Question:
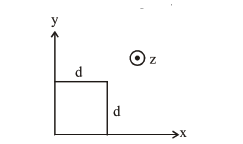
The magnetic field in a region is given by
$\overrightarrow{\mathrm{B}}=\mathrm{B}_{0}\left(\frac{\mathrm{x}}{\mathrm{a}}\right) \hat{\mathrm{k}} .$ A square loop of side $\mathrm{d}$ is placed
with its edges along the $x$ and $y$ axes. The loop is moved with a constant velocity $\overrightarrow{\mathrm{v}}=\mathrm{v}_{0} \hat{\mathrm{i}}$. The emf induced in the loop is :
Correct Option: 3,
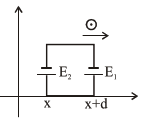
Solution:
$\mathrm{E}_{1}=\frac{\mathrm{B}_{0}(\mathrm{x}+\mathrm{d})}{\mathrm{a}} \mathrm{v}_{0} \mathrm{~d}$
$\mathrm{E}_{2}=\frac{\mathrm{B}_{0}(\mathrm{x})}{\mathrm{a}} \mathrm{v}_{0} \mathrm{~d}$
$\mathrm{E}_{\text {net }}=\mathrm{E}_{1}-\mathrm{E}_{2}$
$\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{net}}=\frac{\mathrm{B}_{0} \mathrm{v}_{0} \mathrm{~d}^{2}}{\mathrm{a}}$