = 4 cm
$O M=4 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\mathrm{MB}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{2}=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{~cm}$
In $\triangle O M B$
$\mathrm{OM}^{2}+\mathrm{MB}^{2}=\mathrm{OB}^{2}$
$(4)^{2}+(3)^{2}=\mathrm{OB}^{2}$
$16+9=\mathrm{OB}^{2}$
$\mathrm{OB}=\sqrt{25}$
$\mathrm{OB}=5 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\ln \Delta O N D$
$\mathrm{OD}=\mathrm{OB}=5 \mathrm{~cm}$
(Radii of the same circle)
$N D=\frac{C D}{2}=\frac{8}{2}=4 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\mathrm{ON}^{2}+\mathrm{ND}^{2}=\mathrm{OD}^{2}$
$\mathrm{ON}^{2}+(4)^{2}=(5)^{2}$
$\mathrm{ON}^{2}=25-16=9$
$\mathrm{ON}=3$
Therefore, the distance of the bigger chord from the centre is $3 \mathrm{~cm}$.

Let AB and CD be two parallel chords in a circle centered at O. Join OB and OD.
Distance of smaller chord AB from the centre of the circle = 4 cm
$O M=4 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\mathrm{MB}=\frac{\mathrm{AB}}{2}=\frac{6}{2}=3 \mathrm{~cm}$
In $\triangle O M B$
$\mathrm{OM}^{2}+\mathrm{MB}^{2}=\mathrm{OB}^{2}$
$(4)^{2}+(3)^{2}=\mathrm{OB}^{2}$
$16+9=\mathrm{OB}^{2}$
$\mathrm{OB}=\sqrt{25}$
$\mathrm{OB}=5 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\ln \Delta O N D$
$\mathrm{OD}=\mathrm{OB}=5 \mathrm{~cm}$
(Radii of the same circle)
$N D=\frac{C D}{2}=\frac{8}{2}=4 \mathrm{~cm}$
$\mathrm{ON}^{2}+\mathrm{ND}^{2}=\mathrm{OD}^{2}$
$\mathrm{ON}^{2}+(4)^{2}=(5)^{2}$
$\mathrm{ON}^{2}=25-16=9$
$\mathrm{ON}=3$
Therefore, the distance of the bigger chord from the centre is $3 \mathrm{~cm}$.
